Abstract
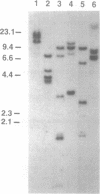
We have isolated a cDNA clone encoding the Xenopus homologue of the transcription factor AP-2 (XAP-2). The predicted amino acid sequence derived from the Xenopus cDNA shows very strong conservation with the amino acid sequence of human AP-2, suggesting that this protein is evolutionarily conserved, at least among vertebrates. This is further substantiated by the demonstration that an in vitro translation product of XAP-2 cDNA bound specifically to an AP-2 binding site from the human MT-IIA gene. Northern blot analysis of Xenopus embryo RNA revealed the existence of three major XAP-2 mRNA species that were only detectable after the midblastula transition (when embryonic transcription is activated), with peak accumulation of the transcripts occurring during gastrulation. Therefore, in contrast to other Xenopus transcription factors, XAP-2 is not maternally derived but arises exclusively from zygotic transcription. Unlike the situation in cultured human teratocarcinoma (NT2) cells, retinoic acid treatment did not induce XAP-2 mRNA in Xenopus embryos, even though the treatment had a pronounced morphogenetic effect on the embryos. Our results suggest that XAP-2 may play a distinctive role during Xenopus embryogenesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN D. D., LITTNA E. RNA SYNTHESIS DURING THE DEVELOPMENT OF XENOPUS LAEVIS, THE SOUTH AFRICAN CLAWED TOAD. J Mol Biol. 1964 May;8:669–687. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durston A. J., Timmermans J. P., Hage W. J., Hendriks H. F., de Vries N. J., Heideveld M., Nieuwkoop P. D. Retinoic acid causes an anteroposterior transformation in the developing central nervous system. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):140–144. doi: 10.1038/340140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppig J. J., Steckman M. L. Comparison of exogenous energy sources for in vitro maintenance of follicle cell-free Xenopus laevis oocytes. In Vitro. 1976 Mar;12(3):173–179. doi: 10.1007/BF02796439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslinger A., Karin M. Upstream promoter element of the human metallothionein-IIA gene can act like an enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8572–8576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila J. J., Darasch S. P., Mosser D. D., Bols N. C. Heat and sodium arsenite act synergistically on the induction of heat shock gene expression in Xenopus laevis A6 cells. Biochem Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;65(4):310–316. doi: 10.1139/o87-040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila J. J., Kloc M., Bury J., Schultz G. A., Browder L. W. Acquisition of the heat-shock response and thermotolerance during early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1985 Feb;107(2):483–489. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W. S., Stocum D. L. Retinoic acid modifies positional memory in the anteroposterior axis of regenerating axolotl limbs. Dev Biol. 1986 Mar;114(1):170–179. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90393-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Mitchell P. J., Williams T., Tjian R. Regulation of transcription factor AP-2 by the morphogen retinoic acid and by second messengers. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1507–1517. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Timmons P. M., Hébert J. M., Rigby P. W., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-2 is expressed in neural crest cell lineages during mouse embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):105–119. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Taylor M. V., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. The CArG promoter sequence is necessary for muscle-specific transcription of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus embryos. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1153–1161. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: I. characterization and timing of cellular changes at the midblastula stage. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: II. Control of the onset of transcription. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):687–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovsenek N., Heikkila J. J. DNA sequence-specific binding activity of the heat-shock transcription factor is heat-inducible before the midblastula transition of early Xenopus development. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):427–433. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovsenek N., Williams G. T., Morimoto R. I., Heikkila J. J. cis-acting sequences and trans-acting factors required for constitutive expression of a microinjected HSP70 gene after the midblastula transition of Xenopus laevis embryogenesis. Dev Genet. 1990;11(1):97–109. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020110111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter K., Grunz H., Dawid I. B. Gene expression in the embryonic nervous system of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8086–8090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Hirai S. I., Yaniv M., Bravo R. Transcriptional activation of c-jun during the G0/G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):535–537. doi: 10.1038/334535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Jamrich M., Dawid I. B. Cell interactions and the control of gene activity during early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1986 Mar;114(1):238–246. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Draper B. W., Harland R. M., Weintraub H. Identification of a retinoic acid-sensitive period during primary axis formation in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):932–942. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snape A. M., Jonas E. A., Sargent T. D. KTF-1, a transcriptional activator of Xenopus embryonic keratin expression. Development. 1990 May;109(1):157–165. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaller C., Eichele G. Identification and spatial distribution of retinoids in the developing chick limb bud. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):625–628. doi: 10.1038/327625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tickle C., Alberts B., Wolpert L., Lee J. Local application of retinoic acid to the limb bond mimics the action of the polarizing region. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):564–566. doi: 10.1038/296564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Admon A., Lüscher B., Tjian R. Cloning and expression of AP-2, a cell-type-specific transcription factor that activates inducible enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1557–1569. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winning R. S., Heikkila J. J., Bols N. C. Induction of glucose-regulated proteins in Xenopus laevis A6 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Aug;140(2):239–245. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]