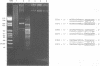
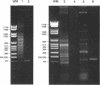
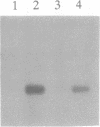
Abstract
The frequency occurrences of K-tuple (overlapping sequences of defined length, K) were computed from the known human genome sequences. The significance of these frequencies for the whole human genome was tested by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A computer programs based on these results was written to choose primers to amplify DNA target sequences, either of human genes or of human infectious agents. The software also gave nested primer sequences which were used to synthesize non radioactive probes by PCR. We applied these two methods, primer selection and non radioactive probes, to easily and quickly set up very efficient PCR sets to work in the human genome context.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alizon M., Wain-Hobson S., Montagnier L., Sonigo P. Genetic variability of the AIDS virus: nucleotide sequence analysis of two isolates from African patients. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90860-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1499–1504. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg J. L., Perelman D., Kasper L. H., Ware P. L., Boothroyd J. C. Molecular analysis of the gene encoding the major surface antigen of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3584–3591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M., Bougueleret L. Heuristic informational analysis of sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):179–196. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M., Sauvaget I., Bougueleret L. K-tuple frequency analysis: from intron/exon discrimination to T-cell epitope mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:237–252. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dartmann K., Schwarz E., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. The nucleotide sequence and genome organization of human papilloma virus type 11. Virology. 1986 May;151(1):124–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai S. M., Kalyanaraman V. S., Casey J. M., Srinivasan A., Andersen P. R., Devare S. G. Molecular cloning and primary nucleotide sequence analysis of a distinct human immunodeficiency virus isolate reveal significant divergence in its genomic sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8380–8384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas J. P., Ninio J. Efficient algorithms for folding and comparing nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):197–206. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffais R., André P. M., Thibon M. Synthesis of digoxigenin-labelled DNA probe by polymerase chain reaction: application to Epstein-Barr virus and Chlamydia trachomatis. Res Virol. 1990 May-Jun;141(3):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(90)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Ghandour G., Ost F., Tavare S., Korn L. J. New approaches for computer analysis of nucleic acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5660–5664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConlogue L., Brow M. A., Innis M. A. Structure-independent DNA amplification by PCR using 7-deaza-2'-deoxyguanosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9869–9869. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Moss H. W., McNab D., Frame M. C. DNA sequence and genetic content of the HindIII l region in the short unique component of the herpes simplex virus type 2 genome: identification of the gene encoding glycoprotein G, and evolutionary comparisons. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):19–38. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minghetti P. P., Ruffner D. E., Kuang W. J., Dennison O. E., Hawkins J. W., Beattie W. G., Dugaiczyk A. Molecular structure of the human albumin gene is revealed by nucleotide sequence within q11-22 of chromosome 4. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6747–6757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M., Hood L., Cantor C., Botstein D. A common language for physical mapping of the human genome. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1434–1435. doi: 10.1126/science.2781285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Rhoads R. E. A computer program for choosing optimal oligonucleotides for filter hybridization, sequencing and in vitro amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8543–8551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador R., Power M. D., Barr P. J., Steimer K. S., Stempien M. M., Brown-Shimer S. L., Gee W. W., Renard A., Randolph A., Levy J. A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of an AIDS-associated retrovirus (ARV-2). Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):484–492. doi: 10.1126/science.2578227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriprakash K. S., Macavoy E. S. Characterization and sequence of a plasmid from the trachoma biovar of Chlamydia trachomatis. Plasmid. 1987 Nov;18(3):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K., Barrell B. G. Sequence of the short unique region, short repeats, and part of the long repeats of human cytomegalovirus. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 20;192(2):177–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90359-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]