Abstract
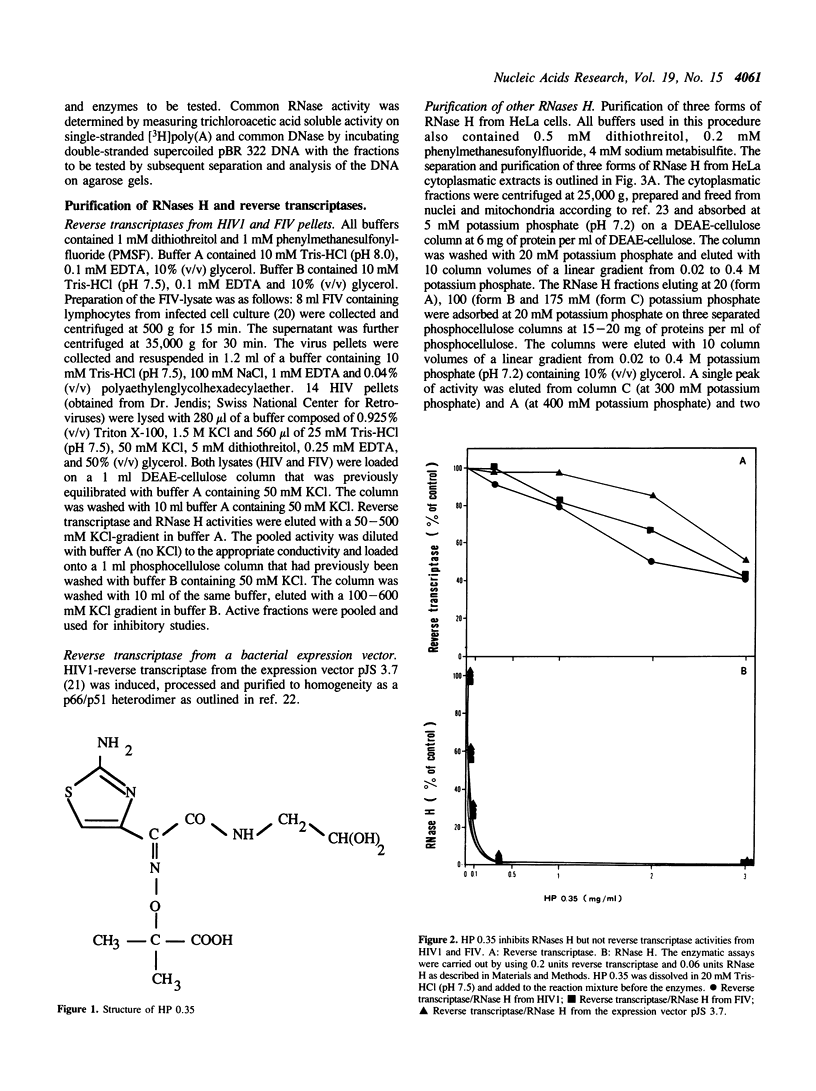
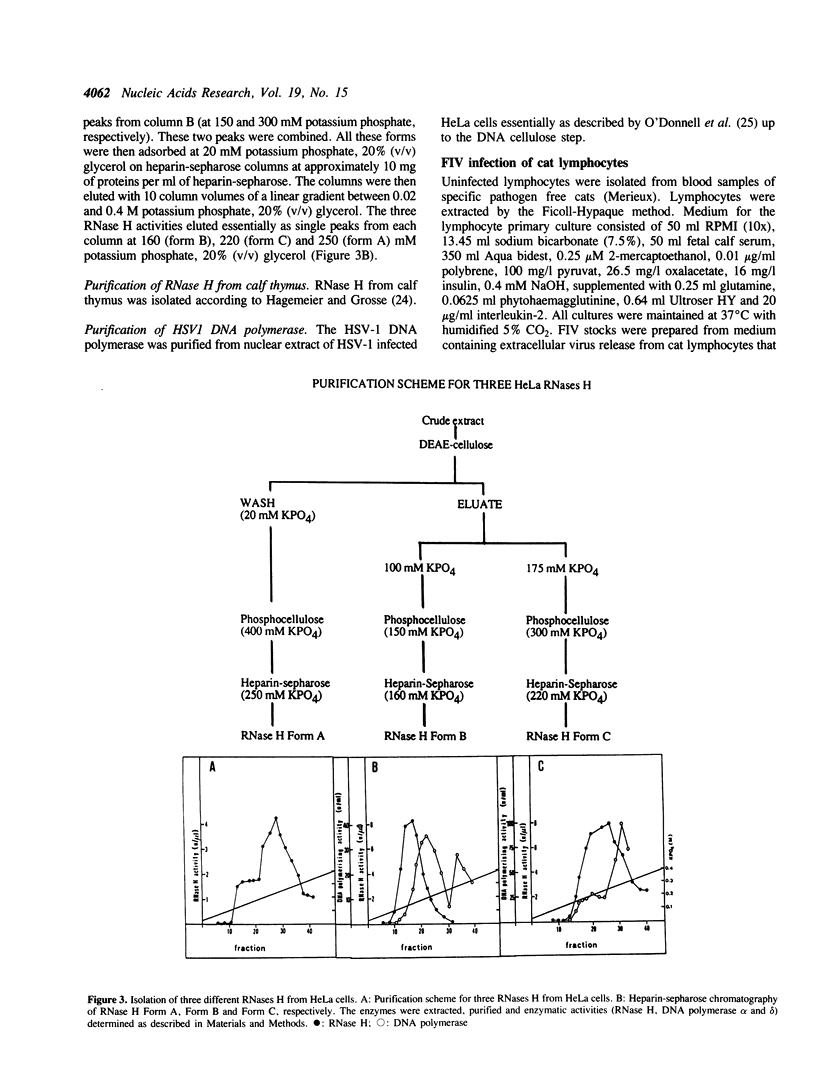
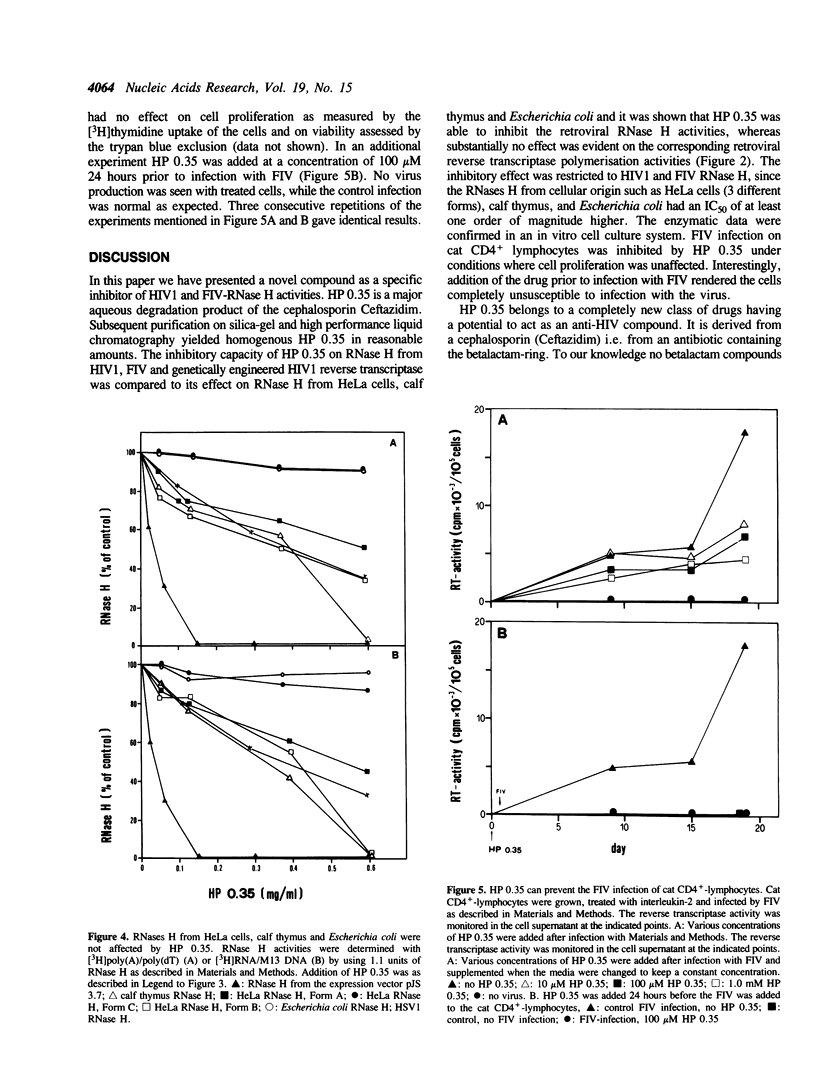
Penicillins, cephalosporins and other betalactam antibiotics are widely used antibacterial drugs. Recently it was found that some of them also have effects on proliferating eukaryotic cells (Neftel, K.A. and Hübscher, U. (1987) Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 31, 1657-1661), and one such effect was shown to be the inhibition of DNA polymerase alpha (Huynh Do,U., Neftel, K.A., Spadari, S. and Hübscher, U. (1987) Nucl. Acids Res. 15, 10495-10506). The data suggested that degradation products of betalactam antibiotics were responsible for the inhibitory effect on DNA polymerase alpha. There is some confirmation at the structural level, since we found that penicillin binding proteins, the natural target of the cephalosporins, share amino-acid homologies to DNA polymerases and also to reverse transcriptase from HIV1 (Hafkemeyer, P., Neftel, K.A. and Hübscher, U. Meth. Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 12, 43-46, 1990). We have purified and determined the structure of one product from the cephalosporin Ceftazidim and found one molecule (HP 0.35) that did not interfere with eukaryotic cell proliferation but rather had a specific inhibitory effect on the RNase H activity of human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV1) and feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) reverse transcriptases, while the DNA polymerising activity of these enzymes was not affected. RNases H from HeLa cells, calf thymus and Escherichia coli on the other hand were much less affected by HP 0.35. The inhibitory concentration of 50% (IC50) was more than 10 times lower compared to those of all cellular RNases H. We therefore tested the effect of HP 0.35 on in vitro lentivirus infection as exemplified by FIV-infection of CD(4+)-cat lymphocytes in cell culture. Under conditions where cell proliferation was absolutely unaffected, HP 0.35 was able to inhibit FIV-infection in CD(4+)-cat lymphocytes. Moreover, preincubation of these lymphocytes with HP 0.35 rendered the cells completely unsusceptible to FIV-infection. These data suggest that a degradation product of a clinically used betalactam antibiotic might represent an effective inhibitor class for lentiviral RNase H.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgers P. M., Bambara R. A., Campbell J. L., Chang L. M., Downey K. M., Hübscher U., Lee M. Y., Linn S. M., So A. G., Spadari S. Revised nomenclature for eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Aug 17;191(3):617–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney D. A., Ahluwalia G., Mitsuya H., Fridland A., Johnson M., Hao Z., Dalal M., Balzarini J., Broder S., Johns D. G. Initial studies on the cellular pharmacology of 2',3'-dideoxyadenosine, an inhibitor of HTLV-III infectivity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 1;36(11):1765–1768. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottagnoud P., Neftel K. A. Beta-lactams act on DNA synthesis in K-562 cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1986 Dec;2(4):523–529. doi: 10.1007/BF00117854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex-1 DNA polymerase. Identification of an intrinsic 5'----3' exonuclease with ribonuclease H activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19266–19270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Do U. H., Neftel K. A., Spadari S., Hübscher U. Betalactam antibiotics interfere with eukaryotic DNA-replication by inhibiting DNA polymerase alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10495–10506. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focher F., Gassmann M., Hafkemeyer P., Ferrari E., Spadari S., Hübscher U. Calf thymus DNA polymerase delta independent of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1805–1821. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafkemeyer P., Neftel K. A., Hübscher U. HIV-reverse transcriptase and human DNA polymerase alpha share amino acid sequence homologies to bacterial penicillin-binding proteins. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Jan-Feb;12(1):43–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeier A., Grosse F. A distinct form of ribonuclease H from calf thymus stimulates its homologous DNA-polymerase-alpha-primase complex. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 20;185(3):621–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Mellert W., Moelling K. Identification and characterization of HIV-specific RNase H by monoclonal antibody. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):239–243. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Huynh U. D., Hässig M., Neftel K. A. Effects of beta-lactams on DNA replication. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1986 Dec;2(4):541–548. doi: 10.1007/BF00117856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Kornberg A. The delta subunit of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme is the dnaX gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6284–6288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L., Darby G. Site-specific mutagenesis of AIDS virus reverse transcriptase. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):716–717. doi: 10.1038/327716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad G., Jonsson G., Falk J. Adenine toxicity: a three week intravenous study in dogs. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1973;32(3):246–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1973.tb01468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz H., Arnold P., Hübscher U., Egberink H., Pedersen N., Horzinek M. C. Specificity assessment of feline T-lymphotropic lentivirus serology. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1988 Dec;35(10):773–778. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1988.tb00559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Namikawa R., Shih C. C., Rabin L., Kaneshima H. Suppression of HIV infection in AZT-treated SCID-hu mice. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):564–566. doi: 10.1126/science.2300816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neftel K. A., Hauser S. P., Müller M. R. Inhibition of granulopoiesis in vivo and in vitro by beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):90–98. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neftel K. A., Hübscher U. Effects of beta-lactam antibiotics on proliferating eucaryotic cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1657–1661. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North T. W., North G. L., Pedersen N. C. Feline immunodeficiency virus, a model for reverse transcriptase-targeted chemotherapy for acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):915–919. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. E., Elias P., Lehman I. R. Processive replication of single-stranded DNA templates by the herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4252–4259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted R. A., Barnes A. K., Yamamoto J. K., Hirsch V. M., Purcell R. H., Johnson P. R. Molecular cloning of feline immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2448–2452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted R. A., Hirsch V. M., Purcell R. H., Johnson P. R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of feline immunodeficiency virus: genome organization and relationship to other lentiviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8088–8092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C., Ho E. W., Brown M. L., Yamamoto J. K. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic virus from domestic cats with an immunodeficiency-like syndrome. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):790–793. doi: 10.1126/science.3643650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek S., Grosse F. A plasmid vector system for the expression of a triprotein consisting of beta-galactosidase, a collagenase recognition site and a foreign gene product. Gene. 1988;62(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90579-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S., Weissbach A. HeLa cell R-deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases. Separation and characterization of two enzymatic activities. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5809–5815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Hübscher U. DNA helicase from calf thymus. Purification to apparent homogeneity and biochemical characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14347–14354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E. Newly made enzymes determine ongoing cell wall synthesis and the antibacterial effects of cell wall synthesis inhibitors. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):535–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.535-543.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Wong S. W., Korn D. Human DNA polymerase alpha: predicted functional domains and relationships with viral DNA polymerases. FASEB J. 1989 Jan;3(1):14–21. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.1.2642867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Grosse F. Fidelity of human immunodeficiency virus type I reverse transcriptase in copying natural DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1379–1393. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Mitsuya H., Myers C. E., Broder S. Clinical pharmacology of 3'-azido-2',3'-dideoxythymidine (zidovudine) and related dideoxynucleosides. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 14;321(11):726–738. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909143211106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


