Abstract
A set of 67 novel LTR-retrotransposon has been identified by in silico analyses of the Culex quinquefasciatus genome using the LTR_STRUC program. The phylogenetic analysis shows that 29 novel and putatively functional LTR-retrotransposons detected belong to the Ty3/gypsy group. Our results demonstrate that, by considering only families containing potentially autonomous LTR-retrotransposons, they account for about 1% of the genome of C. quinquefasciatus. In previous studies it has been estimated that 29% of the genome of C. quinquefasciatus is occupied by mobile genetic elements.
The potential role of retrotransposon insertions strictly associated with host genes is described and discussed along with the possible origin of a retrotransposon with peculiar Primer Binding Site region. Finally, we report the presence of a group of 38 retrotransposons, carrying tandem repeated sequences but lacking coding potential, and apparently lacking “master copy” elements from which they could have originated. The features of the repetitive sequences found in these non-autonomous LTR retrotransposons are described, and their possible role discussed.
These results integrate the existing data on the genomics of an important virus-borne disease vector.
Introduction
Transposable elements are ubiquitous component of eukaryotic genomes and, besides their mutagenic role [1], they are considered as the major source of variability that can change genomes and their expression, either considering short term or large evolutionary scale time. The action exerted by transposable elements on genomes is predominantly described in studies performed in insect where the abundance of both active and inactive forms of mobile elements have shaped their genomes structurally, functionally and evolutionarily.
The post-genomic era offers a great opportunity to shed light on the evolution of mobile genetic elements with respect to eukaryotic genome. The results obtained from several genomic studies allow the comparison of related sequences from different organisms. In addition, the great amount of sequence data produced have led to the identification of novel families of mobile genetic elements and posed a problem concerning their classification [2], [3]. Looking at their transposition mechanism, transposons can be classified into two main classes [4]. Class I elements, or retrotransposons, reverse transcribe a RNA intermediate into cDNA molecules, which is then inserted in the genome. Class I elements can be further categorized in LTR- and non-LTR retrotransposons depending on the presence or absence of direct terminal repeats. Retrotransposons are major components of eukaryotic genomes; they are among the strongest evolutionary driving force acting on the genomes [5], and are potentially able to change gene expression patterns [6] [7]. Their ability to inflate eukaryotic genome size [8] is also at the basis for their use as molecular markers in organisms of socio-economic interest [9].
In the last years the rising interest in the field of mosquitoes' genomics is demonstrated by the completion of three genome sequences, and this mainly comes from their role as vectors of virus-borne diseases.
Three mosquitoes' genomes have been sequenced and assembled to date. The first mosquito genome to be sequenced was the Anopheles gambiae [10] followed by the sequencing of the Aedes aegypti's genome [11].
Culex quinquefasciatus is the main vector of the nematode W. bancrofti, one of the known causes of the lymphatic filariasis, and its genome (about 540 Mbp) [12] has been recently sequenced [13]. Among the Culicidae family, the Anophelinae and the Culicinae subfamilies have diverged about 145–200 Mya, while within the Culicinae subfamily, Aedes and Culex genera have diverged about 52–54 Mya [13]. With this effort, a solid genomic platform for mosquito comparative genomics has been established.
Few Culex transposon families have been described in reports published before the publication of the Culex genome paper, being limited to few DNA transposon [14] [15] and retrotransposon [16] [17] [18] families.
The genomic sequence analysis performed by Arensburger et al. [13] has revealed that nearly 30% of the Culex genome is composed of TEs. Compared with the TEs content in the genomes of A. gambiae (16%) and A. aegypti (50%), this appears to be an intermediate value, as well as intermediate is the genome size of C. quinquefasciatus compared to the above mentioned genomes (286 Mbp and 1,3 Gbp respectively). The LTR retrotransposons identified and described in the genome sequencing paper have been deposited in the TEfam database [19], a specialized database for transposable elements retrieval and analyses, which focus on mosquito species. In its Culex quinquefasciatus section TEfam contains 81 families of Bel/Pao elements, 32 families of Ty1/copia elements and 57 families of Ty3/gypsy elements in addition to 179 families of non-LTR retrotransposons, 32 families of “cut and paste” transposons families, 3 helitrons families and 100 MITEs families.
A novel class of mobile elements with striking features has been previously described in C. quinquefasciatus. Twin is a family of atypical SINE elements with a dimer-like structure similar to a tRNA gene. It has been proposed that Twin family is probably a moderately repetitive sequence specific of the genus Culex, as it is absent in the genome of Aedes species [20].
Furthermore we have recently described a family of Osvaldo-like elements with peculiar structure of the LTRs [17].
Here, we report the presence of twenty-nine families of LTR retrotransposons in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus, identified using the LTR_STRUC program [21] and not reported in the TEfam database. One of these elements has an atypical Primer Binding Site region probably generated by the insertion of a tRNA dimer immediately downstream the 5′ LTR. Furthermore we have identified a group of 38 families probably composed of non-autonomous elements, apparently unrelated to any known retrotransposon family, which contain tandem repeated sequences between the LTRs.
The results of the genomic distribution analysis show that the novel retrotransposons identified in this paper are preferentially located in intergenic regions or in intron sequences in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus. Several insertions that may potentially contribute to the organization of protein-coding genes have been identified. The possible functional role of these insertions on the host gene organization is discussed.
Materials and Methods
LTR_STRUC analysis and classification of LTR retrotransposons
The genome sequence of C. quinquefasciatus was downloaded from the Broad Institute website (http://www.broad.mit.edu/index.html) and scanned with the LTR_STRUC program [21] using the default parameters. 1179 putative retrotransposon sequences obtained as output were subjected to an “all against all” BLAST in order to group sequences with % identity greater than 98% over a sequence of at least 1 Kb. 157 groups containing at least one sequences were obtained after this step. The final subset of LTR retrotransposons was then BLAST-searched against the TEfam database in order to define families and to highlight previously not annotated sequences. In order to confirm the results obtained by LTR_STRUC we have performed a LTR-retrotransposon search using the LTRharvest program [22]. The results obtained were compared to the TEfam database and the LTR_STRUC output.
Criteria for defining LTR-retrotransposons were identical to the previously described criteria adopted during A. aegypti TE analysis [17]. Briefly, sequences of the Ty3/gypsy LTR retrotransposons are considered as belonging to the same element if they share at least 85% nucleotide identity along at least 400 bp in their coding region. Ty1/Copia sequences that share at least 85% identity at the nucleotide level over at least 1000 bp are considered belonging to the same element. Copies of Pao/Bel retrotransposons are considered as belonging to the same element if they show at least 70% identity at the nucleotide level in their coding sequences.
The names assigned to the newly discovered retrotransposons follow the nomenclature adopted in the Repbase database [23] and contain the prefix “Cq” for species (Culex) and genera (quinquefasciatus), the specification of the family (namely Ty3/gypsy, Ty1/copia, BEL, etc.) and a number suffix.
Analysis of insertions
The ORF finder program (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html) was used to determine the ORF number of each element detected.
The TSD (Target Site Duplicated upon insertion) and the length of the LTRs of each element obtained were determined by visual inspection of sequences. In absence of a reported list of the tRNA gene sequences in C. quinquefasciatus the PBS sequences were determined by comparison of a tRNA dataset of A.gambiae at the http://lowelab.ucsc.edu/GtRNAdb/Agamb/ website. The tRNA genes of A. gambiae are highly similar (if not identical in most of the cases) to the tRNA of C. quinquefasciatus, as demonstrated by BLAST analysis (not shown). This data ensure that a good PBS prediction has been done using the A. gambiae tRNA dataset.
To detect retrotransposon insertions near (or overlapping) host genes, a BLAST search at the Vectorbase database (http://www.vectorbase.org/) was performed using the following arbitrary criteria: 1) only insertions with average similarity greater than 85% were counted; 2) insertions shorter than 180 bp were not taken in account; 3) the E value was lower than 1E−40. These criteria allow the detection of full-length elements and defective elements without missing solo LTR and preventing misleading results coming from low quality alignments. The analyses of tandem repeats contained into retrotransposon were performed with the Tandem Repeat Finder program [24] using the basic option.
RepeatMasker analysis
RepeatMasker software (version 3.2.9) [25] was used to estimate the retrotransposons occupancy as percent of the genome fraction. Repeats search was performed using Cross_Match as sequence search engine. A repeats library was built starting from the LTR retrotransposon group described in this paper (file S1), and it was used to scan the genome sequence. Scanning was carried out using a cutoff value of 250.
Multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis
As previously described [26] the best way to reconstruct phylogeny of retroelements is to perform multiple alignment of RT-RnaseH-INT domains. These domains encoded by each putatively active element were extracted from the translated ORF encoding the POL polyprotein and used to reconstruct the phylogenetic history of C. quinquefasciatus Ty3/gypsy like retrotransposons. We have no evidence of domain swapping by performing multiple alignment using RnaseH, RT or INT domains (data not shown) at least for the elements analyzed in this paper. Either MUSCLE [27] or ClustalX [28] were used to perform multiple alignments. After a manual check of the alignments Neighbor-joining tree with bootstrap analyses were generated using MEGA5 [29]. As reference, previously described elements in other species [19] [17] [26] were used to establish relationships between C. quinquefasciatus retroelements.
Multiple alignments are available as file S2.
Results
The genome sequence of C. quinquefasciatus (assembly version CpipJ1) was analyzed using the LTR_STRUC program, in order to obtain LTR-retrotransposon sequences.
The 1179 insertions obtained were clustered into groups of nearly identical sequences (see Material and Methods section). This allowed the identification of 157 families of elements containing at least one retrotransposon copy. The DNA sequence of representative elements of each family was BLAST-searched against the TEfam database. Only sequences that did not match any of the elements reported in TEfam were further analyzed. This led to the identification of 29 previously not described and potentially active elements (i.e. containing the genetic specification for the transposition machinery and the required cis-acting sequences). A single representative element of each family was used in the phylogenetic analysis. Representative elements were chosen among those having the best match between the two LTRs, the longest sequence and the simplest ORF structure, coding for the entire set of protein domain typically found in the family. Furthermore, elements with such features could be potentially functional and transpositionally active. Although we have identified Ty1-copia and Bel-Pao elements, they were not further analyzed due to the presence of identical sequences in the TEfam database.
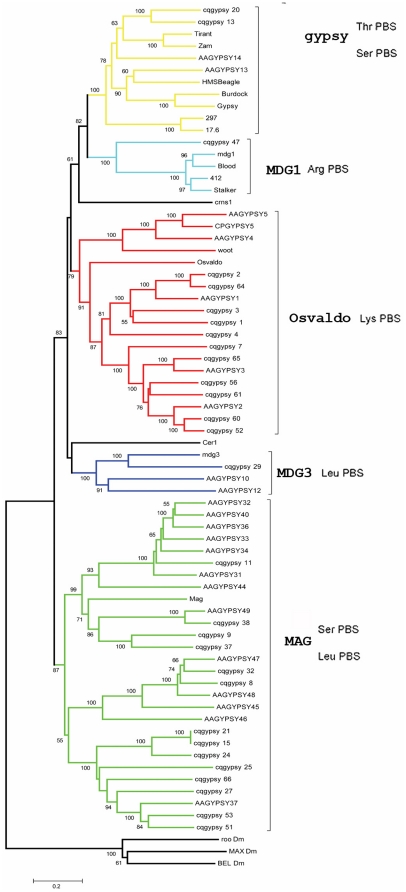
A phylogenetic analysis was performed in order to identify the origin of each group of sequences extrapolated from the LTR_STRUC output. The RT-RNaseH-INT domains of the POL polyproteins were aligned along with the corresponding domains of reference elements. This multiple alignment was then used to generate a NJ tree. As can be observed in figure 1, all the novel elements identified fall into the Ty3-gypsy superfamily of LTR-retrotransposons. Furthermore, the results reported in figure 1 clearly show that the new elements reported belong to five distinct lineages (namely gypsy, Osvaldo, Mag mdg3 and mdg1). No novel CsRn1-like elements were detected despite they are well represented in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus, as demonstrated by the presence of nine CsRn1-like elements in the TEfam database.
Figure 1. Evolutionary relationships of C. quinquefasciatus LTR-retrotransposons.
Phylogenetic relationships of the LTR retrotransposons based on the amino acids alignment of the conserved RT, RNase H and INT domains. The clades in which fall retrotransposons detected in this paper are indicated with different colors, along with the most common tRNA complementary to the PBS is indicated for each homogeneous group. Elements from this study are indicated as “cpgypsy_” followed by a number. AAGYPSY# elements are LTR retrotransposons identified in previous analyses [17]. The N-J bootstrap values supporting the internal branches are indicated at the nodes. Only bootstrap values greater than 50% are reported. Bel-like elements were used as outgroup. Note that, for families composed of two or more copies (see table 1), representative elements (see file S1) were used for the phylogenetic analyses.
The structural features of the retrotransposons identified in this study were also analyzed and reported in table 1. Except for few cases that will be discussed below, the main features of these elements (namely PBS type and LTR mean length) are in agreement with those of known elements belonging to the same lineage and described in other species. In table 1 is also reported the percent nucleotide identity between the LTR of each insertion detected. This value gives an approximate idea of the age of the insertions. To the best of our knowledge, the synonymous substitution rate has not been estimated for C.quinquefasciatus; consequently we are not able to make more precise estimations of the age of insertions.
Table 1. Structural features of the C. quinquefasciatus LTR-retrotransposons detected.
| Lineage | Family | copies | Element | length | LTRs | %LNI | ORFs | PBS | TSD | supercont |
| Mag | cqgypsy_8 | 3 | cqgypsy_8.1 | 4993 | 179 | 100 | 1 | Leu | gtcac | 3.1653 |
| Mag | cqgypsy_9 | 1 | cqgypsy_9.1 | 4568 | 145 | 100 | 1 | Leu | tttag | 3.1194 |
| Mag | cqgypsy_11 | 11 | cqgypsy_11.1 | 5129 | 169/181 | 99 | 2 | Ser | ataa | 3.429 |
| Mag | cqgypsy_15 | 4 | cqgypsy_15.1 | 4851 | 197 | 99 | 1 | Ser | tccag | 3.1361 |
| Mag | cqgypsy_21 | 2 | cqgypsy_21.1 | 6184 | 287 | 99 | 2 | Ser | tcctt | 3.770 |
| Mag | cqgypsy_24 | 6 | cqgypsy_24.1 | 10446 | 304 | 99 | 2 | Ser | accag | 3.163 |
| Mag | cqgypsy_25 | 6 | cqgypsy_25.1 | 7859 | 198 | 99 | 2 | Arg | ggaag | 3.176 |
| Mag | cqgypsy_27 | 4 | cqgypsy_27.1 | 5260 | 196 | 97 | 2 | Ser | gtgcc | 3.790 |
| Mag | cqgypsy_32 | 3 | cqgypsy_32.1 | 4918 | 190 | 99.5 | 1 | Leu | ggaat | 3.540 |
| cqgypsy_32.2 | 4779 | 182 | 97.8 | 3 | Leu | attac | 3.1290 | |||
| Mag | cqgypsy_37 | cqgypsy_37.1 | 4078 | 139/143 | 92.4 | 1 | Ser | cttgc | 3.100 | |
| cqgypsy_37.2 | 9065 | 152 | 98.7 | 1 | Ser | ataat | 3.30 | |||
| Mag | cqgypsy_38 | 5 | cqgypsy_38.1 | 4472 | 164 | 97.6 | 2 | Ser | cctgg | 3.723 |
| cqgypsy_38.2 | 4534 | 164 | 97.6 | 2 | Ser | ttaat | 3.1068 | |||
| cqgypsy_38.3 | 3248 | 119 | 97.3 | 2 | Ser | attcc | 3.1314 | |||
| Mag | cqgypsy_53 | 31 | cqgypsy_53.1 | 5310 | 211 | 97.2 | 1 | Ser | cactt | 3.144 |
| cqgypsy_53.2 | 2887 | 211/213 | 99.1 | frag | Ser | aggac | 3.1107 | |||
| Mag | cqgypsy_51 | 5 | cqgypsy_51.1 | 4904 | 179 | 100 | 2 | Ser | acctg | 3.1151 |
| cqgypsy_51.2 | 6291 | 179 | 98.9 | 2 | Ser | gacac | 3.243 | |||
| cqgypsy_51.3 | 4575 | 188 | 100 | frag | Ser | aacac | 3.1291 | |||
| Mag | cqgypsy_66 | cqgypsy_66.1 | 7544 | 208 | 100 | 2 | Ser | ctatt | 3.7 | |
| Gypsy | cqgypsy_13 | 7 | cqgypsy_13.1 | 7249 | 302 | 100 | 3 | Thr | tatata | 3.734 |
| Gypsy | cqgypsy_20 | 3 | cqgypsy_20.1 | 7438 | 357 | 100 | 3 | Ser | atata | 3.1285 |
| Mdg3 | cqgypsy_29 | 4 | cqgypsy_29.1 | 5316 | 264 | 100 | 2 | Leu | gttg | 3.462 |
| cqgypsy_29.2 | 5343 | 263 | 99.6 | 2 | Leu | atag | 3.168 | |||
| Mdg1 | cqgypsy_47 | 25 | cqgypsy_47.1 | 6771 | 431 | 100 | 2 | Arg | cttc | 3.2173 |
| cqgypsy_47.2 | 8540 | 444 | 100 | 1 | Arg | gaac | 3.13 | |||
| cqgypsy_47.3 | 6623 | 444 | 100 | 2 | Arg | ccac | 3.33 | |||
| cqgypsy_47.4 | 6751 | 432 | 99.3 | 2 | Arg | cagg | 3.508 | |||
| cqgypsy_47.5 | 6772 | 431 | 99.9 | 2 | Arg | gccg | 3.346 | |||
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_1 | 3 | cqgypsy_1.1 | 11926 | 2137 | 99 | 2 | Lys | ggtt | 3.62 |
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_2 | 21 | cqgypsy_2.1 | 12138 | 2055/2056 | 99 | 2 | Lys | aact | 3.1399 |
| cqgypsy_2.2 | 5491 | 2054/2057 | 99.7 | frag | Lys | tgct | 3.72 | |||
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_3 | 7 | cqgypsy_3.1 | 10049 | 1591/1596 | 99 | 2 | Lys | aagt | 3.349 |
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_4 | 6 | cqgypsy_4.1 | 10581 | 1742 | 99 | 2 | Lys | caac | 3.169 |
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_7 | 5 | cqgypsy_7.1 | 6914 | 997 | 99 | 1 | Lys | aagt | 3.38 |
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_52 | 29 | cqgypsy_52.1 | 10354 | 1340 | 99.6 | 1 | Lys | caaa | 3.458 |
| cqgypsy_52.2 | 7373 | 1345/1346 | 99.4 | frag | Lys | agct | 3.70 | |||
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_56 | 14 | cqgypsy_56.1 | 9473 | 1384 | 100. | 2 | Lys | aaat | 3.568 |
| cqgypsy_56.2 | 9393 | 1369/1368 | 95.1 | 2 | Lys | ttat | 3.83 | |||
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_61 | 15 | cqgypsy_61.1 | 9196 | 1151 | 99.6 | 2 | Lys | caaaag | 3.1285 |
| cqgypsy_61.2 | 10261 | 246 | 97 | frag | Lys | attat | 3.330 | |||
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_60 | 48 | cqgypsy_60.1 | 10172 | 1308 | 99.3 | 2 | Lys | acaac | 3.133 |
| cqgypsy_60.2 | 10164 | 1310 | 99.9 | frag | Lys | actt | 3.784 | |||
| cqgypsy_60.3 | 9985 | 1224 | 99.6 | 2 | Lys | cagg | 3.215 | |||
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_64 | 41 | cqgypsy_64.1 | 12479 | 2045/2046 | 99.8 | 2 | Lys | acgt | 3.82 |
| cqgypsy_64.2 | 12368 | 2038/2037 | 98.6 | 2 | Lys | aagc | 3.191 | |||
| cqgypsy_64.3 | 8014 | 2047/234 | 98. | frag | Lys | agat | 3.141 | |||
| cqgypsy_64.4 | 7680 | 1857 | 100 | frag | Lys | ctat | 3.82 | |||
| Osvaldo | cqgypsy_65 | 20 | cqgypsy_65.1 | 10447 | 1565 | 99% | 2 | Lys | aacc | 3.254 |
“Lineage” indicates the major lineage they belong to; the estimated copy number detected by BLAST analysis is indicated in the column “copies”; copies enumerated in column “Elements” are those identified by the LTR_STRUC program; “length” indicates the overall element length; “ORFs” indicates the number of ORFs detected in each element; TSD shows the target sequence duplicated upon insertion, Primer Binding Site (PBS); LTR indicates the LTR length; supercontig indicates the supercontig where a given element was identified. %LNI: percent LTRs nucleotide identity.
Note that two values are reported in the LTRs column if the two LTRs of an element differ in size. “frag” indicates fragmented coding regions.
No target site preference was observed for any of the retrotransposons analyzed.
A closer view of the phylogenetic analysis results indicates that eleven elements can be classified as Osvaldo-like, two fall in the gypsy lineage, one in the Mdg1 and Mdg3 lineages respectively. The analysis performed was aimed to dissect the structural properties for each family detected, and to compare them with those of known elements of the same phylogenetic lineage.
Gypsy lineage
Two novel gypsy-like elements have been identified in this study. The structural analyses have revealed that the first base of the putative PBS overlaps the last base of the 5′ LTR in these elements; this was also observed for the gypsy element of D. melanogaster [30]. It can be assumed that this a general rule for the members of the gypsy lineage identified in other organisms.
Several members of the gypsy lineage identified so far in other organisms contain an ORF that could potentially encode for the envelope protein (ENV), a typical retrovirus like protein reported to be important in the horizontal transmission process [31]. The two gypsy-like elements detected in this study also contain an ORF that potentially encodes an ENV-like protein. The conceptual translation of these putative env-coding regions reveals typical domains of ENV proteins (not shown).
Mag lineage
Members of this lineage have been previously identified in several insect genomes such as B. mori [32], A. gambiae, D. melanogaster [33] and C. elegans [34] [35].
Thirteen families are phylogenetically related to the Mag element. The PBS of the Mag-like elements identified is complementary either to the tRNALeu or to the tRNASer. A single element (cqgypsy_25) with an atypical PBS sequence, complementary to the tRNAArg, has been identified. Three elements (namely cqgypsy_24, cqgypsy_25 and cqgypsy_66) contain tandem repeated sequences in the 5′ UTR. The unusual size of the cqgypsy_24 element (greater than 10 Kbp) is due to the size of a repeated region (about 3 Kbp).
The phylogenetic analysis shows that the Mag clade is formed by two subgroups strongly supported by high bootstrap values. Four elements of C. quinquefasciatus co-cluster with the Mag element, while 9 elements fall into the second cluster with five elements from A. aegypti used as reference elements.
Mdg1 and Mdg3 lineages
Two elements identified in this paper belong to the Mdg1 and Mdg3 clades respectively. cqgypsy_47 belongs to the Mdg1 clade while cqgypsy_29 belongs to the Mdg3 lineage. Looking at the TEfam database, eight Mdg1-like elements and three Mdg3-like elements can be retrieved. This suggests the possibility that these two clades could be poorly represented in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus.
Osvaldo lineage
Existing data in the TEfam database, suggest that these elements are abundant in the family Culicidae. Twenty-nine Osvaldo-like elements are annotated in the genome of A. aegypti and five elements in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus.
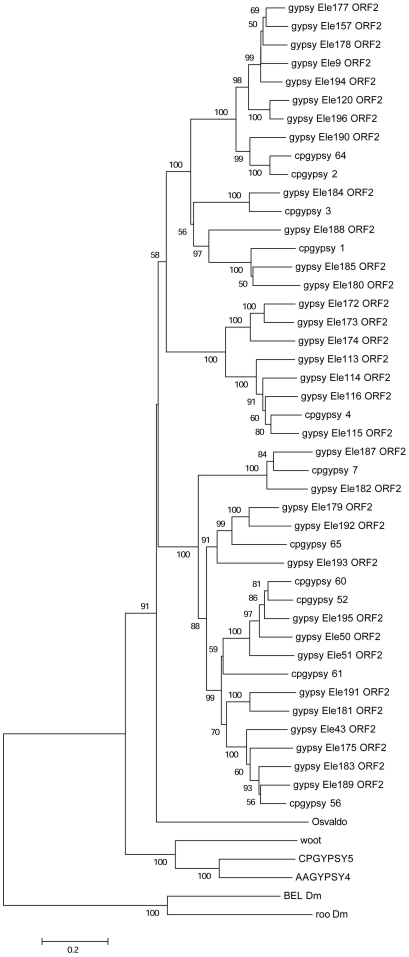
Querying the TEfam dataset for Osvaldo-like elements in C. quinquefasciatus results in five annotated elements. We have identified 11 unreported Osvaldo-like elements in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus. Their LTRs length ranges from 997 to 2055 bp, a feature that characterizes members of the Osvaldo lineage. In figure 2 are showed the phylogenetic relationships of the Osvaldo-like elements identified in A. aegypti and C. quinquefasciatus. No species-specific cluster was observed in the distribution of these elements. Copy number varies among different families of Osvaldo-like elements (see table 1) and the PBS is invariantly complementary to the 3′ end of the tRNALys. This is also the initiator tRNA used by Osvaldo [36]. As reported in our previous analyses, both genomes of A. aegypti and C. quinquefasciatus contain retrotransposons that are strictly related to the woot element of T. castaneum [17], but containing unusually short LTRs. The CPGYPSY5 element identified by Minervini et al by BLAST similarity search was also identified during the course of this analysis by the LTR_STRUC program.
Figure 2. Evolutionary relationships of Osvaldo-like elements of C. quinquefasciatus LTR-retrotransposons.
Phylogenetic relationships of the Osvaldo-like retrotransposons based on the amino acids alignment of the conserved RT, RNase H and INT domains CPGYPSY5 and AAGYPSY# are LTR retrotransposons identified in previous analyses [17]. Elements “gypsy ELE ###” were retrieved from the TEfam database. The N-J bootstrap values supporting the internal branches are indicated at the nodes. Only bootstrap values greater than 50% are reported. Bel-like elements were used as outgroup.
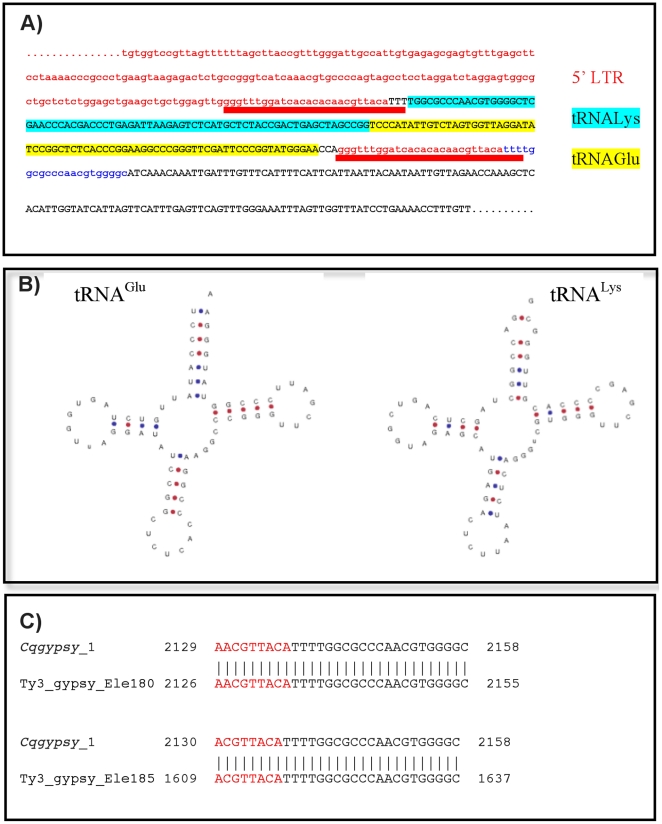
cqgypsy_1 is a peculiar element of the Osvaldo lineage. It has been detected as single copy retrotransposon by LTR_STRUC analysis, but probably present in multiple copies in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus as revealed by BLAST analyses on the trace archive (not shown). The structural analysis of its PBS region shows that it has a non-canonical PBS. Instead of a short nucleotide stretch complementary to the 3′ end of a tRNA, we have found a 149 bp long sequence identical to two tRNA arranged in a head to head fashion. The 149 bp sequence is recognized by the tRNAscan program, which in turn gives two perfectly folded tRNA molecules as output (figure 3B)
Figure 3. Organization of the LTR-PBS region of cqgypsy_1.
A) The tRNA sequences inserted into the 5′LTR of the cqgypsy_1 element. The LTR sequence is colored in red, while the PBS sequence is colored in blue. The red bar indicates the duplicated sequence surrounding the putative Twin element. Each of the tRNA halves of the putative Twin is highlighted in turquoise (tRNALys) or in yellow (tRNAGlu). The PBS is depicted in blue. B) tRNAscan output showing the secondary structure of the two halves of the insertion as a cloverleaf structure. C) Local alignment results of cqgypsy_1 with the gypsy_Ele180 and gypsy_Ele185. The aligned region correspond to the 5′LTR (red)/PBS(black) boundary.
The unusual configuration of the PBS region of cqgypsy_1 has been analyzed in details. As can be observed in figure 3, both tRNA-like sequences have the terminal CCA sequences. Furthermore a direct duplication of 26 nucleotides of the 5′LTR has been found at both sides of the tandem tRNA copies. The tandem copies of tRNA identified in cqgypsy_1 are somehow reminiscent of the structure of Twin elements described by Feschotte and co-authors [20]. Twin has been described as a novel type of SINE element consisting of two tRNA related regions separated by a 39 bp spacer.
We have also analyzed in detail the phylogenetic relationships of cqgypsy_1 with other elements of the Osvaldo lineage belonging to different mosquito genomes. Its closest relative is the Ty3_gypsy_Ele185 and Ty3_gypsy_Ele180 elements annotated in the TEfam database (TEfam ID TF000935 and TF000939 respectively). None of the related elements of A. aegypti contain such tandem copy of tRNA. We do not expect to observe significant sequence similarity at the nucleotide level when Culex and Aedes elements were compared in a pair-wise alignment, despite the strict relationship observed at the protein level. By comparing the three Osvaldo-like elements, cqgypsy_1, Ty3_gypsy_Ele185 and Ty3_gypsy_Ele180, we have detected a similarity region in a 29–30 nucleotides region encompassing the boundary between the 5′LTR and the PBS region (see figure 3C), suggesting an unusually strong cross-species conservation of the LTR sequence flanking the PBS. This conservation across the 5′LTR boundary and the PBS was not observed after comparison of any of the retrotransposons analyzed in this paper with their relatives in Aedes aegypti. Taken together, these results confirm the phylogenetic relationship among these elements and indicate a strong conservation of the 30-nucleotide long sequence across the 5′ LTR shared by Culex and Aedes elements, which is probably under functional constrains.
Non-autonomous elements
Non-autonomous elements are important to understand the evolutionary dynamics of transposable elements in the genomic context [37]. Non-autonomous elements were also detected and analyzed in this work. The LTR_STRUC program is also able to find aberrant retrotransposon sequences (i.e. LTR-retrotransposon with internal deletions of various size); in this case a lower score is assigned respect to a potentially active retrotransposon. However, most of the defective LTR retrotransposons detected are false positives resulting from a couple of direct repeats (mimicking the LTRs) but lacking PBS, PPT, the target site duplication and the coding sequences. A certain number of low scoring sequences extracted by LTR_STRUC are bona fide defective elements. Several nested elements were also found in the output of LTR_STRUC, but no significant bias of nesting was observed. In general, truncated retrotransposons are related to at least one putatively active element, in the TEfam dataset or in our output, thus falling into a specific family of elements that, for this reason, will be composed by autonomous and non-autonomous elements.
Notably, we have found a group of non-autonomous elements lacking coding sequences, and that cannot be related to any of the known putatively active elements annotated in TEfam, nor to any of the elements identified in this work. The features of these elements are summarized in table 2.
Table 2. Features of the non-autonomous LTR retrotransposons identified in this paper.
| Element | supercont | length | LTR | PBS | TSD | Rep Position | Period | Copies | Entropy | % |
| cqUNK_1 | 3.2 | 2994 | 261 | Arg | caagg | 583–1963 | 155 | 8.9 | 1.96 | |
| 2188–2226 | 16 | 2.4 | 1.40 | 52.9 | ||||||
| 2206–2380 | 22 | 8.0 | 1.40 | |||||||
| cqUNK_3 | 3.322 | 14602 | 315/337 | Leu | attcc | 3252–3314 | 2 | 31.5 | 1.10 | 0.9 |
| 13294–13367 | 33 | 2.2 | 1.63 | |||||||
| cqUNK_4 | 3.720 | 2990 | 389 | Arg | ttct | 540–625 | 34 | 2.5 | 1.94 | 2.8 |
| cqUNK_5 | 3.49 | 6237 | 931 | Asn | nd | 2701–2763 | 12 | 5.3 | 1.28 | |
| 2933–3723 | 164 | 4.8 | 1.97 | 14.2 | ||||||
| 5366–5398 | 17 | 1.9 | 1.94 | |||||||
| cqUNK_6 | 3.403 | 1629 | 125 | Pro | nd | 323–375 | 16 | 3.3 | 1.50 | |
| 536–1337 | 164 | 4.9 | 1.97 | |||||||
| 2086–2447 | 129 | 2.8 | 1.75 | 94.9 | ||||||
| 4245–4281 | 18 | 2.1 | 1.50 | |||||||
| 7914–7960 | 16 | 3.0 | 1.86 | |||||||
| cqUNK_7 | 3.506 | 2267 | 182 | Arg | ggtgc | 608–1551 | 117 | 8.1 | 1.96 | 41.6 |
| cqUNK_9 | 3.65 | 4795 | 193 | Ser | gatc | 1365–1740 | 49 | 7.7 | 1.92 | 7.8 |
| cqUNK_10 | 3.176 | 3540 | 194 | Ser | agaag | 1278–1780 | 144 | 3.5 | 1.91 | 14.2 |
| cqUNK_11 | 3.710 | 2554 | 170 | Arg | catt | 1040–2015 | 298 | 3.3 | 2.00 | 38.2 |
| cqUNK_12 | 3.654 | 5450 | 280 | Leu | acaag | 3411–4140 | 88 | 8.3 | 1.94 | 20.1 |
| 4176–4541 | 50 | 7.3 | 1.95 | |||||||
| cqUNK_13 | 3.450 | 4810 | 573 | Tyr | nd | 1481–1731 | 82 | 3.0 | 1.93 | 5.2 |
| cqUNK_14 | 3.563 | 4105 | 176 | Arg | ggcta | 1564–3072 | 93 | 16.7 | 1.97 | 36.5 |
| cqUNK_15 | 3.622 | 5405 | 182 | Arg | nd | 1805–2384 | 92 | 6.3 | 1.98 | 10.7 |
| cqUNK_16 | 3.54 | 6178 | 334 | Ser | nd | 2066–2417 | 159 | 2.2 | 2.00 | 5.7 |
| cqUNK_17 | 3.456 | 5460 | 194 | Met | actac | 2105–3007 | 51 | 19.7 | 1.98 | 13.0 |
| cqUNK_18 | 3.688 | 4616 | 205 | Asp | acaga | 2097–2230 | 72 | 1.9 | 1.91 | |
| 3114–3334 | 51 | 4.3 | 1.96 | 14.2 | ||||||
| 3345–3646 | 48 | 6.3 | 1.92 | |||||||
| cqUNK_19 | 3.258 | 3639 | 360/337 | Tyr | aatac | 970–1162 | 103 | 1.9 | 1.95 | 14.5 |
| 1226–1561 | 154 | 2.2 | 1.95 | |||||||
| cqUNK_20 | 3.707 | 6208 | 519 | Ser | atctg | 2130–2843 | 39 | 18.2 | 1.97 | 11.5 |
| cqUNK_21 | 3.144 | 5520 | 269 | Ser | acgac | 642–734 | 44 | 2.1 | 1.80 | |
| 1286–1714 | 114 | 3.7 | 1.96 | 20.2 | ||||||
| 1960–2554 | 88 | 6.8 | 1.92 | |||||||
| cqUNK_22 | 3.589 | 8814 | 182 | Ser | tactc | 1373–3671 | 164 | 14.0 | 1.97 | 40.1 |
| 5792–6779 | 164 | 6.0 | 1.97 | |||||||
| 7247–7500 | 27 | 9.7 | 1.91 | |||||||
| 7526–7852 | 160 | 2.0 | 1.80 | |||||||
| cqUNK_23 | 3.1311 | 1909 | 193 | Arg | gtaac | 1003–1633 | 76 | 8.3 | 1.98 | 33.0 |
| cqUNK_24 | 3.393 | 4023 | 185 | Ser | ttcat | 401–444 | 9 | 5.1 | 1.40 | 9.2 |
| 3370–3696 | 41 | 8.0 | 1.84 | |||||||
| cqUNK_25 | 3.2077 | 2965 | 276 | Met | ttggg | 1389–1758 | 68 | 5.4 | 1.98 | 12.4 |
| cqUNK_26 | 3.220 | 3444 | 337 | Ser | cagcc | 593–2143 | 150 | 10.3 | 1.89 | 51.4 |
| 2332–2552 | 73 | 3.0 | 1.64 | |||||||
| cqUNK_27 | 3.124 | 4080 | 219 | Arg | gcctt | 1118–2136 | 217 | 4.7 | 1.98 | 31.1 |
| 2160–2411 | 64 | 3.9 | 1.97 | |||||||
| cqUNK_28 | 3.537 | 5520 | 197 | Arg | caccc | 942–1803 | 72 | 12.0 | 1.99 | 15.6 |
| 3221–3349 | 65 | 2.0 | 1.69 | |||||||
| cqUNK_29 | 3.172 | 3300 | 176 | Arg | caagc | 968–1807 | 78 | 10.7 | 1.97 | 25.4 |
| cqUNK_31 | 3.1198 | 3124 | 371 | Ser | gtcca | 1001–1586 | 159 | 3.7 | 1.93 | 31.4 |
| 1633–2047 | 40 | 11.3 | 1.76 | |||||||
| cqUNK_32 | 3.496 | 5091 | 318 | Ser | nd | 835–1520 | 62 | 11.0 | 1.92 | 13.4 |
| cqUNK_33 | 3.1048 | 5047 | 694 | Tyr | nd | 915–1217 | 167 | 1.8 | 2.00 | 6.0 |
| cqUNK_35 | 3.492 | 6910 | 224 | Gln | nd | 2243–5096 | 44 | 67.3 | 1.95 | 39.6 |
| cqUNK_37 | 3.343 | 5389 | 189 | Met | actgg | 2792–3519 | 179 | 4.1 | 1.99 | 13.5 |
| cqUNK_38 | 3.1148 | 7609 | 246 | Arg | ggtat | 558–812 | 74 | 3.4 | 1.94 | |
| 914–1124 | 31 | 6.8 | 1.88 | 7.5 | ||||||
| 1200–1303 | 31 | 3.4 | 1.88 | |||||||
| cqUNK_39 | 3.820 | 5080 | 573/581 | Tyr | tgatg | 2829–2899 | 35 | 2.0 | 1.95 | 1.4 |
| cqUNK_41 | 3.723 | 10955 | 223 | Ala | gtggt | 3037–4288 | 408 | 3.1 | 1.92 | |
| 4795–5140 | 45 | 7.6 | 1.91 | |||||||
| 9068–9146 | 39 | 1.9 | 1.64 | 17.0 | ||||||
| 9288–9395 | 48 | 2.2 | 1.65 | |||||||
| 9446–9533 | 42 | 2.1 | 1.49 | |||||||
| cqUNK_42 | 3.7 | 7544 | 208 | Ser | ctatt | 691–1175 | 127 | 3.9 | 1.90 | 6.4 |
| cqUNK_43 | 3.2654 | 6161 | 224 | Thr | caagg | 1199–3865 | 46 | 58.1 | 1.93 | 43.3 |
| cqUNK_45 | 3.590 | 3246 | 315 | Gln | nd | 2382–2901 | 278 | 1.9 | 1.99 | 16.0 |
For each non-autonomous element is reported the supercontig in which a representative element can be found, the overall length, the LTR size, the tRNA complementary to the PBS. It is also indicated the position, the period and the copies of the repeated DNA contained in the elements listed. The entropy value gives an estimation of the complexity of the repeats (see main text). The portion occupied by repeats in terms of % of the total size of the element is also indicated (column %).
Elements belonging to this group are featured by highly similar LTR sequences (>98% identity), a sharply definable PBS sequence immediately downstream the 5′LTR, a PPT upstream the 3′LTR and a duplicated sequence at the insertion site. We were unable to classify these elements using phylogenetic criteria, due to the lack of coding sequences that would enable common RT-based phylogenetic analyses.
In addition, a common feature of all these elements is the presence of tandemly repeated sequences bracketed by the retrotransposon LTRs.
The presence of repeated sequences into a retrotransposon seems to be a nearly exclusive feature of this group of elements. The exception is represented by three putatively active elements belonging to the Mag lineage (cqgypsy_24, cqgypsy_25 and cqgypsy_66), carrying tandemly repeated sequences, identified during the genome wide screening in C. quinquefasciatus. Moreover, the exceptional size of these three Mag-like elements is due to the presence of repeats.
The repeated region sequence varies among families, and constitute as much as 95% of the entire length of a given element. Tandem repeats Finder [24] allows the estimation of the entropy value for a given DNA sequence, a parameter based on the percent base composition and whose value is comprised between zero (indicating low sequence complexity) and two (indicating high sequence complexity). A base composition analysis of the repeated sequences in these LTR-retrotransposons suggests that only in few cases they are composed by simple di-nucleotide iterations (i.e. cqUNK_3, first repeat), while in most of the cases repeats are complex stretches of DNA as demonstrated by entropy values very close to two (table 2).
LTR-retrotransposons containing repeats have been so far identified in other species [38]. Such repeats are usually located in the 5′ UTR or in the 3′ UTR of these retroelements. It has been demonstrated that tandem repeated sequences carried by retrotransposons of Drosophila melanogaster could behave as powerful regulatory sequences, such as enhancers of the gene expression or genetic insulators. As an example, the tandem repeat in the 5′UTR of gypsy is a powerful insulator [39].
Retrotransposon lacking coding sequences and not relatable to any known master copy have been also identified in A. gambiae in previous genome wide searches (Marsano RM unpublished results). Unlike the non-autonomous elements identified in C. quinquefasciatus and described above, those identified in A. gambiae do not contain tandemly repeated sequences.
Distribution of the retrotransposons in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus
We have performed distribution analysis at the genomic level using BLAST and RepeatMasker [25]. RepeatMasker allows a rapid estimation of the genomic fraction occupied by the sequences analyzed. The analysis was performed using a custom library of repeats identified in this paper.
The genome fraction occupied by the retrotransposon sequences showed in table 1 is 0.82% (4,75 Mbp/579 Mbp). This is likely to be an underestimation due to the criteria used (see materials and methods section). Furthermore, we have intentionally excluded from this analysis the defective retrotransposons described in the previous paragraph, as they could inflate the genomic fraction due to the presence of tandem repeats, which can be found as part of complex satellite rather than retrotransposons.
The BLAST search was performed against C. quinquefasciatus genomic database in order to discriminate among insertions in gene free (or intergenic) genomic regions. A great number of insertions are represented by rearranged elements and by solo-LTRs that can be generated by homologous recombination events between the 5′ and 3′ LTRs.
It has been reported that several families of gypsy-like elements are loaded with potent regulatory elements such as enhancers [40], and insulators [41]. Such cis-regulatory elements, when brought in proximity of genes by mean of novel insertions, are able to modify their original expression pattern, in a way that is dependent of the strength of the regulatory element carried by the retrotransposon and of the distance from the endogenous gene. In order to define the distance occurring between LTR-retrotransposons and nearby genes, we performed our analysis using an arbitrary window length of 5 Kb upstream the transcriptional start site or 5 Kbp downstream the termination of transcription of genes annotated in Vectorbase and in which insertions have been detected. This analysis also enables to know if there is a contribution in the gene organization and evolution in C. quinquefasciatus.
Due to the large number of BLAST hits (more than 7000) obtained by searching non-autonomous elements against the genomic sequence, we have performed the BLAST search against the transcripts database and considering only insertions in the coding region of predicted genes. The results of these analyses are reported in table 3 and table 4.
Table 3. The contribution of LTR-retrotransposons to C. quinquefasciatus gene organization.
| Element | Interaction | Description | GENE ID | Supercont:position |
| Cqgypsy_2 | Within intron | Dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase | CPIJ004687 | 3.72: 556,787–583,090 |
| Exon-Intron junction | 5′-3′ exoribonuclease, putative | CPIJ016423 | 3.746: 154,787–166,602 | |
| 1–2 Kbp upstream | fimbrin/plastin | CPIJ004008 | 3.57: 387,682–393,342 | |
| 2–3 Kbp downstream | allergen, putative | CPIJ018993 | 3.1504: 58,993–71,374 | |
| 0–1 Kbp downstream | Adenylyltransferase and sulfurtransferase MOCS3 | CPIJ001621 | 3.19: 246,047–247,568 | |
| Cqgypsy_3 | 0–1 Kbp downstream | disulfide oxidoreductase | CPIJ018966 | 3.1505: 2,834–13,165 |
| Cqgypsy_5 | 1–2 Kbp downstream | chaperonin | CPIJ013429 | 3.475: 239,574–242,207 |
| Exon-Intron junction | 40 S ribosomal protein S2 | CPIJ012693 | 3.480: 10,936–19,727 | |
| 4–5 Kbp upstream | serine threonine-protein kinase | CPIJ018896 | 3.1443: 17,857–21,694 | |
| Cqgypsy_7 | Within intron | Brahma associated protein 170 kD, putative | CPIJ002241 | 3.30: 656,859–677,280 |
| Overlap first exon | ribosomal protein L23a | CPIJ016489 | 3.858: 52,166–53,573 | |
| Cqgypsy_8 | 1–2 Kbp upstream | suppressor of ty3 | CPIJ014381 | 3.539: 307,272–309,528 |
| 1–2 Kbp downstream | suppressor of ty3 | CPIJ014381 | 3.539: 307,272–309,528 | |
| intron | suppressor of ty3 | CPIJ014381 | 3.539: 307,272–309,528 | |
| Cqgypsy_13 | 0–1 Kbp downstream | transcription factor IIIB 90 kDa subunit | CPIJ008270 | 3.167: 169,563–182,965 |
| Cqgypsy_15 | Within intron | dystrophin major muscle isoform | CPIJ013032 | 3.423: 50,593–185,416 |
| Cqgypsy_20 | 0–1 Kbp downstream | histone-lysine n-methyltransferase | CPIJ000732 | 3.6: 1,790,053–1,797,972 |
| Cqgypsy_21 | 0–1 Kbp upstream | flotillin-2 | CPIJ007626 | 3.148: 169,798–180,783 |
| Cqgypsy_25 | Exon-Intron junction | phd finger protein | CPIJ014131 | 3.545: 75,916–92,572 |
| Cqgypsy_29 | 3–4 Kbp downstream | protein phosphatase-1 | CPIJ008212 | 3.168: 687,712–708,602 |
| 0–1 Kbp downstream | helicase | CPIJ019431 | 3.1585: 41,788–51,610 | |
| Cqgypsy_37 | 1–2 Kbp downstream | sphingomyelin synthetase | CPIJ002233 | 3.30: 541,656–542,535 |
| 2–3 Kbp downstream | DEAD box ATP-dependent RNA helicase | CPIJ006204 | 3.118: 567,640–586,793 | |
| Cqgypsy_47 | 2–3 Kbp downstream | sodium/iodide cotransporter | CPIJ002364 | 3.33: 789,851–792,666 |
| 4–5 Kbp upstream | serine protease inhibitor, serpin | CPIJ012013 | 3.346: 385,437–397,533 | |
| 3–4 Kbp downstream | pre-mrna splicing factor prp17 | CPIJ011807 | 3.365: 424,340–426,137 | |
| 1–2 KbpUpstream | uridine cytidine kinase i | CPIJ016204 | 3.736: 44,070–45,560 | |
| 1–2 Kbp downstream | uridine cytidine kinase i | CPIJ016204 | 3.736: 44,070–45,560 | |
| 1–2 Kbp downstream | coatomer | CPIJ014834 | 3.606: 201,807–202,272 | |
| 1–2 Kbp downstream | poly a polymerase | CPIJ014835 | 3.606: 205,341–209,830 | |
| Cqgypsy_51 | 1–2 Kbp upstream | zinc finger protein | CPIJ009854 | 3.243: 281,133–285,737 |
| 2–3 Kbp upstream | DNA replication licensing factor MCM7 | CPIJ009855 | 3.243: 295,787–306,221 | |
| 2–3 Kbp downstrean | mitochondrial 39 S ribosomal protein L3 | CPIJ017407 | 3.941: 86,591–87,964 | |
| 1–2 Kbp downstream | 26 S protease regulatory subunit 6a | CPIJ017405 | 3.941: 78,697–79,175 | |
| Cqgypsy_53 | 3–4 Kbp downstream | esterase B1 precursor | CPIJ016336 | 3.777: 170,027–172,021 |
| 4–5 Kbp upstream | ATP synthase D chain, mitochondrial | CPIJ011691 | 3.328: 179,978–180,887 | |
| 2–3 Kbp downstream | Eftud2 protein, putative | CPIJ000064 | 3.1: 1,221,757–1,228,225 | |
| 1–2 Kbp upstream | cell division protein kinase 5 | CPIJ000065 | 3.1: 1,233,232–1,234,222 | |
| Exon-Intron junction | sarcolemmal associated protein-2, putative | CPIJ011313 | 3.310: 56,964–69,006 | |
| Cqgypsy_56 | Exon-Intron junction | semaphorin | CPIJ001593 | 3.17: 1,304,933–1,339,494 |
| Exon-Intron junction | microfibrillar-associated protein, putative | CPIJ020039 | 3.2342: 8,606–17,792 | |
| Exon-Intron junction | male-specific doublesex protein | CPIJ004057 | 3.59: 681,384–685,772 | |
| 1–2 Kbp downstream | polypeptide of 976aa, putative | CPIJ018525 | 3.1222: 14,705–19,317 | |
| Cqgypsy_59 | 1 Kbp upstream | negative elongation factor E | CPIJ000025 | 3.1: 727,264–728,238 |
| 4–5 Kbp downstream | semaphorin | CPIJ000027 | 3.1: 744,915–761,147 | |
| 4–5 Kbp downstream | superoxide dismutase, putative | CPIJ005173 | 3.91: 822,776–823,755 | |
| Within intron | enhancer of polycomb | CPIJ018246 | 3.1131: 70,175–80,884 | |
| Cqgypsy_60 | Overlaps last exon | serine protease inhibitors putative | CPIJ007021 | 3.133: 747,858–748,701 |
| 0–1 Kbp upstream | serine protease inhibitor | CPIJ007023 | 3.133: 758,924–759,336 | |
| 1 Kbp downstream | nucleoporin | CPIJ013031 | 3.426: 362,618–363,727 | |
| 0–1 Kbp upstream | 40 S ribosomal protein S14-A | CPIJ012110 | 3.400: 69,850–70,191 | |
| Cqgypsy_61 | Overlaps last exon | cytochrome c oxidase subunit I | CPIJ016836 | 3.816: 17,796–33,791 |
| Cqgypsy_63 | Within intron | Dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase | CPIJ004687 | 3.72: 556,787–583,090 |
| Exon-Intron junction | 5′-3′ exoribonuclease, putative | CPIJ016423 | 3.746: 154,787–166,602 | |
| 4–5 Kbp upstream | alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase | CPIJ006409 | 3.128: 202,128–218,875 | |
| Cqgypsy_64 | Exon-Intron junction | arsenite inducible RNA associated protein aip-1 | CPIJ005006 | 3.82: 520,914–524,059 |
| Exon-Intron junction | nk homeobox protein | CPIJ019260 | 3.1511: 40,639–44,852 | |
| 2–3 Kbp downstream | 60 S ribosomal protein L7 | CPIJ017548 | 3.961: 25,320–28,131 |
For each insertions detected in proximity (+/− 5 Kbp) or into genes are reported the kind of interaction (upstream, downstream, exon, intron), the Vectorbase identifier of the gene, its description and its position in the supercontig.
Table 4. Contribution of the non-autonomous elements identified in this paper to the formation of mature mRNAs of C. quinquefasciatus genes.
| Element | Description | gene ID | Supercontig:position |
| CqUNK_3 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DHX8 | CPIJ011263 | 3.322: 64334–68170 |
| cell cycle control protein cwf8 | CPIJ011261 | 3.322: 54937–56710 | |
| tRNA methyltransferase | CPIJ011262 | 3.322: 62963–64258 | |
| carboxylesterase-6 | CPIJ006908 | 3.137: 13520–18988 | |
| bombesin receptor subtype-3 | CPIJ017637 | 3.980: 85049–99690 | |
| N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 7 | CPIJ014647 | 3.660: 5557–7406 | |
| saposin | CPIJ014133 | 3.545: 130173–138797 | |
| CqUNK_5 | bombesin receptor subtype-3 | CPIJ017637 | 3.980: 85049–99690 |
| CqUNK_9 | dopamine beta hydroxylase | CPIJ019622 | 3.1797: 2222–17524 |
| CqUNK_11 | midasin | CPIJ010145 | 3.251: 518823–535901 |
| sterol desaturase, putative | CPIJ009637 | 3.227: 524825–527033 | |
| CqUNK_19 | malate dehydrogenase | CPIJ015299 | 3.611: 78722–91118 |
| igf2 mRNA binding protein, putative | CPIJ011349 | 3.312: 412154–436319 | |
| CqUNK_20 | regulator of chromosome condensation | CPIJ019976 | 3.2094: 4450–9107 |
| CqUNK_23 | midasin | CPIJ010145 | 3.251: 518823–535901 |
| centaurin-alpha 2 | CPIJ019112 | 3.1516: 3934–9235 | |
| sterol desaturase, putative | CPIJ009637 | 3.227: 524825–527033 | |
| CqUNK_28 | zinc finger protein 40 | CPIJ018875 | 3.1321: 31848–32423 |
| allatostatin receptor | CPIJ016163 | 3.734: 81478–87202 | |
| aldehyde oxidase 2 | CPIJ016888 | 3.821: 149733–154740 | |
| bombesin receptor subtype-3 | CPIJ017637 | 3.980: 85049–99690 | |
| defective proboscis extension response, putative | CPIJ017115 | 3.897: 12891–19932 | |
| 40 S ribosomal protein S14 | CPIJ010397 | 3.291: 138109–144395 | |
| CqUNK_32 | choline O-acetyltransferase | CPIJ001609 | 3.19: 128455–132041 |
| CqUNK_33 | phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type i | CPIJ006826 | 3.145: 280313–292406 |
| CqUNK_42 | Transcription factor Ken 2 | CPIJ012629 | 3.427: 256203–270029 |
| laminin gamma-3 chain | CPIJ005194 | 3.96: 903006–924273 | |
| trypsin | CPIJ004641 | 3.70: 338878–341919 | |
| f-actin capping protein alpha | CPIJ011271 | 3.322: 247301–257388 | |
| malate dehydrogenase | CPIJ008123 | 3.169: 118442–121449 | |
| CqUNK_43 | elongation factor tu | CPIJ002277 | 3.30: 1195429–1198055 |
| zinc finger protein | CPIJ002883 | 3.37: 1030192–1037437 | |
| kakapo | CPIJ003239 | 3.41: 533346–586465 | |
| CqUNK_45 | monocarboxylate transporter | CPIJ008119 | 3.184: 607328–610272 |
| pol-like protein | CPIJ018514 | 3.1248: 73743–87450 | |
| elongation factor 1 alpha | CPIJ009557 | 3.231: 370372–372795 | |
| olfactory receptor, putative | CPIJ013754 | 3.526: 317670–324857 |
The results summarized in table 3 have been obtained using the elements listed in table 1 as query for BLAST analyses; 84% (313 out of 371) of the insertions detected lay in intergenic regions (i.e. outside the 5 Kbp window upstream/downstream the genes). The remaining 16% (58 insertions) lay in genomic loci where also genes reside (i.e. within 5 Kb upstream/downstream of validated mosquito genes). It is possible that such insertions could contribute to define the spatial and temporal pattern of expression of strictly linked genes.
Among the insertions in proximity of annotated genes, nineteen insertions (5% of the insertions detected) hit genes, and, among them, six insertions (less than 2%) are localized in introns. Standing to the exon-intron organization reported in Vectorbase, the remaining insertions contribute to entire exons or part of them or are localized at exon-intron boundaries. These data suggest that at least a fraction of the LTR retrotransposon insertions that we have considered, could contribute to define the protein-coding regions of genes.
The results obtained using the elements listed in table 2 as query for BLAST analyses indicate that such non-autonomous elements can also be found in genes. Similarly they seem to contribute at the same strength in the building of protein-coding regions of genes in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus (table 4). However, after extensive searches against the ESTs databases, we have not been able to find evidences supporting that the retrotransposons analyzed are recruited as exons in the mature transcripts of the genes in which they are inserted. Furthermore, the comparison (not shown) of the genes reported in tables 3 and 4 with the respective orthologs in Aedes aegypti suggests that, such insertions are probably recent, and have occurred specifically in the evolutionary lineage of C. quinquefasciatus.
These results could be an underestimation, because we intentionally excluded from the BLAST output insertions into, or in proximity to hypothetical protein coding genes that, with the ongoing annotation of the genome could be classified as C. quinquefasciatus genes.
Discussion
In this paper we present data from the LTR_STRUC scan of the Culex quinquefasciatus genome. We have been able to identify, by the use of an alternative in silico approach, the presence of 67 novel LTR-retrotransposons in the Culex genome. These results contribute to increase the already large dataset of retrotransposons present in the TEfam database. The first consideration to be done is that, in order to identify the repeats complement of a eukaryotic genome the implementation of different methods is necessary. Until now several criteria for the identification of transposable elements have been successfully applied in sequenced genomes. As for the prediction of protein coding genes, two different approaches can be considered for predicting sequences related to transposable element: intrinsic and extrinsic methods. Intrinsic methods allow the identification of transposable elements through identification of genomic sequences having structural properties typical of mobile genetic elements. In contrast extrinsic methods are based on the identification of transposable elements by sequence similarity. It is evident that the latter methods rely on the use of a known transposable element's sequence as query sequence. This constitutes the main limitation of these methods, which makes difficult the identification of novel elements with low sequence similarity respect to the queries. This problem is overcome by the use of intrinsic methods, which look for structures rather than sequence similarity. LTR_STRUC is a program designed for the identification of LTR-retrotransposons [21]. It has been successfully used to identify LTR retrotransposons in mammalian [42] as well as in insect genomes [17] [43]. It is noteworthy that several LTR-retrotransposon finding tools have been recently developed. LTRharvest [22] is a recently described program with best performances respect to other de novo finders, including LTR_STRUC. In fact LTRharvest was able to find nearly all the Culex LTR retrotransposons annotated in TEfam, failing in the identification of a single Ty1/copia-like element and a single gypsy-like element. Furthermore LTRharvest has identified all the elements identified by LTR_STRUC. By contrast the LTR_STRUC program have identified 63/81 Bel/Pao-like elements, 16/32 Ty1/copia-like elements, 44/57 gypsy-like elements. The simplest explanation for the identification of the additional elements in this paper rely into possible differences in the algorithm of different programs or simply because these retrotransposons have been overlooked during former analyses. This underlines the importance of the use of multiple methods, if complex eukaryotic genomic sequences are to be analyzed.
The results obtained integrate the considerably large amount of data existing for mosquitoes' genomes. Indeed, our analyses have uncovered the existence of an additional fraction of the C. quinquefasciatus genome related to LTR retrotransposons. This fraction accounts for the 0,8% of the genome occupied by only 29 out of the 67 LTR retrotransposon families detected in this study. In fact, if the non-autonomous elements were also taken in account then this value would have been considerably greater (about 8%).
Our results suggest that a number of LTR retrotransposons insertions could contribute to the built the exon-intron structure of genes in Culex quinquefasciatus. Standing to the predicted exon-intron structures of genes in Culex some of the insertions detected could potentially give a contribution in term of exons or parts of them, to the mature form of mRNA expressed from endogenous genes, underlining the importance of retrotransposons and, in general, of mobile elements in shaping the eukaryotic genomes. This aspect could be particularly important for organisms of social relevance, like C. quinquefasciatus, because polymorphic TE insertion sites can be at the basis of the resistance emergence that characterize some populations [44]. However we were not able to find ESTs in support of this hypothesis, as well as no homologous genes in related species, such as Aedes aegypti, contain retrotransposon related sequences.
Among the novel element identified the vast majority can be classified using conventional criteria, such as combination of phylogenetic clustering and structural features. Unfortunately, these criteria are not sufficient to classify elements lacking coding sequences. This is the case for 38 LTR retrotransposon sequences identified in this study that contain tandemly repeated sequences between LTRs.
Non-autonomous elements lacking ORFs have been well documented especially in plant genomes [45]. Typically, these elements lack all coding sequences but have retained the LTRs, the primer-binding site and the polypurinic tract. These are the minimal features required for replication, because the LTRs contain the promoter needed to produce a template RNA, and the primer-binding site and the polypurine tract are needed to prime the reverse transcription steps. They are extremely heterogeneous in size varying from few hundreds base pairs (TRIM retrotransposons [46] to few Kilobase pairs (LARDS retrotransposons [47]. In mammalian genomes MaLRs retrotransposons (Mammalian Apparent LTR Retrotransposons) [48] have been also described with similar features.
Very interestingly, Arensburger et al. [13] have detected a single element resembling in structure a LARDS retrotransposon in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus.
At least two types of observations can be made, looking at the non-autonomous elements described in this paper. First, they apparently lack any functional master copy from which they could have originated. This can be due to the fact that the genome assembly is still in progress or there are genomic regions (such as heterochromatin) that suffer of local low coverage sequencing. The second observation concerns the nature of the repeated sequences, which are not family-specific (i.e. copies belonging to the same family do not share necessarily the same repeat and/or copies of different families could share the same repeat).
It has been suggested that a potential function for the tandem repeats embedded in the LTR retrotransposons could be to facilitate recombination and acquisition of new coding information through gene transduction [49]. A suggestive hypothesis that can be proposed, is that once a LTR retrotransposon acquire, in some way, a repeated sequence it tend to become transpositionally inactive by mean of internal deletions of its coding sequences in C. quinquefasciatus. Alternatively, it can be hypothesized that these elements are still capable of transposition if they could use the transpositional machinery of related retroelements in trans. In the latter case, the repeated sequences could be disseminated in the genome by passive retrotransposition.
In conclusion, we want to point out that other works have demonstrated the presence of potent regulatory sequences in the repeats carried by retrotransposons, simply by the analysis of their sequence complexity [38] [50]. Similarly, the presence of complex repeats into these non-autonomous elements could be used as starting point to identify similar regulatory elements in Culex quinquefasciatus.
In addition, our analysis demonstrates that the genome of C. quinquefasciatus contains LTR-retroelements with peculiar features. This was also evident from previous works, which have demonstrated the presence of the Twin elements in this genome [13] and have allowed the identification of Osvaldo-like elements with a non-canonical structure of the LTRs [17].
In this paper we have also reported the identification of cqgypsy_1, an Osvaldo-like element with an atypical PBS with a tRNA-dimer structure. The tRNA-dimer is somehow reminiscent of the structure of Twin elements described by Feschotte and co-authors. Twin has been described as a novel type of SINE element consisting of two tRNA related regions separated by a 39 bp spacer. Twin retroelements were found to be abundant in transposon rich genomic regions of C. quinquefasciatus [13].
The tandemly repeated tRNAs copies in cqgypsy_1 display a direct duplication of 26 nucleotides belonging to the 5′LTR.
Indeed, the 26 bp duplication is reminiscent of the target site duplication occurring upon integrase-mediated insertion, suggesting that the tRNA-dimer has been integrated by a transpositional mechanism.
As can be observed from figure 3A both tRNA like sequence halves have the terminal CCA sequences. This structural feature would suggest that the mature form of endogenous tRNA molecules have been incorporated into the retrotransposon backbone after a reverse transcription process. As far as we know, dimerization or aggregation of tRNAs in vitro is a known phenomenon, but it typically occurs under non-physiological conditions [51] [52]. On the other hand differences can be highlighted between Twin elements and the head to head tRNA repeat found in cqgypsy_1. The target site duplication, where it was found, of Twin is an AT rich sequence. A poly-A tract derived from the retroposition event is located downstream Twin elements. These features are absent in the Twin-like structure that we have detected, suggesting a different origin of the insertion detected in cqgypsy_1 element.
In conclusion, findings from this and previous reports make C. quinquefasciatus a potential niche-genome in which the evolution of transposable elements occurs and generates strong genomic diversity.
The importance of studying the mosquito's mobilome also resides in the possibility to use such DNA sequences as molecular biomarkers [53], or for the control of insecticide resistance populations in order to contrast the spread of virus borne diseases [54]. In this view our results could be helpful for future studies concerning such topics.
Supporting Information
DNA sequences of the 67 LTR-retrotransposons identified in this paper. Each sequence contains 50 bases upstream and downstream allowing unique identification of a reference copy in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus.
(TXT)
Acknowledgments
We thank anonymous Reviewers and the Editor for their comments, which significantly contributed to improving the quality of the manuscript.
The Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Puglia, which granted the project “Genomica degli elementi trasponibili applicata all'identificazione e caratterizzazione molecolare di specie di Culex presenti sul territorio Barese” is gratefully acknowledged.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: This work was funded by the Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Puglia (granted to RMM). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Kidwell MG, Lisch DR. Transposable elements as source of genomic variation. In: Craig N, Craigie R, Gellert M, Lambowitz A, editors. Mobile DNA II. American Society for Microbiology Press; 2002. pp. 59–90. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, et al. A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:973–982. doi: 10.1038/nrg2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kapitonov VV, Jurka J. A universal classification of eukaryotic transposable elements implemented in Repbase. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:411–412; author reply 414. doi: 10.1038/nrg2165-c1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Finnegan DJ. Transposable elements. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992;2:861–867. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Deragon JM, Casacuberta JM, Panaud O. Plant transposable elements. Genome Dyn. 2008;4:69–82. doi: 10.1159/000126007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jordan IK, Rogozin IB, Glazko GV, Koonin EV. Origin of a substantial fraction of human regulatory sequences from transposable elements. Trends in Genetics: TIG. 2003;19:68–72. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(02)00006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Medstrand P, van de Lagemaat LN, Dunn CA, Landry JR, Svenback D, et al. Impact of transposable elements on the evolution of mammalian gene regulation. Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 2005;110:342–352. doi: 10.1159/000084966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kumar A, Bennetzen JL. Plant retrotransposons. Annual Review of Genetics. 1999;33:479–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.33.1.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kalendar R, Flavell AJ, Ellis TH, Sjakste T, Moisy C, et al. Analysis of plant diversity with retrotransposon-based molecular markers. Heredity. 2011;106:520–530. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2010.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Holt RA, Subramanian GM, Halpern A, Sutton GG, Charlab R, et al. The genome sequence of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Science. 2002;298:129–149. doi: 10.1126/science.1076181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nene V, Wortman JR, Lawson D, Haas B, Kodira C, et al. Genome sequence of Aedes aegypti, a major arbovirus vector. Science. 2007;316:1718–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.1138878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rao PN, Rai KS. Genome evolution in the mosquitoes and other closely related members of superfamily Culicoidea. Hereditas. 1990;113:139–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1990.tb00077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Arensburger P, Megy K, Waterhouse RM, Abrudan J, Amedeo P, et al. Sequencing of Culex quinquefasciatus establishes a platform for mosquito comparative genomics. Science. 2010;330:86–88. doi: 10.1126/science.1191864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Feschotte C, Zhang X, Wessler SR. Miniature inverted repeat transposable elements and their relationship to established DNA transposons. In: Craig N, Craigie R, Gellert M, Lambowitz A, editors. Mobile DNA II. American Society for Microbiology Press; 2002. pp. 1147–1158. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Coy MR, Tu Z. Genomic and evolutionary analyses of Tango transposons in Aedes aegypti, Anopheles gambiae and other mosquito species. Insect Mol Biol. 2007;16:411–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2007.00735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Biedler JK, Tu Z. The Juan non-LTR retrotransposon in mosquitoes: genomic impact, vertical transmission and indications of recent and widespread activity. BMC Evol Biol. 2007;7:112. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Minervini CF, Viggiano L, Caizzi R, Marsano RM. Identification of novel LTR retrotransposons in the genome of Aedes aegypti. Gene. 2009;440:42–49. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.03.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bensaadi-Merchermek N, Cagnon C, Desmons I, Salvado JC, Karama S, et al. CM-gag, a transposable-like element reiterated in the genome of Culex pipiens mosquitoes, contains only a gag gene. Genetica. 1997;100:141–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.TEfam database. Available: http://tefam.biochem.vt.edu/tefam/ Accessed 2011 Dec 04.
- 20.Feschotte C, Fourrier N, Desmons I, Mouches C. Birth of a retroposon: the Twin SINE family from the vector mosquito Culex pipiens may have originated from a dimeric tRNA precursor. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2001;18:74–84. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.McCarthy EM, McDonald JF. LTR_STRUC: a novel search and identification program for LTR retrotransposons. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:362–367. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btf878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ellinghaus D, Kurtz S, Willhoeft U. LTRharvest, an efficient and flexible software for de novo detection of LTR retrotransposons. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jurka J, Kapitonov VV, Pavlicek A, Klonowski P, Kohany O, et al. Repbase Update, a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 2005;110:462–467. doi: 10.1159/000084979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Benson G. Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27:573–580. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.2.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Smit AFA, Hubley R, Green P. RepeatMasker Open-3.0. 1996. Available: http://www.repeatmasker.org.
- 26.Malik HS, Eickbush TH. Modular evolution of the integrase domain in the Ty3/Gypsy class of LTR retrotransposons. Journal of Virology. 1999;73:5186–5190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.6.5186-5190.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research. 2004;32:1792–1797. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research. 1997;25:4876–4882. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.24.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, et al. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2011 doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Inouye S, Saigo K, Yamada K, Kuchino Y. Identification and nucleotide sequence determination of a potential primer tRNA for reverse transcription of a Drosophila retrotransposon, 297. Nucleic Acids Research. 1986;14:3031–3043. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.3031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Syomin BV, Leonova TY, Ilyin YV. Evidence for horizontal transfer of the LTR retrotransposon mdg3, which lacks an env gene. Molecular Genetics and Genomics. 2002;267:418–423. doi: 10.1007/s00438-002-0678-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Michaille JJ, Mathavan S, Gaillard J, Garel A. The complete sequence of mag, a new retrotransposon in Bombyx mori. Nucleic Acids Research. 1990;18:674. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tubio JM, Naveira H, Costas J. Structural and evolutionary analyses of the Ty3/gypsy group of LTR retrotransposons in the genome of Anopheles gambiae. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2005;22:29–39. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Malik HS, Henikoff S, Eickbush TH. Poised for contagion: evolutionary origins of the infectious abilities of invertebrate retroviruses. Genome Research. 2000;10:1307–1318. doi: 10.1101/gr.145000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ganko EW, Fielman KT, McDonald JF. Evolutionary history of Cer elements and their impact on the C. elegans genome. Genome Research. 2001;11:2066–2074. doi: 10.1101/gr.196201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pantazidis A, Labrador M, Fontdevila A. The retrotransposon Osvaldo from Drosophila buzzatii displays all structural features of a functional retrovirus. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 1999;16:909–921. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kazazian HH., Jr Mobile elements: drivers of genome evolution. Science. 2004;303:1626–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.1089670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Minervini CF, Marsano RM, Casieri P, Fanti L, Caizzi R, et al. Heterochromatin protein 1 interacts with 5′UTR of transposable element ZAM in a sequence-specific fashion. Gene. 2007;393:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.12.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Spana C, Harrison DA, Corces VG. The Drosophila melanogaster suppressor of Hairy-wing protein binds to specific sequences of the gypsy retrotransposon. Genes & Development. 1988;2:1414–1423. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Conte C, Dastugue B, Vaury C. Coupling of enhancer and insulator properties identified in two retrotransposons modulates their mutagenic impact on nearby genes. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2002;22:1767–1777. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.6.1767-1777.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gdula DA, Gerasimova TI, Corces VG. Genetic and molecular analysis of the gypsy chromatin insulator of Drosophila. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1996;93:9378–9383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.18.9378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.McCarthy EM, McDonald JF. Long terminal repeat retrotransposons of Mus musculus. Genome Biology. 2004;5:R14. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-3-r14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Marsano RM, Caizzi R. A genome-wide screening of BEL-Pao like retrotransposons in Anopheles gambiae by the LTR_STRUC program. Gene. 2005;357:115–121. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Darboux I, Charles JF, Pauchet Y, Warot S, Pauron D. Transposon-mediated resistance to Bacillus sphaericus in a field-evolved population of Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). Cellular Microbiology. 2007;9:2022–2029. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sabot F, Schulman AH. Parasitism and the retrotransposon life cycle in plants: a hitchhiker's guide to the genome. Heredity. 2006;97:381–388. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Witte CP, Le QH, Bureau T, Kumar A. Terminal-repeat retrotransposons in miniature (TRIM) are involved in restructuring plant genomes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001;98:13778–13783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.241341898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kalendar R, Vicient CM, Peleg O, Anamthawat-Jonsson K, Bolshoy A, et al. Large retrotransposon derivatives: abundant, conserved but nonautonomous retroelements of barley and related genomes. Genetics. 2004;166:1437–1450. doi: 10.1534/genetics.166.3.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Smit AF. Identification of a new, abundant superfamily of mammalian LTR-transposons. Nucleic Acids Research. 1993;21:1863–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sanz-Alferez S, SanMiguel P, Jin YK, Springer PS, Bennetzen JL. Structure and evolution of the Cinful retrotransposon family of maize. Genome. 2003;46:745–752. doi: 10.1139/g03-061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Minervini CF, Ruggieri S, Traversa M, D'Aiuto L, Marsano RM, et al. Evidences for insulator activity of the 5′UTR of the Drosophila melanogaster LTR-retrotransposon ZAM. Molecular Genetics and Genomics. 2010;283(5):503–509. doi: 10.1007/s00438-010-0529-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Loehr JS, Keller EB. Dimers of alanine transfer RNA with acceptor activity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1968;61:1115–1122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kholod NS. Dimer formation by tRNAs. Biochemistry (Mosc) 1999;64:298–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Byarugaba W, Kajumbula H, Wayengera M. In silico evidence for the species-specific conservation of mosquito retroposons: implications as a molecular biomarker. Theoretical Biology & Medical Modelling. 2009;6:14. doi: 10.1186/1742-4682-6-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Diao Y, Qi Y, Ma Y, Xia A, Sharakhov I, et al. Next-generation sequencing reveals recent horizontal transfer of a DNA transposon between divergent mosquitoes. PLoS One. 2011;6:e16743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
DNA sequences of the 67 LTR-retrotransposons identified in this paper. Each sequence contains 50 bases upstream and downstream allowing unique identification of a reference copy in the genome of C. quinquefasciatus.
(TXT)