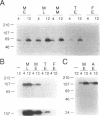
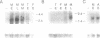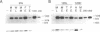Abstract
We have directly compared the ability of four promoters and three polyadenylation (poly(A)) signals to direct heterologous gene expression in stably transfected Drosophila melanogaster S2 cells. We compared two constitutive Drosophila promoters, the actin 5C distal promoter and the alpha 1-tubulin promoter, with the tightly regulated Drosophila metallothionein (Mtn) promoter and the Bombyx mori fibroin promoter. We find that the actin 5C and induced Mtn promoters generate comparable high levels of RNA and protein in this system. The alpha 1-tubulin promoter generates about four-fold lower levels, and the fibroin promoter shows no detectable activity in S2 cells. Interestingly, genes expressed from the constitutive actin 5C and alpha 1-tubulin promoters are consistently present at three- to four-fold lower copy numbers than genes expressed from the inducible Mtn promoter or the inactive fibroin promoter. Poly(A) signals of both mammalian (SV40) and Drosophila (Mtn) origin efficiently directed stable RNA synthesis in S2 cells, and, as in mammalian cells, the SV40 late poly(A) signal was more efficient than the SV40 early poly(A) signal. Thus the process of polyadenylation appears to be conserved between mammalian and Drosophila cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bond-Matthews B., Davidson N. Transcription from each of the Drosophila act5C leader exons is driven by a separate functional promoter. Gene. 1988;62(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell S., Alwine J. C. Efficiency of utilization of the simian virus 40 late polyadenylation site: effects of upstream sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4248–4258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung Y. T., Keller E. B. Positive and negative regulatory elements mediating transcription from the Drosophila melanogaster actin 5C distal promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6172–6180. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culp J. S., Johansen H., Hellmig B., Beck J., Matthews T. J., Delers A., Rosenberg M. Regulated expression allows high level production and secretion of HIV-1 gp120 envelope glycoprotein in Drosophila Schneider cells. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Feb;9(2):173–177. doi: 10.1038/nbt0291-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Dawid I. B. Transient expression of genes introduced into cultured cells of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7095–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Bond B. J., Hershey N. D., Mixter K. S., Davidson N. The actin genes of Drosophila: protein coding regions are highly conserved but intron positions are not. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimmi E. R., Soprano K. J., Rosenberg M., Reff M. E. Deletions in the SV40 late polyadenylation region downstream of the AATAAA mediate similar effects on expression in various mammalian cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8977–8997. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Sweet R. W., Sathe G., Yokoyama S., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Wigler M., Rosenberg M. Purification and characterization of human H-ras proteins expressed in Escherichia coli. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1015–1024. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Levine M. S., Manley J. L. Synergistic activation and repression of transcription by Drosophila homeobox proteins. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Scott M. P. What determines the specificity of action of Drosophila homeodomain proteins? Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90492-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. C., Matsuno K., Suzuki Y. Fibroin gene promoter contains a cluster of homeodomain binding sites that interact with three silk gland factors. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):651–670. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80253-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey-Hoyle M., Culp J. S., Chaikin M. A., Hellmig B. D., Matthews T. J., Sweet R. W., Rosenberg M. Envelope glycoproteins from biologically diverse isolates of immunodeficiency viruses have widely different affinities for CD4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):512–516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey-Hoyle M., Rosenberg M. Rev-dependent expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp160 in Drosophila melanogaster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6152–6159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen H., van der Straten A., Sweet R., Otto E., Maroni G., Rosenberg M. Regulated expression at high copy number allows production of a growth-inhibitory oncogene product in Drosophila Schneider cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):882–889. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalfayan L., Wensink P. C. alpha-Tubulin genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt N., Briggs D., Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. Definition of an efficient synthetic poly(A) site. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1019–1025. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroni G., Otto E., Lastowski-Perry D. Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a metallothionein gene of Drosophila. Genetics. 1986 Mar;112(3):493–504. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto E., Allen J. M., Young J. E., Palmiter R. D., Maroni G. A DNA segment controlling metal-regulated expression of the Drosophila melanogaster metallothionein gene Mtn. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1710–1715. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfarr D. S., Sathe G., Reff M. E. A highly modular cloning vector for the analysis of eukaryotic genes and gene regulatory elements. DNA. 1985 Dec;4(6):461–467. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore E. M., Guild G. M. Larval salivary gland secretion proteins in Drosophila structural analysis of the Sgs-5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Tsuda M., Takiya S., Hirose S., Suzuki E., Kameda M., Ninaki O. Tissue-specific transcription enhancement of the fibroin gene characterized by cell-free systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9522–9526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theurkauf W. E., Baum H., Bo J., Wensink P. C. Tissue-specific and constitutive alpha-tubulin genes of Drosophila melanogaster code for structurally distinct proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8477–8481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Suzuki Y. Transcription modulation in vitro of the fibroin gene exerted by a 200-base-pair region upstream from the "TATA" box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7442–7446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]