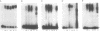Abstract
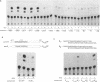
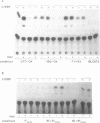
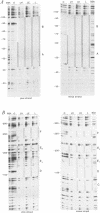
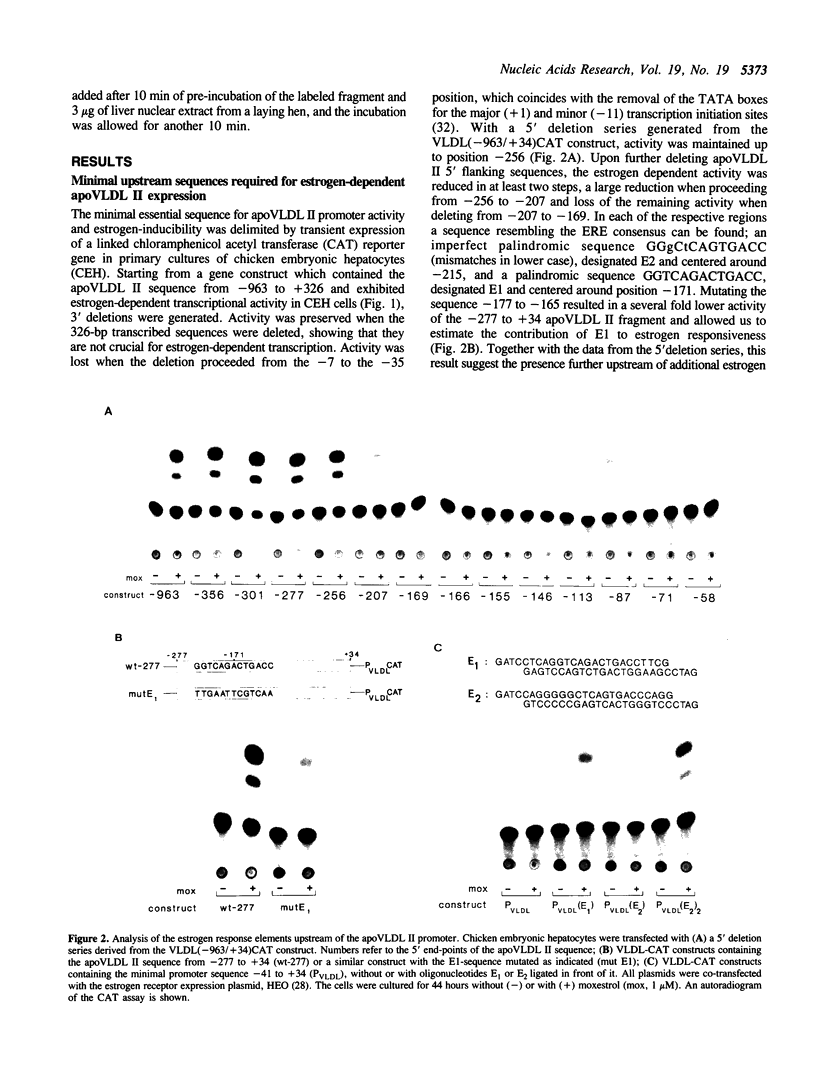
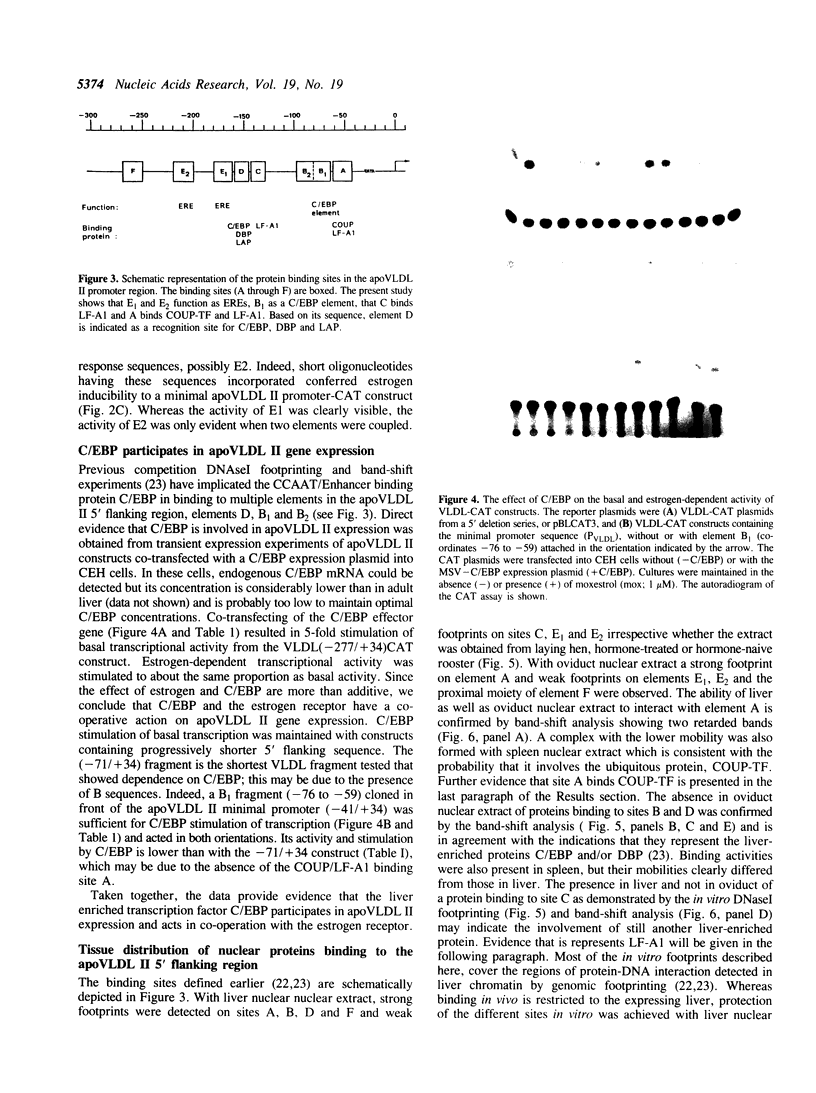
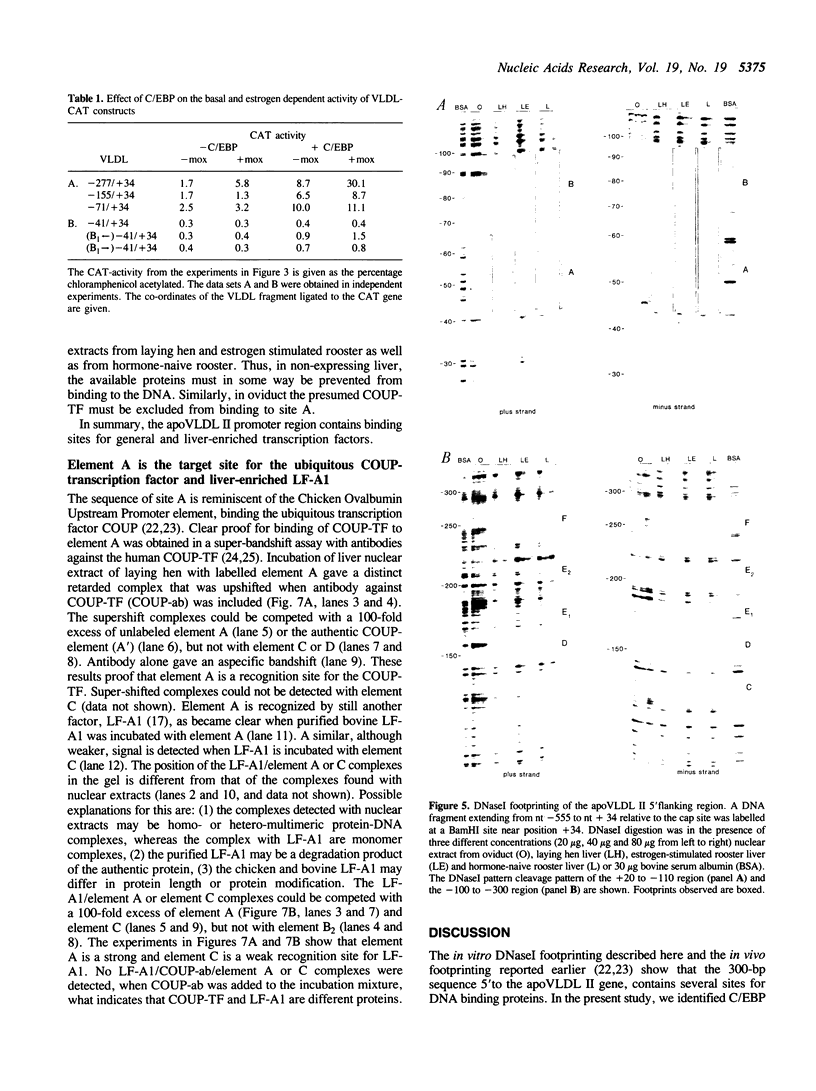
The chicken Very-Low-Density Apolipoprotein II (apoVLDL II) gene is specifically expressed in liver in response to estrogen. In this study, we performed a functional analysis of the 300-base pair region immediately 5' to the gene by gene transfer of chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) constructs into chicken embryonic hepatocytes (CEH). Two estrogen response elements (EREs) could be distinguished which together form a potent estrogen response unit. Stimulation of transient expression by co-transfection with a plasmid expressing rat C/EBP confirmed that a similar protein in chicken liver may be involved in apoVLDL II transcription. In vitro DNaseI footprinting and band-shift analysis with liver, oviduct and spleen nuclear extract revealed the tissue distribution of the proteins binding to the promoter region. A liver-specific protein bound to multiple sites of which some resembled the recognition sequence of the CCAAT/Enhancer binding protein, C/EBP. Of the other proteins binding to the apoVLDL II promoter, one was identified as the liver-specific LF-A1 by mobility shift analysis, using purified bovine LF-A1, and another as the general COUP-transcription factor, using an antiserum against the human COUP-TF.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corthésy B., Corthésy-Theulaz I., Cardinaux J. R., Wahli W. A liver protein fraction regulating hormone-dependent in vitro transcription from the vitellogenin genes induces their expression in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):159–169. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corthésy B., Hipskind R., Theulaz I., Wahli W. Estrogen-dependent in vitro transcription from the vitellogenin promoter in liver nuclear extracts. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1137–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2830672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Baumhueter S., Crabtree G. R. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7937–7941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Oestradiol induction of a glucocorticoid-responsive gene by a chimaeric receptor. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):75–78. doi: 10.1038/325075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardon E. M., Frain M., Paonessa G., Cortese R. Two distinct factors interact with the promoter regions of several liver-specific genes. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1711–1719. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Kaling M., Ryffel G. U. Synergism of closely adjacent estrogen-responsive elements increases their regulatory potential. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90635-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok K., Snippe L., Ab G., Gruber M. Nuclease-hypersensitive sites in chromatin of the estrogen-inducible apoVLDL II gene of chicken. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5189–5202. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugler W., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. Tissue-specificity of liver gene expression: a common liver-specific promoter element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3165–3174. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The role of cis-acting promoter elements in tissue-specific albumin gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2711183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Givel F., Wahli W. The estrogen-responsive element as an inducible enhancer: DNA sequence requirements and conversion to a glucocorticoid-responsive element. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3719–3727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A., Notides A. C. Identification of an estrogen-responsive element from the 5'-flanking region of the rat prolactin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4247–4254. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Heber A., Schmid W., Danesch U., Posseckert G., Beato M., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R., Maire P., Schibler U. DBP, a liver-enriched transcriptional activator, is expressed late in ontogeny and its tissue specificity is determined posttranscriptionally. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90808-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Brüggemeier U., Beato M. Nucleosome positioning modulates accessibility of regulatory proteins to the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90087-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Schütz G., von der Ahe D., Beato M. Sequences in the promoter region of the chicken lysozyme gene required for steroid regulation and receptor binding. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Kugler W., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. Hepatocyte-specific promoter element HP1 of the Xenopus albumin gene interacts with transcriptional factors of mammalian hepatocytes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütz G. Tenth Adolf Butenandt lecture. Control of gene expression by steroid hormones. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 Feb;369(2):77–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Sagami I., Wang H., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Interactions between a DNA-binding transcription factor (COUP) and a non-DNA binding factor (S300-II). Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Cook R. G., Beattie W. G., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. COUP transcription factor is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):163–166. doi: 10.1038/340163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnholds J., Muller E., Ab G. Oestrogen facilitates the binding of ubiquitous and liver-enriched nuclear proteins to the apoVLDL II promoter in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):33–41. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnholds J., Philipsen J. N., Ab G. Tissue-specific and steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the oestrogen-inducible apoVLDL II promoter in vivo. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Bensky P., Dower W., Goldberger R. F., Gordon J. I., Deeley R. G. Coordinate regulation of two estrogen-dependent genes in avian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Ruben G., Siegel B., Jay E., Spielman P., Tu C. P. Synchronous digestion of SV40 DNA by exonuclease III. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):734–740. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van het Schip A. D., Meijlink F. C., Strijker R., Gruber M., van Vliet A. J., van de Klundert J. A., Ab G. The nucleotide sequence of the chicken apo very low density lipoprotein II gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2529–2540. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]