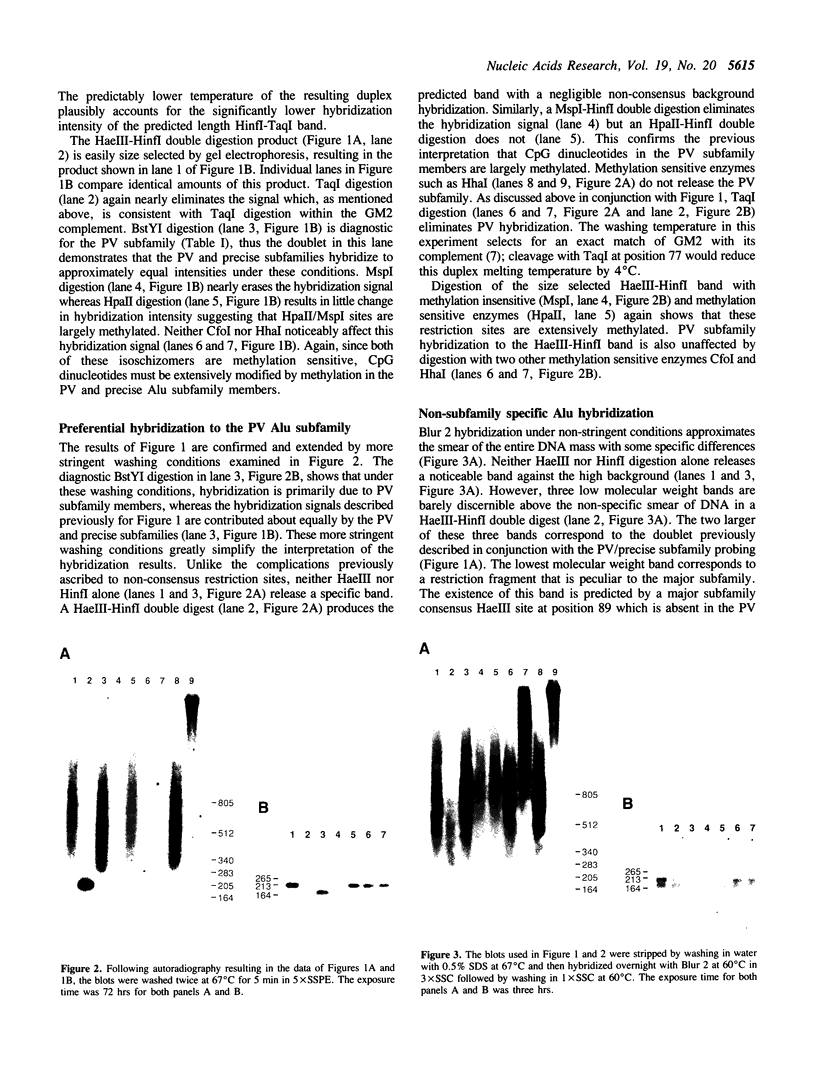
Abstract
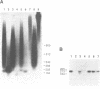
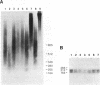
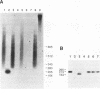
By a simple direct blot hybridization strategy, the existence of human Alu family subfamilies is confirmed. Using consensus restriction cleavage sites, individual bands can be resolved from genomic human DNA digests corresponding to three distinct Alu subfamilies. Digestion with methylation sensitive and insensitive restriction enzymes shows that the numerous CpG residues in the youngest Alu subfamilies are largely methylated in vivo, suggesting a model for the transcriptional regulation of Alu repeats.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batzer M. A., Deininger P. L. A human-specific subfamily of Alu sequences. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):481–487. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90414-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzer M. A., Kilroy G. E., Richard P. E., Shaikh T. H., Desselle T. D., Hoppens C. L., Deininger P. L. Structure and variability of recently inserted Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6793–6798. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besser D., Götz F., Schulze-Forster K., Wagner H., Kröger H., Simon D. DNA methylation inhibits transcription by RNA polymerase III of a tRNA gene, but not of a 5S rRNA gene. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81193-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1499–1504. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Baron W. F., Stout D. B., Davidson E. H. Sources and evolution of human Alu repeated sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4770–4774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohjoh H., Minakami R., Sakaki Y. Selective cloning and sequence analysis of the human L1 (LINE-1) sequences which transposed in the relatively recent past. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4099–4104. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurka J., Smith T. A fundamental division in the Alu family of repeated sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4775–4778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labuda D., Striker G. Sequence conservation in Alu evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2477–2491. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Hellmann U., Hintz M. F., Schmid C. W. Recently transposed Alu repeats result from multiple source genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6019–6023. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Hellmann U., Schmid C. W. A transpositionally and transcriptionally competent Alu subfamily. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5424–5432. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quentin Y. The Alu family developed through successive waves of fixation closely connected with primate lineage history. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(3):194–202. doi: 10.1007/BF02100074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWARTZ M. N., TRAUTNER T. A., KORNBERG A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XI. Further studies on nearest neighbor base sequences in deoxyribonucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1961–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slagel V., Flemington E., Traina-Dorge V., Bradshaw H., Deininger P. Clustering and subfamily relationships of the Alu family in the human genome. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jan;4(1):19–29. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard C., Nguyen H. T., Schmid C. W. Existence of at least three distinct Alu subfamilies. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(3):180–186. doi: 10.1007/BF02099850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Loflin P. T., Gehrke C. W., Andrews P. A., Ehrlich M. Hypermethylation of human DNA sequences in embryonal carcinoma cells and somatic tissues but not in sperm. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9429–9449. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]