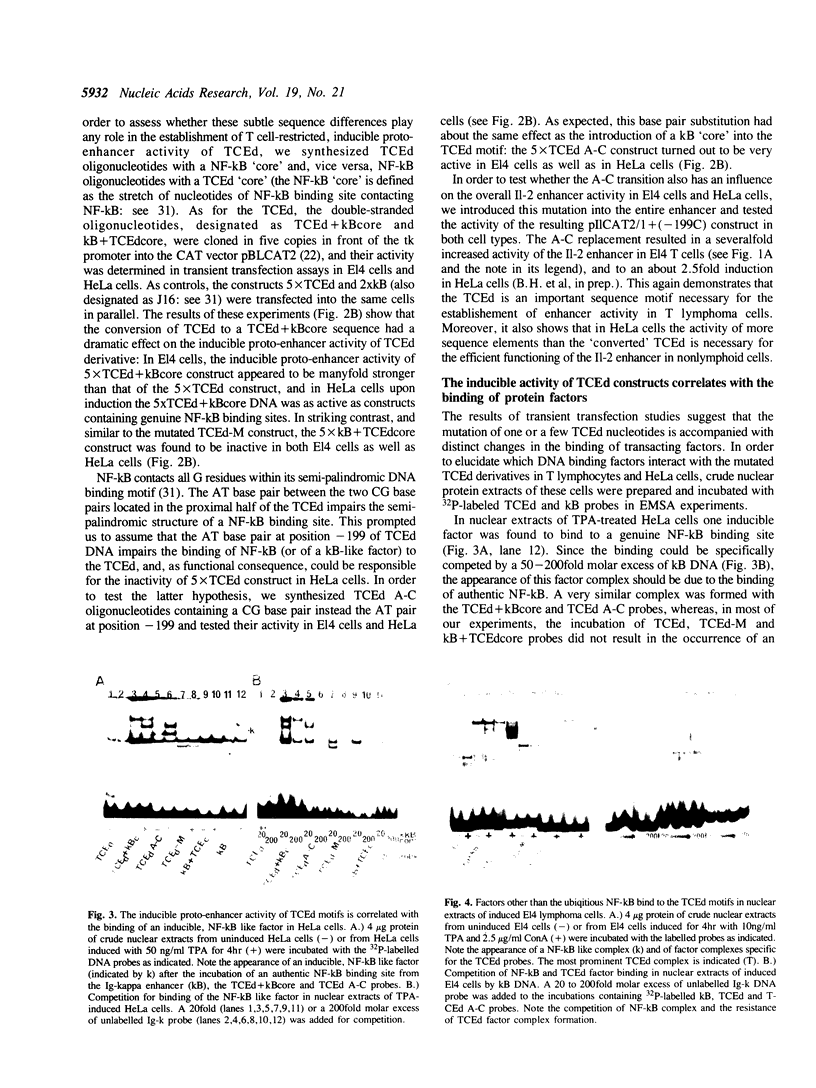
Abstract
The inducible, T cell-specific enhancers of murine and human Interleukin 2 (Il-2) genes contain the kB-like sequence GGGATTTCACC as an essential cis-acting enhancer motif. When cloned in multiple copies this so-called TCEd (distal T cell element) acts as an inducible proto-enhancer element in E14 T lymphoma cells, but not in HeLa cells. In extracts of induced, Il-2 secreting El4 cells three individual protein factors bind to TCEd DNA. The binding of the most prominent factor, named TCF-1 (T cell factor 1), is correlated with the proto-enhancer activity of TCEd. TCF-1 consists of two polypeptides of about 50 kD and 105 kD; the former seems to be related to the 50 kD polypeptide of NF-kB. Purified NF-kB is also able to bind to the TCEd, but TCF-1 binds stronger than NF-kB to TCEd DNA. The conversion of the TCEd to a 'perfect' NF-kB binding site leads to a tighter binding of NF-kB to TCEd DNA and, as a functional consequence, to the activity of the 'converted' TCEd motifs in HeLa cells. Thus, the substitution of the underlined A residue to a C within the GGGATTTCACC motif abolishes its T cell-restricted activity and leads to its functioning in both El4 cells and HeLa cells. These results indicate that lymphocyte-specific factors binding to the TCEd are involved in the control of T cell specific-transcription of the Il-2 gene.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. A 65-kappaD subunit of active NF-kappaB is required for inhibition of NF-kappaB by I kappaB. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1689–1698. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, LeClair K. P., Singh H., Sharp P. A. A large protein containing zinc finger domains binds to related sequence elements in the enhancers of the class I major histocompatibility complex and kappa immunoglobulin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1406–1414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabletz T., Pietrowski I., Serfling E. The immunosuppressives FK 506 and cyclosporin A inhibit the generation of protein factors binding to the two purine boxes of the interleukin 2 enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):61–67. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Siekevitz M., Ballard D. W., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. The same inducible nuclear proteins regulates mitogen activation of both the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and type 1 HIV. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Baeuerle P., Vassalli P. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha transcription in macrophages: involvement of four kappa B-like motifs and of constitutive and inducible forms of NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. B., Bush M. R., Morgan J. G., Weiss A., Crabtree G. R. A 275 basepair fragment at the 5' end of the interleukin 2 gene enhances expression from a heterologous promoter in response to signals from the T cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):395–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. B., Shaw J. P., Bush M. R., Replogle R. E., Belagaje R., Crabtree G. R. Characterization of antigen receptor response elements within the interleukin-2 enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1715–1724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. A DNA-binding protein containing two widely separated zinc finger motifs that recognize the same DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–42. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Ohashi T., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Regulation of human interleukin-2 gene: functional DNA sequences in the 5' flanking region for the gene expression in activated T lymphocytes. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90660-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Böhnlein E., Ballard D. W. HIV-1, HTLV-1 and normal T-cell growth: transcriptional strategies and surprises. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos B., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Siekevitz M., Greene W. C. Kappa B-specific DNA binding proteins: role in the regulation of human interleukin-2 gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):457–460. doi: 10.1126/science.2497518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Kuang A., Gifford A., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B protein purification from bovine spleen: nucleotide stimulation and binding site specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8825–8829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Sudo T., Ishii S. Putative metal finger structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer binding protein HIV-EP1. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14591–14593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio F., Karin M. Transcription factors AP-3 and AP-2 interact with the SV40 enhancer in a mutually exclusive manner. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1455–1460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Otsuka T., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor: comparison of the mouse and human genes. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2561–2568. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03971.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B: a family of inducible and differentially expressed enhancer-binding proteins in human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10028–10032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Donovan D. M., Hamada K., Sax C. M., Norman B., Flanagan J. R., Ozato K., Westphal H., Piatigorsky J. Regulation of the mouse alpha A-crystallin gene: isolation of a cDNA encoding a protein that binds to a cis sequence motif shared with the major histocompatibility complex class I gene and other genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3700–3708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Oligonucleotide that binds nuclear factor NF-kappa B acts as a lymphoid-specific and inducible enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1482–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radler-Pohl A., Pfeuffer I., Karin M., Serfling E. A novel T-cell trans-activator that recognizes a phorbol ester-inducible element of the interleukin-2 promoter. New Biol. 1990 Jun;2(6):566–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randak C., Brabletz T., Hergenröther M., Sobotta I., Serfling E. Cyclosporin A suppresses the expression of the interleukin 2 gene by inhibiting the binding of lymphocyte-specific factors to the IL-2 enhancer. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2529–2536. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07433.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA). EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4221–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serfling E., Barthelmäs R., Pfeuffer I., Schenk B., Zarius S., Swoboda R., Mercurio F., Karin M. Ubiquitous and lymphocyte-specific factors are involved in the induction of the mouse interleukin 2 gene in T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):465–473. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03399.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakhov A. N., Collart M. A., Vassalli P., Nedospasov S. A., Jongeneel C. V. Kappa B-type enhancers are involved in lipopolysaccharide-mediated transcriptional activation of the tumor necrosis factor alpha gene in primary macrophages. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):35–47. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon M. F., Pell L. M., Lenardo M. J., Kuczek E. S., Occhiodoro F. S., Dunn S. M., Vadas M. A. A novel tumor necrosis factor-responsive transcription factor which recognizes a regulatory element in hemopoietic growth factor genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2950–2959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya H., Yoneyama M., Taniguchi T. Involvement of a common transcription factor in the regulated expression of IL-2 and IL-2 receptor genes. Int Immunol. 1989;1(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E., Metcalf D., Sobieszczuk P., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R. The structure and expression of the murine gene encoding granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor: evidence for utilisation of alternative promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2569–2573. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03972.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. DNA binding of purified transcription factor NF-kappa B. Affinity, specificity, Zn2+ dependence, and differential half-site recognition. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):252–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]