Abstract
A soluble protein EF-P (elongation factor P) from Escherichia coli has been purified and shown to stimulate efficient translation and peptide-bond synthesis on native or reconstituted 70S ribosomes in vitro. Based on the partial amino acid sequence of EF-P, 18- and 24-nucleotide DNA probes were synthesized and used to screen lambda phage clones from the Kohara Gene Bank. The entire EF-P gene was detected on lambda clone #650 which contains sequences from the 94 minute region of the E.coli genome. Two DNA fragments, 3.0 and 0.78 kilobases in length encompassing the gene, were isolated and cloned into pUC18 and pUC19. Partially purified extracts from cells transformed with these plasmids overrepresented a protein which co-migrates with EF-P upon SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and also exhibited increased EF-P mediated peptide-bond synthetic activity. Based on DNA sequence analysis of this gene, the EF-P protein consists of 187 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 20,447. The sequence and chromosomal location of EF-P establishes it as a unique gene product.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G., Glick B. R., Friesen J. D., Ganoza M. C. Identification and quantitation of elongation factor EF-P in Escherichia coli cell-free extracts. Can J Biochem. 1980 Nov;58(11):1312–1314. doi: 10.1139/o80-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. M., Zahid N. L16, a bifunctional ribosomal protein and the enhancing effect of L6 and L11. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Mar 3;155(2):273–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauclerk A. A., Cundliffe E. The binding site for ribosomal protein L2 within 23S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3589–3594. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C., Nakayama N., Goebl M., Tanaka K., Toh-e A., Matsumoto K. CDC33 encodes mRNA cap-binding protein eIF-4E of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3556–3559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt H., Lührmann R. Recognition by initiator transfer ribonucleic acid of a uridine 5' adjacent to the AUG codon: different conformational states of formylatable methionine-accepting transfer ribonucleic acid at the ribosomal peptidyl site. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2075–2080. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Sullivan P., Cunningham C., Hader P., Kofoid E. C., Neilson T. Effect of bases contiguous to AUG on translation initiation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8228–8232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Zahid N., Baxter R. M. Stimulation of peptidyltransferase reactions by a soluble protein. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):287–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. R. A molecular model of peptide chain propagation. J Theor Biol. 1980 Jan 7;82(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(80)90094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. R., Chládek S., Ganoza M. C. Peptide bond formation stimulated by protein synthesis factor EF-P depends on the aminoacyl moiety of the acceptor. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):23–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. R., Ganoza M. C. Characterization and site of action of a soluble protein that stimulates peptide-bond synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):483–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. R., Ganoza M. C. Identification of a soluble protein that stimulates peptide bond synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4257–4260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. R., Green R. M., Ganoza M. C. Purification and Best Department of Medical Research, University of Toronto, Ont., Canada. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):749–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. R. The role of Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins L7 and L12 in peptide chain propagation. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Jacobzone M., Mercier R. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r43–r74. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. H., Glick B. R., Ganoza M. C. Requirements for in vitro reconstruction of protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 31;126(2):792–798. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUCAN Z., LIPMANN F. DIFFERENCES IN CHLORAMPHENICOL SENSITIVITY OF CELL-FREE AMINO ACID POLYMERIZATION SYSTEMS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:516–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
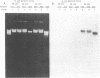
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin S. L., Xie A. G., Bonato M. C., McLaughlin C. S. Sequence analysis of the translational elongation factor 3 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1903–1912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlík I., Cerná J., Chládek S., Pulkrábek P., Zemlicka J. Substrate specificity of ribosomal peptidyl transferase. The effect of the nature of the amino acid side chain on the acceptor activity of 2'(3')-O-aminoacyladenosines. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;16(1):136–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze H., Nierhaus K. H. Minimal set of ribosomal components for reconstitution of the peptidyltransferase activity. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):609–613. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit-McBride Z., Dever T. E., Hershey J. W., Merrick W. C. Sequence determination and cDNA cloning of eukaryotic initiation factor 4D, the hypusine-containing protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1578–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumpter V. G., Tate W. P., Nowotny P., Nierhaus K. H. Modification of histidine residues on proteins from the 50S subunit of the Escherichia coli ribosome. Effects on subunit assembly and peptidyl transferase centre activity. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 14;196(2):255–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUT R. R., MONRO R. E. THE PUROMYCIN REACTION AND ITS RELATION TO PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:63–72. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Hutton M. E., Neidhardt F. C. Gene-protein database of Escherichia coli K-12: edition 3. Electrophoresis. 1990 Dec;11(12):1131–1166. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150111205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vester B., Garrett R. A. The importance of highly conserved nucleotides in the binding region of chloramphenicol at the peptidyl transfer centre of Escherichia coli 23S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3577–3587. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G. Architecture of prokaryotic ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:35–65. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]