Abstract
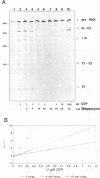
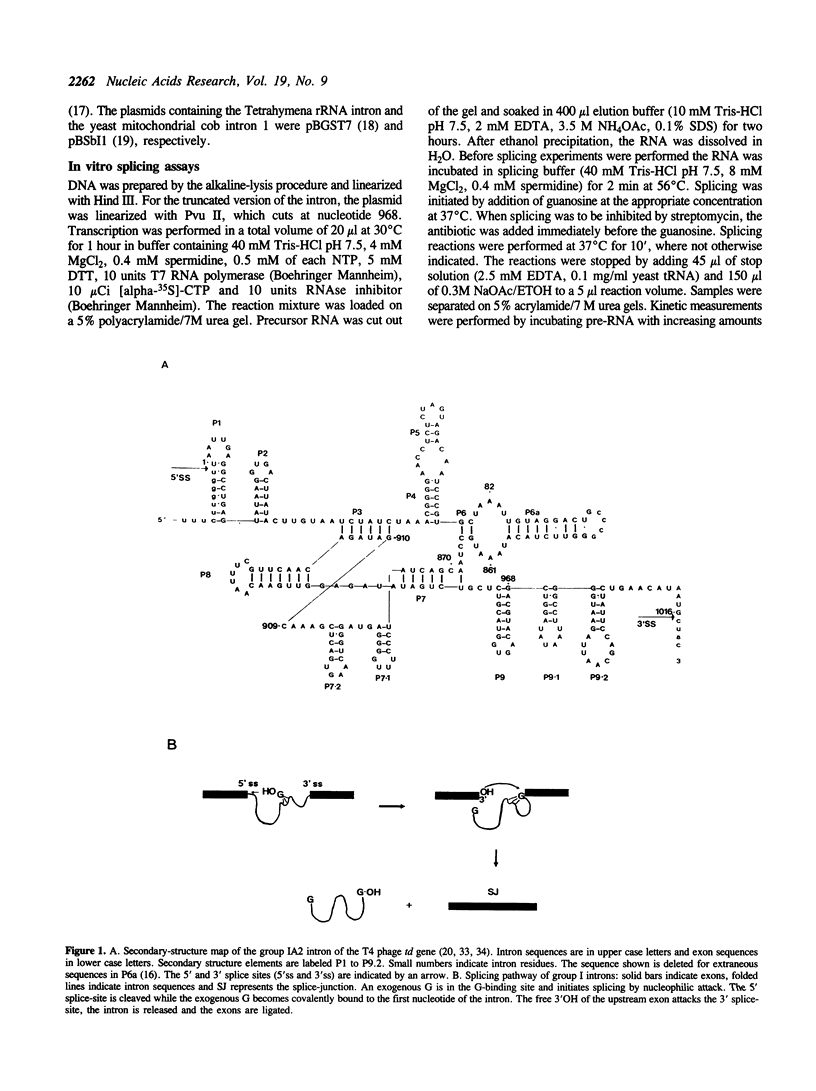
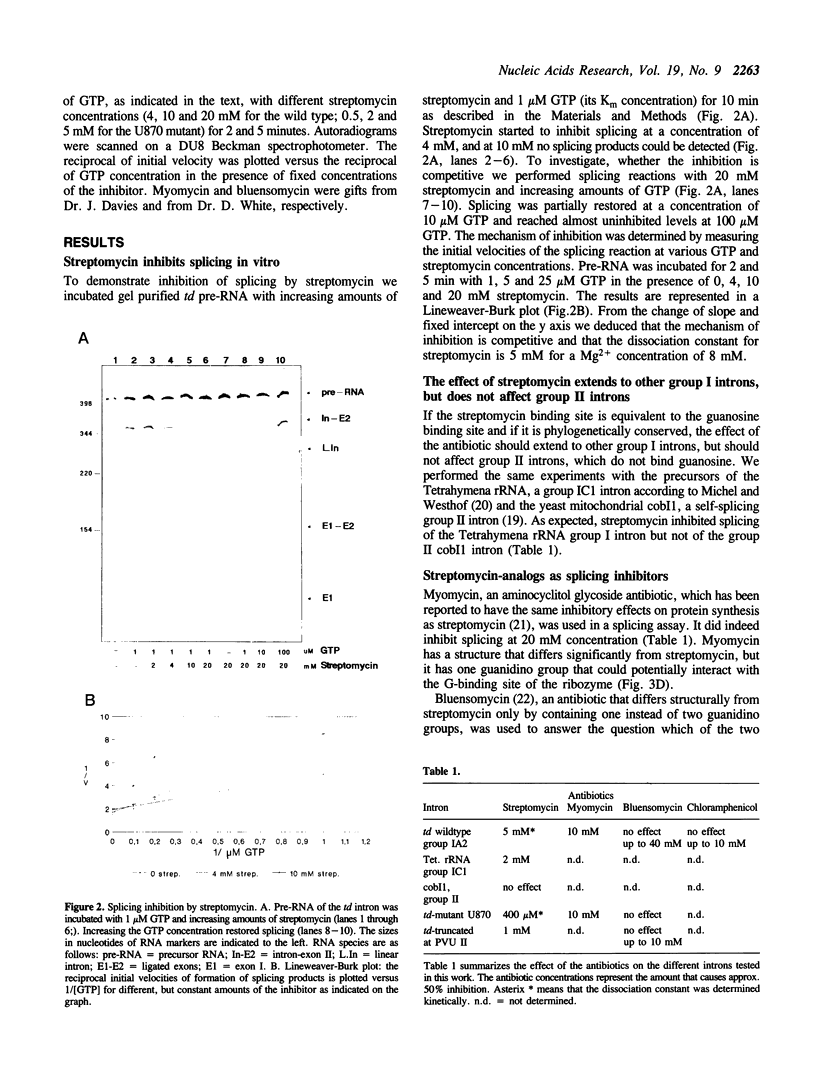
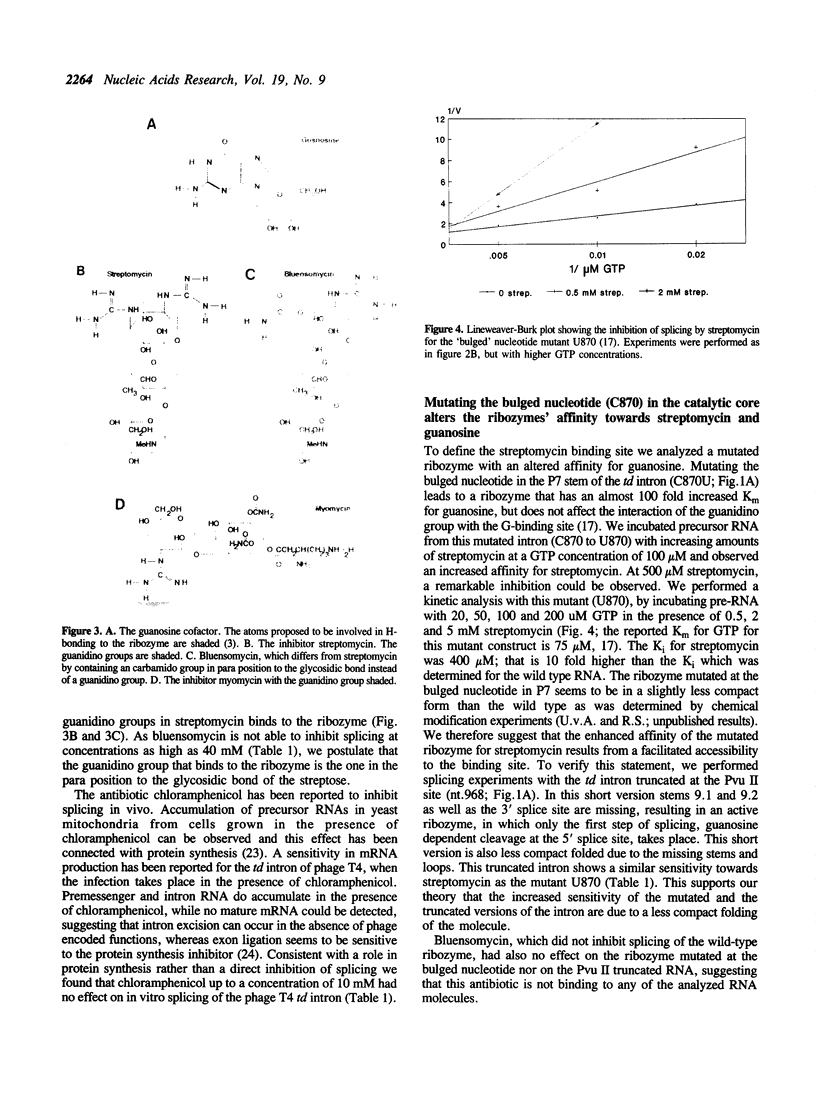
Streptomycin is an aminocyclitol glycoside antibiotic, which interferes with prokaryotic protein synthesis by interacting with the ribosomal RNA. We report here that streptomycin is also able to inhibit self splicing of the group I intron of the thymidylate synthase gene of phage T4. The inhibition is kinetically competitive with the substrate guanosine. Streptomycin and guanosine have in common a guanidino group, which has been shown to undergo hydrogen bonds with the ribozyme (Bass & Cech, Biochemistry, 25, 1986, 4473). The inhibitory effect of streptomycin extends to other group I introns, but does not affect group II introns. Mutating the bulged nucleotide in the conserved P7 secondary structure element of the td intron alters the affinity of the ribozyme for both guanosine and streptomycin. Myomycin, an antibiotic with similar effects on protein synthesis as streptomycin, is also able to inhibit splicing. In contrast, bluensomycin, which is structurally related to streptomycin, but contains only one guanidino group does not inhibit splicing. We discuss these findings in support of an evolutionary model that stresses the antiquity of antibiotics (J. Davies, Molecular Microbiology 4, 1990, 1227).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass B. L., Cech T. R. Ribozyme inhibitors: deoxyguanosine and dideoxyguanosine are competitive inhibitors of self-splicing of the Tetrahymena ribosomal ribonucleic acid precursor. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4473–4477. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. One binding site determines sequence specificity of Tetrahymena pre-rRNA self-splicing, trans-splicing, and RNA enzyme activity. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Pedersen-Lane J., West D., Ehrenman K., Maley G., Chu F., Maley F. Processing of the intron-containing thymidylate synthase (td) gene of phage T4 is at the RNA level. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M. Self-splicing introns in prokaryotes: migrant fossils? Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90201-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge E. A., Kurland C. G. Altered ribosomal protein in streptomycin-dependent Escherichia coli. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1282–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas D. K., Gorini L. Restriction, de-restriction and mistranslation in missense suppression. Ribosomal discrimination of transfer RNA's. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):119–134. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., Belfort M., Cech T. R., Davies R. W., Schweyen R. J., Shub D. A., Szostak J. W., Tabak H. F. Structural conventions for group I introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7217–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. S., LICHTENSTEIN J. Polyamines and ribosome structure. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:2112–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Cannon M., Mauer M. B. Myomycin: mode of action and mechanism of resistance. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1988 Mar;41(3):366–372. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.41.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. Structure-activity relationships among the aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:297–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenman K., Pedersen-Lane J., West D., Herman R., Maley F., Belfort M. Processing of phage T4 td-encoded RNA is analogous to the eukaryotic group I splicing pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5875–5879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway Salvo J. L., Coetzee T., Belfort M. Deletion-tolerance and trans-splicing of the bacteriophage T4 td intron. Analysis of the P6-L6a region. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 5;211(3):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90264-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhsel M. G., Strickland R., Palmer J. D. An ancient group I intron shared by eubacteria and chloroplasts. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1570–1573. doi: 10.1126/science.2125748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham J. A., Cech T. R. Defining the inside and outside of a catalytic RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):276–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2501870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGER J., BENEDICT M., ARTMAN M. A common site of action of polyamines and streptomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 30;62:202–204. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90519-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Hanna M., Green R., Bartel D. P., Szostak J. W. The guanosine binding site of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):391–395. doi: 10.1038/342391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Westhof E. Modelling of the three-dimensional architecture of group I catalytic introns based on comparative sequence analysis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):585–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90386-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Wagner R., Stutz E. E. coli ribosomes with a C912 to U base change in the 16S rRNA are streptomycin resistant. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3705–3708. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Identification and functional characterization of the protein controlled by the streptomycin-resistant locus in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):333–339. doi: 10.1038/222333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruusala T., Kurland C. G. Streptomycin preferentially perturbs ribosomal proofreading. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):100–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00328707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schweyen R. J. Evidence for ribosomes involved in splicing of yeast mitochondrial transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):513–524. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schweyen R. J. Self-splicing of group II introns in vitro: mapping of the branch point and mutational inhibition of lariat formation. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senaldi G., Peakman M., McManus T., Davies E. T., Tee D. E., Vergani D. Activation of the complement system in human immunodeficiency virus infection: relevance of the classical pathway to pathogenesis and disease severity. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1227–1232. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smailov S. K., Gavrilova L. P. Effect of streptomycin on the stoichiometry of GTP hydrolysis in a poly(U)-dependent cell-free translation system. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Dix D. B., Gerson R. B., Karim A. M. Effect of Mg2+ concentration, polyamines, streptomycin, and mutations in ribosomal proteins on the accuracy of the two-step selection of aminoacyl-tRNAs in protein biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6676–6681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vioque A. Protein synthesis inhibitors and catalytic RNA. Effect of puromycin on tRNA precursor processing by the RNA component of Escherichia coli RNase P. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 27;246(1-2):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M. Q., Kathe S. D., Goodrich-Blair H., Nierzwicki-Bauer S. A., Shub D. A. Bacterial origin of a chloroplast intron: conserved self-splicing group I introns in cyanobacteria. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1566–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2125747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M. A specific amino acid binding site composed of RNA. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1751–1758. doi: 10.1126/science.3381099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M., Christian E. L. Genetic code origins. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):349–350. doi: 10.1038/342349b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Ahsen U., Schroeder R. Streptomycin and self-splicing. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):801–801. doi: 10.1038/346801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]