Abstract
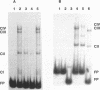
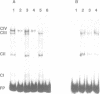
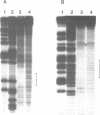
The mouse thymidylate synthase (TS) promoter lacks a TATAA box and directs transcriptional initiation at multiple sites over a 60 nucleotide region. All of the sequences that are important for transcription are located within close proximity to the first initiation site. Gel mobility shift and footprinting analyses with various sequences from this region of the TS promoter identified three major protein-DNA interactions. One of these corresponds to Sp1 interacting with a nonconsensus binding site downstream of the first transcriptional initiation site. Inactivation of the binding site by site-directed mutagenesis led to a 3-fold reduction in gene expression as well as a significant change in distribution of transcriptional start sites. The proteins responsible for the other two complexes (CII and CIII) do not appear to correspond to any of the common transcription factors that have been studied previously. The CII protein binds very close to the first initiation site. Inactivation of the binding site by site-directed mutagenesis had little effect on expression. The CIII protein binds immediately upstream of CII. Inactivation of this site led to a 12-fold reduction in expression, indicating that it is important for expression of the TS gene.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atchison M. L., Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Localization of transcriptional regulatory elements and nuclear factor binding sites in mouse ribosomal protein gene rpL32. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2067–2074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayusawa D., Shimizu K., Koyama H., Kaneda S., Takeishi K., Seno T. Cell-cycle-directed regulation of thymidylate synthase messenger RNA in human diploid fibroblasts stimulated to proliferate. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Jambou R. C., Swick A. G., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Transcriptional initiation is controlled by upstream GC-box interactions in a TATAA-less promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6632–6641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad A. H. Thymidylate synthetase activity in cultured mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1318–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danenberg P. V. Thymidylate synthetase - a target enzyme in cancer chemotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 23;473(2):73–92. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(77)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWille J. W., Jenh C. H., Deng T., Harendza C. J., Johnson L. F. Construction and expression of mouse thymidylate synthase minigenes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):84–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T. L., Li D. W., Jenh C. H., Johnson L. F. Structure of the gene for mouse thymidylate synthase. Locations of introns and multiple transcriptional start sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16000–16005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T. L., Li Y., Johnson L. F. Thymidylate synthase gene expression is stimulated by some (but not all) introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):645–658. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T., Li Y., Jolliff K., Johnson L. F. The mouse thymidylate synthase promoter: essential elements are in close proximity to the transcriptional initiation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4079–4082. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harendza C. J., Johnson L. F. Polyadenylylation signal of the mouse thymidylate synthase gene was created by insertion of an L1 repetitive element downstream of the open reading frame. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2531–2535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Equipotent mouse ribosomal protein promoters have a similar architecture that includes internal sequence elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1789–1800. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L., Lubon H. Interaction of protein with DNA in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:721–735. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenh C. H., Deng T. L., Li D. W., DeWille J., Johnson L. F. Mouse thymidylate synthase messenger RNA lacks a 3' untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8482–8486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenh C. H., Geyer P. K., Johnson L. F. Control of thymidylate synthase mRNA content and gene transcription in an overproducing mouse cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2527–2532. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Role of an adenovirus E2 promoter binding factor in E1A-mediated coordinate gene control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2180–2184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard A. C., Fried M. The bidirectional promoter of the divergently transcribed mouse Surf-1 and Surf-2 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1281–1294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navalgund L. G., Rossana C., Muench A. J., Johnson L. F. Cell cycle regulation of thymidylate synthetase gene expression in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7386–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Walmsley R. M., Lesko J. G., Airhart S. D., Ledbetter D. H. Thymidylate synthase-deficient Chinese hamster cells: a selection system for human chromosome 18 and experimental system for the study of thymidylate synthase regulation and fragile X expression. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Nov;37(6):1192–1205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossana C., Gollakota Rao L., Johnson L. F. Thymidylate synthetase overproduction in 5-fluorodeoxyuridine-resistant mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1118–1125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]