Abstract
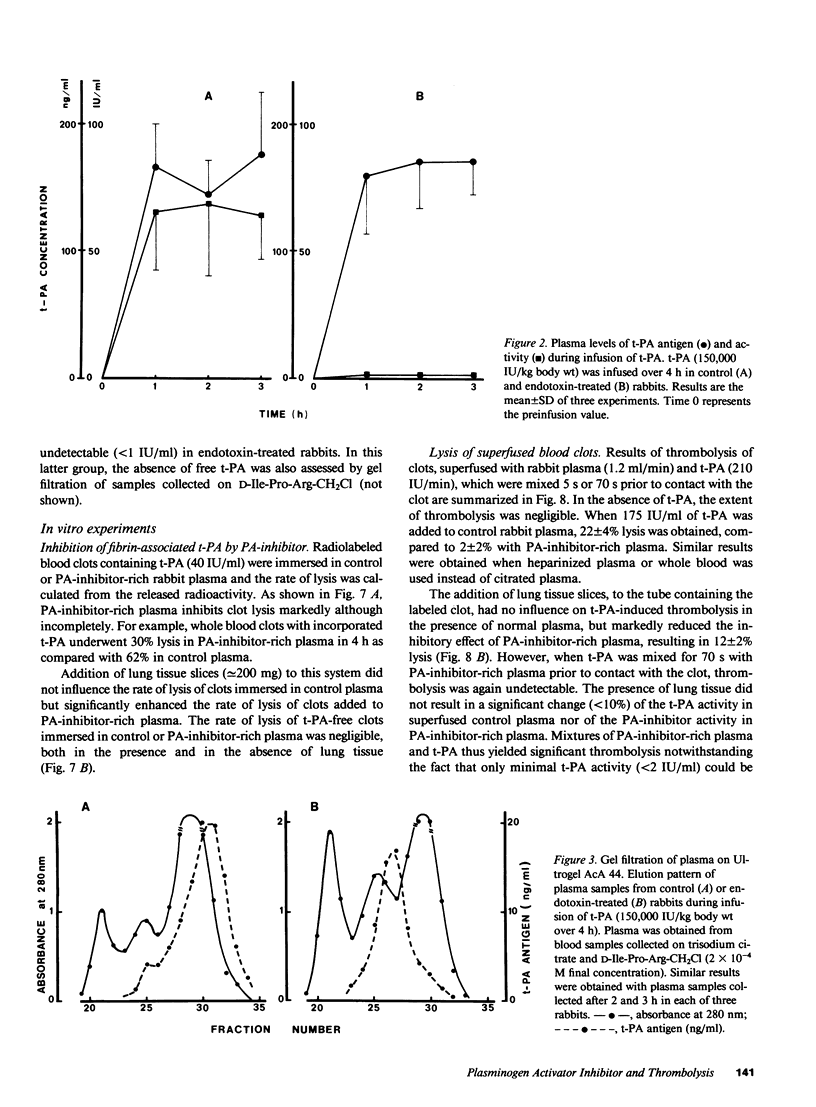
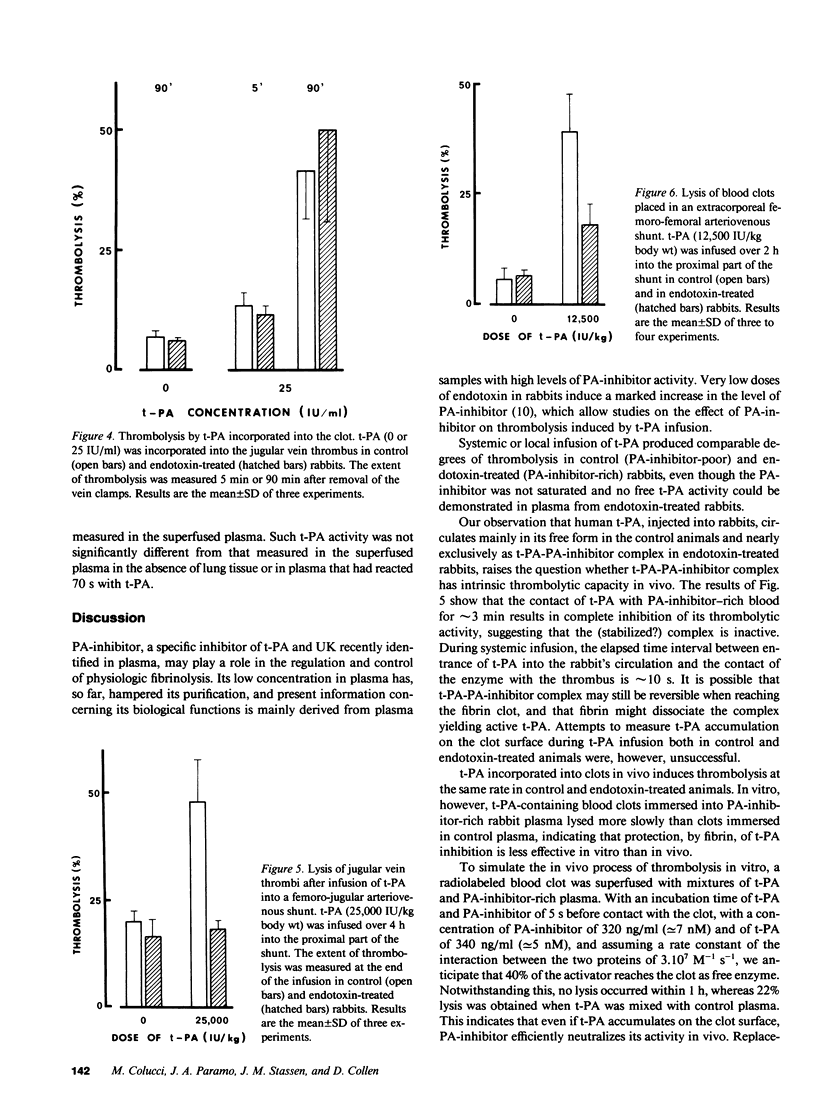
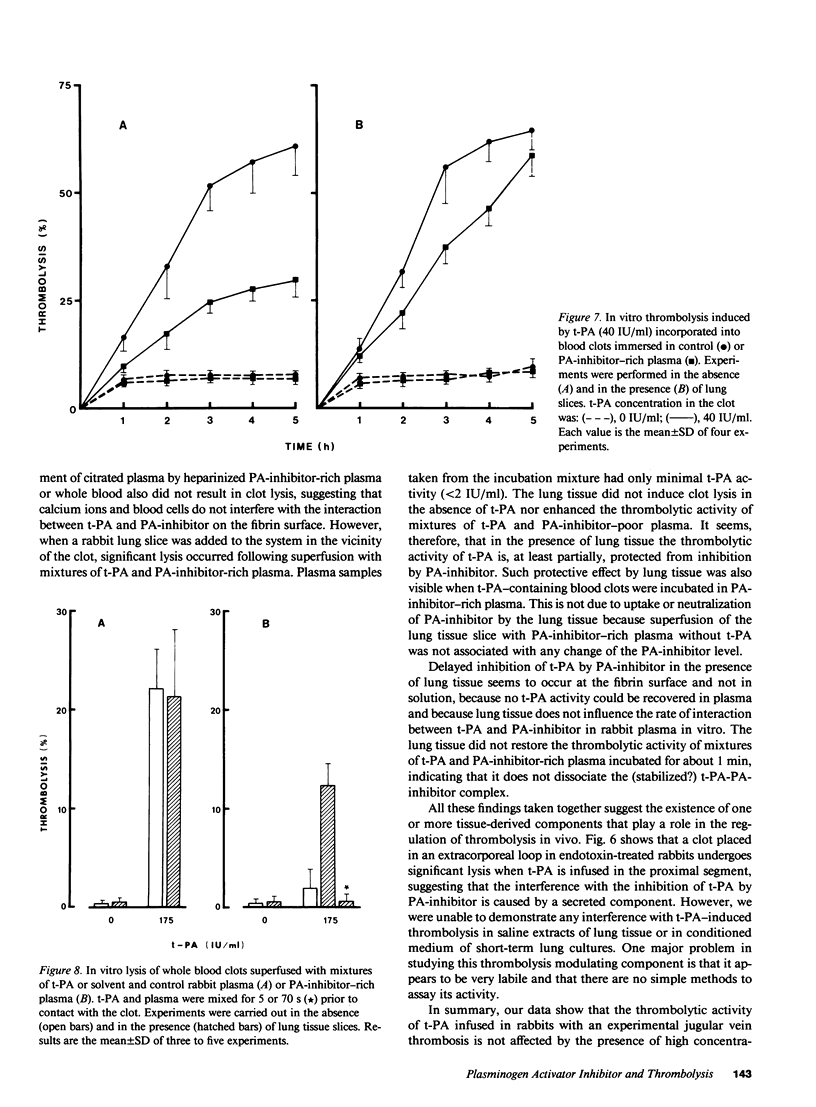
The influence of endotoxin-induced elevated plasma levels of the fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator (PA-inhibitor) on thrombolysis was investigated in rabbits with a jugular vein thrombus. Infusion of human tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) produced similar degrees of thrombolysis in control and endotoxin-treated rabbits, although no free t-PA could be demonstrated in plasma of endotoxin-treated animals. Infusion of t-PA in an extracorporeal arteriovenous shunt resulted in loss of thrombolytic activity in endotoxin-treated animals but not in control animals. Blood clots superfused in vitro with mixtures of t-PA and normal plasma lysed in contrast to clots superfused with t-PA and PA-inhibitor-rich plasma. However, addition of rabbit lung slices to the plasma surrounding the blood clot, reversed the inhibition of thrombolysis by PA-inhibitor-rich plasma. This indicates that tissue-derived factor(s) are involved in the regulation of in vivo thrombolysis. These hypothetical factor(s) are, however, very unstable in plasma, which has thus far precluded their further characterization.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRUP T., MULLERTZ S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Stassen J. M., Verstraete M. Thrombolysis with human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in rabbits with experimental jugular vein thrombosis. Effect of molecular form and dose of activator, age of the thrombus, and route of administration. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):368–376. doi: 10.1172/JCI110778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Paramo J. A., Collen D. Generation in plasma of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator in response to endotoxin stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):818–824. doi: 10.1172/JCI111777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edy J., De Cock F., Collen D. Inhibition of plasmin by normal and antiplasmin-depleted human plasma. Thromb Res. 1976 Apr;8(4):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., van Hinsbergh V. W., Verheijen J. H., Wijngaards G. Inhibition of tissue-type plasminogen activator by conditioned medium from cultured human and porcine vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney P. J., Curtis A. D. A collaborative study of a proposed international standard for tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA). Thromb Haemost. 1985 Feb 18;53(1):134–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan-Vague I., Moerman B., De Cock F., Aillaud M. F., Collen D. Plasma levels of a specific inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator (and urokinase) in normal and pathological conditions. Thromb Res. 1984 Mar 1;33(5):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korninger C., Collen D. Studies on the specific fibrinolytic effect of human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in human blood and in various animal species in vitro. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Aug 28;46(2):561–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Tran-Thang C., Ransijn A., Bachmann F. Demonstration of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activators in human plasma. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):907–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G. Latent tissue plasminogen activator produced by human endothelial cells in culture: evidence for an enzyme-inhibitor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6804–6808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Uytterhoeven M., Collen D. Inhibition of trypsin-like serine proteinases by tripeptide arginyl and lysyl chloromethylketones. Thromb Res. 1984 Jun 1;34(5):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90247-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., van Mourik J. A., Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. Detection of an unusually stable fibrinolytic inhibitor produced by bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Juhan-Vague I., de Cock F., Collen D. Measurement of human tissue-type plasminogen activator by a two-site immunoradiometric assay. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Feb;101(2):274–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen S., Philips M. Isolation of tissue-type plasminogen activator-inhibitor complexes from human plasma. Evidence for a rapid plasminogen activator inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 6;802(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERMYLEN C., DE VREKER R. A., VERSTRAETE M. A rapid enzymatic method for assay of fibrinogen fibrin polymerization time (FPT test). Clin Chim Acta. 1963 May;8:418–424. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(63)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen J. H., Chang G. T., Kluft C. Evidence for the occurrence of a fast-acting inhibitor for tissue-type plasminogen activator in human plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Jul 29;51(3):392–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen J. H., Mullaart E., Chang G. T., Kluft C., Wijngaards G. A simple, sensitive spectrophotometric assay for extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator applicable to measurements in plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Dec 27;48(3):266–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Csemiczky G., Marsk L., Robbe H. The fast inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator in plasma during pregnancy. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Oct 31;52(2):124–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamarron C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Influence of exogenous and endogenous tissue-type plasminogen activator on the lysability of clots in a plasma milieu in vitro. Thromb Res. 1984 Aug 1;35(3):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90364-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


