Abstract
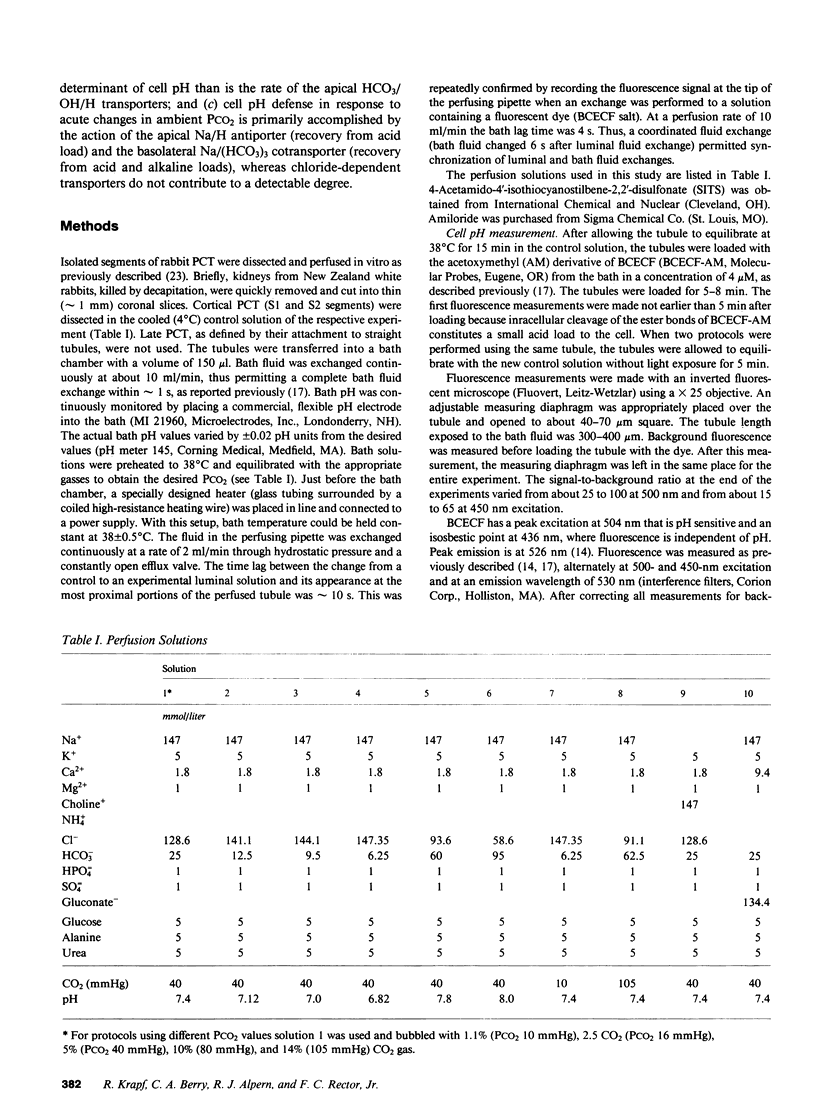
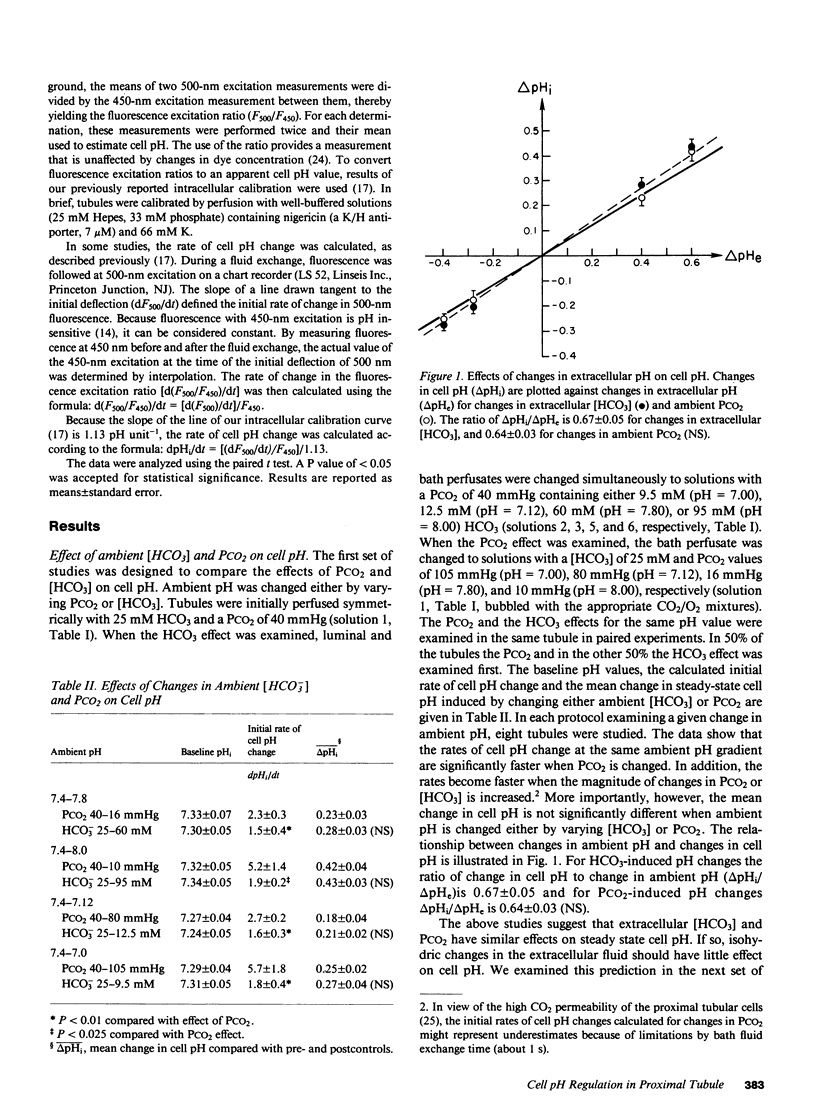
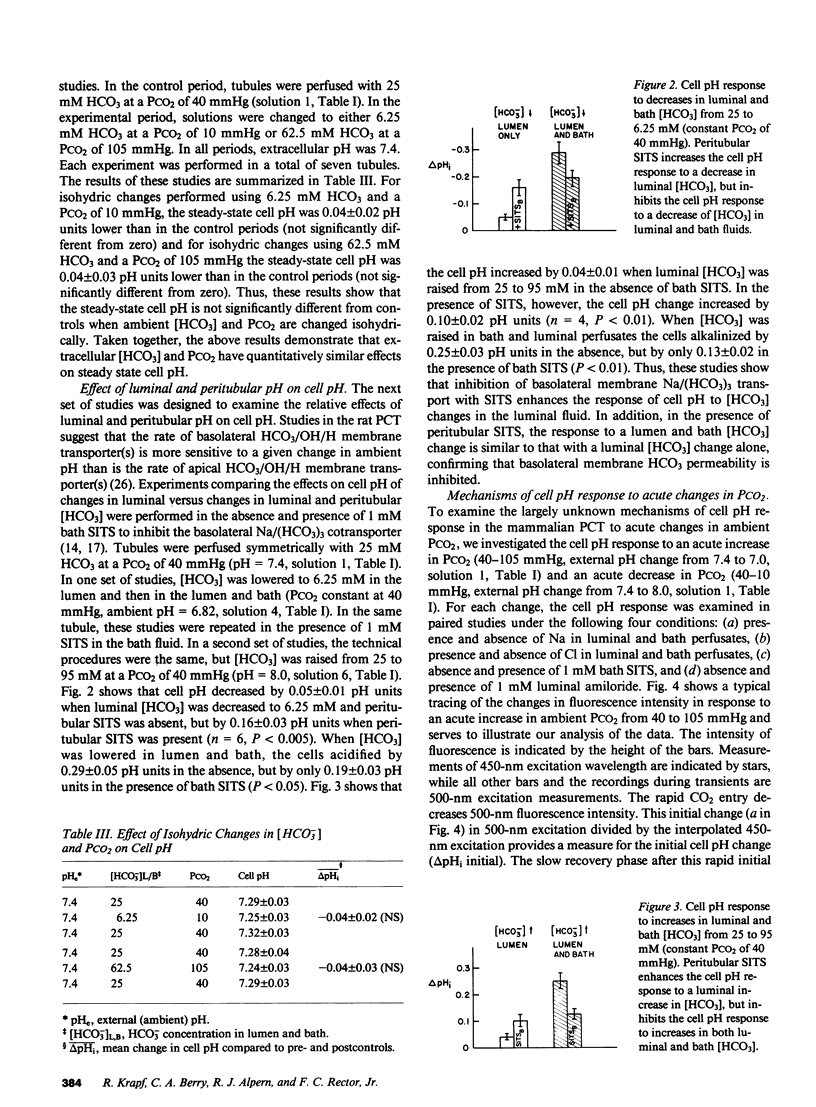
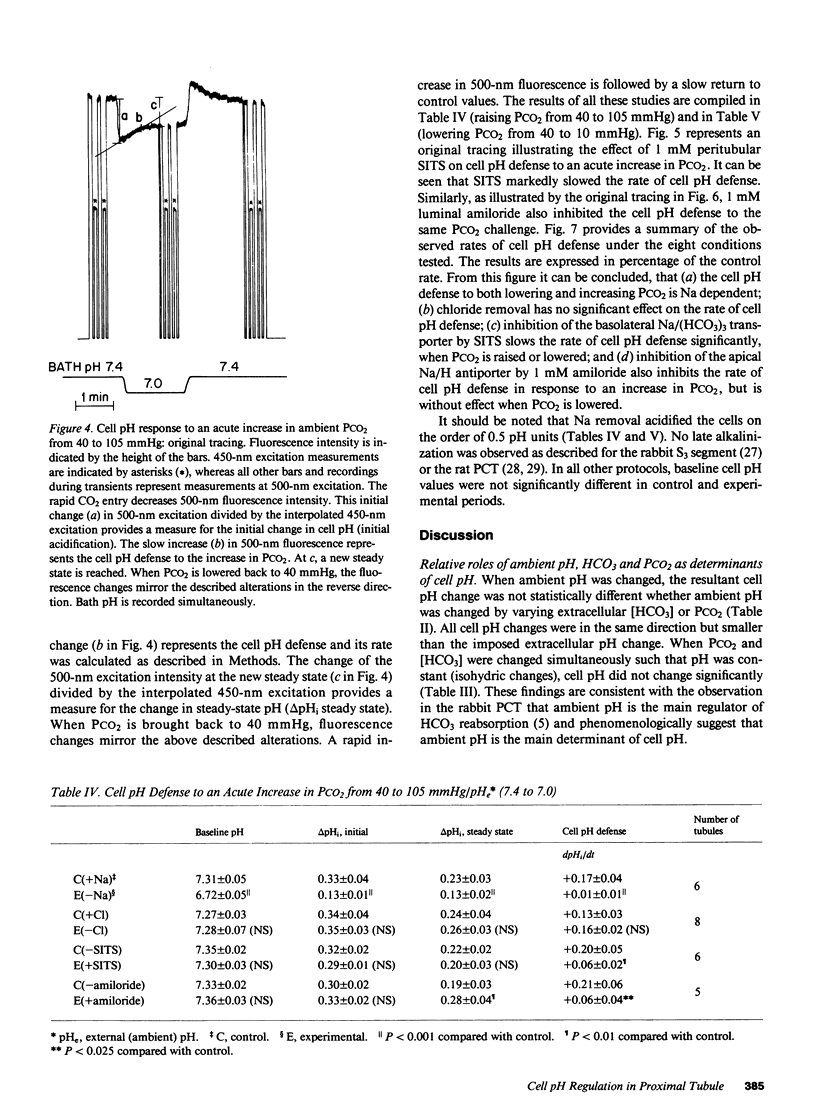
To study the regulation of cell pH by ambient pH, carbon dioxide tension (PCO2), and bicarbonate (HCO3), cell pH was measured in the isolated, in vitro microperfused rabbit proximal convoluted tubule using the fluorescent dye (2',7')-bis-(carboxyethyl)-(5,6)-carboxyfluorescein. For the same changes in external pH, changes in [HCO3] and PCO2 affected cell pH similarly ([HCO3]: pHi/pHe = 0.67, PCO2: pHi/pHe = 0.64, NS). Isohydric changes in extracellular [HCO3] and PCO2 did not change cell pH significantly. Changes in peritubular [HCO3] elicited larger changes in cell pH than changes in luminal [HCO3], which were enhanced by peritubular 4-acetamido-4'-isothiocyanostilbene-2,2'-disulfonate (SITS). The cell pH defense against acute increases and decreases in PCO2 was inhibited by sodium, but not by chloride removal. Peritubular SITS inhibited the cell pH defense against increases and decreases of PCO2, whereas luminal amiloride inhibited cell pH defense against increases in PCO2. Conclusions: (a) Steady-state cell pH changes in response to changes in extracellular [HCO3] and PCO2 are quantitatively similar for a given change in extracellular pH; (b) the rate of the basolateral Na/(HCO3)3 cotransporter is a more important determinant of cell pH than the rate of the apical membrane mechanism(s); (c) cell pH defense against acute changes in PCO2 depends on the basolateral Na/(HCO3)3 cotransporter (acid and alkaline loads) and the luminal Na/H antiporter (acid loads).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER S., ROY A., RELMAN A. S. INTRACELLULAR ACID-BASE REGULATION. I. THE RESPONSE OF MUSCLE CELLS TO CHANGES IN CO2 TENSION OR EXTRACELLULAR BICARBONATE CONCENTRATION. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jan;44:8–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI105129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiba T., Alpern R. J., Eveloff J., Calamina J., Warnock D. G. Electrogenic sodium/bicarbonate cotransport in rabbit renal cortical basolateral membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1472–1478. doi: 10.1172/JCI112738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J. Apical membrane chloride/base exchange in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1026–1030. doi: 10.1172/JCI112914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Chambers M. Basolateral membrane Cl/HCO3 exchange in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Na-dependent and -independent modes. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Apr;89(4):581–598. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Chambers M. Cell pH in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Regulation by luminal and peritubular pH and sodium concentration. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):502–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI112602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Effect of luminal bicarbonate concentration on proximal acidification in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):F53–F59. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.1.F53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Effects of extracellular fluid volume and plasma bicarbonate concentration on proximal acidification in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):736–746. doi: 10.1172/JCI110821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J. Mechanism of basolateral membrane H+/OH-/HCO-3 transport in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. A sodium-coupled electrogenic process. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Nov;86(5):613–636. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.5.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Nee J., Suhm M. A. Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):161–163. doi: 10.1038/299161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Suhm M. A., Nee J. Interaction of external H+ with the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6767–6771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum M. Evidence that parallel Na+-H+ and Cl(-)-HCO3-(OH-) antiporters transport NaCl in the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 2):F338–F345. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.2.F338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biagi B. A., Sohtell M. Electrophysiology of basolateral bicarbonate transport in the rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 2):F267–F272. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.2.F267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Basolateral HCO3- transport. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):53–94. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Green N. Bicarbonate transport by isolated perfused rabbit proximal convoluted tubules. Am J Physiol. 1977 Oct;233(4):F307–F314. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.4.F307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Biagi B., Giebisch G. Control mechanisms of bicarbonate transport across the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):F532–F543. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.5.F532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan M. G. Effects of acute alterations in PCO2 on proximal HCO-3, Cl-, and H2O reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 2):F21–F26. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.1.F21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebisch G., Malnic G., De Mello G. B., De Mello Aires M. Kinetics of luminal acidification in cortical tubules of the rat kidney. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;267(3):571–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassl S. M., Aronson P. S. Na+/HCO3-co-transport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8778–8783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson H. R. Effects of CO2 and acetazolamide on bicarbonate and fluid transport in rabbit proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):F54–F62. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.1.F54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniski L. P., Aronson P. S. Chloride/formate exchange with formic acid recycling: a mechanism of active chloride transport across epithelial membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6362–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunau R. T., Jr, Hart J. I., Walker K. A. Effect of metabolic acidosis on proximal tubular total CO2 absorption. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 2):F62–F68. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.1.F62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. Z. Effect of acute hypercapnia on proximal tubular water and bicarbonate reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1164–1170. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucci M. S., Warnock D. G. Effects of anion-transport inhibitors on NaCl reabsorption in the rat superficial proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):570–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI109495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., de Mello-Aires M. Kinetic study of bicarbonate reabsorption in proximal tubule of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jun;220(6):1759–1767. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.6.1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Burg M. B. Biocarbonate and fluid absorption by renal proximal straight tubules. Kidney Int. 1977 Jul;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mello Aires M., Malnic G. Peritubular pH and PCO'2 in renal tubular acidification. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1766–1774. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. R., Civitelli R., Westbrook S. L., Avioli L. V., Hruska K. A. Cytoplasmic pH regulation in canine renal proximal tubule cells. Kidney Int. 1987 May;31(5):1113–1120. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Berry C. A. Mechanism of bicarbonate exit across basolateral membrane of the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):F889–F896. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.6.F889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Berry C. A., Rector F. C., Jr Effect of luminal and peritubular HCO3(-) concentrations and PCO2 on HCO3(-) reabsorption in rabbit proximal convoluted tubules perfused in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):639–649. doi: 10.1172/JCI110658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Weinstein A. M., Steele R. E., Stephenson J. L., Burg M. B. Carbon dioxide permeability of rabbit proximal convoluted tubules. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):F231–F244. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.3.F231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., Roos A. Regulation of intracellular pH in human neutrophils. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Mar;85(3):443–470. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani M., Grassi S. M., Aronson P. S. Stoichiometry of Na+-HCO-3 cotransport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1172/JCI112948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struyvenberg A., Morrison R. B., Relman A. S. Acid-base behavior of separated canine renal tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):1155–1162. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Rumrich G., Baumann K. Renal proximal tubular buffer-(glycodiazine) transport. Inhomogeneity of local transport rate, dependence on sodium, effect of inhibitors and chronic adaptation. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Jun 26;357(3-4):149–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00585971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitomi K., Burckhardt B. C., Frömter E. Rheogenic sodium-bicarbonate cotransport in the peritubular cell membrane of rat renal proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):360–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00595689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


