Abstract
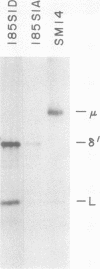
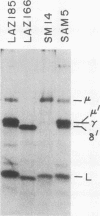
We report an unusual phenotype of B cells in a patient with X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA), and cellular evidence for Lyonization of B cells from his mother and sister. The patient has a failure of B cell maturation at the stage of early B lymphocytes, associated with production of D(mu delta) H chain. The phenotype of his B cells includes: (a) limitation to expression of the mu and delta H chain isotypes, (b) production of mu and delta H chains of reduced size and (c) delayed expression of L chain. Peripheral blood and B cell lines from the patient's mother and sister include 50% cells that express H chain without L chain. B cell lines from the mother and sister produce full-length mu and gamma H chains and truncated mu and delta chains corresponding to the H chains produced by the patient's B cells. Clones with normal and XLA phenotype have been isolated from B cell lines derived from the patient's mother. We conclude that the dimorphism of mother's and sister's B cells results from Lyonization, implying that the gene defect in XLA is intrinsic to B lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF
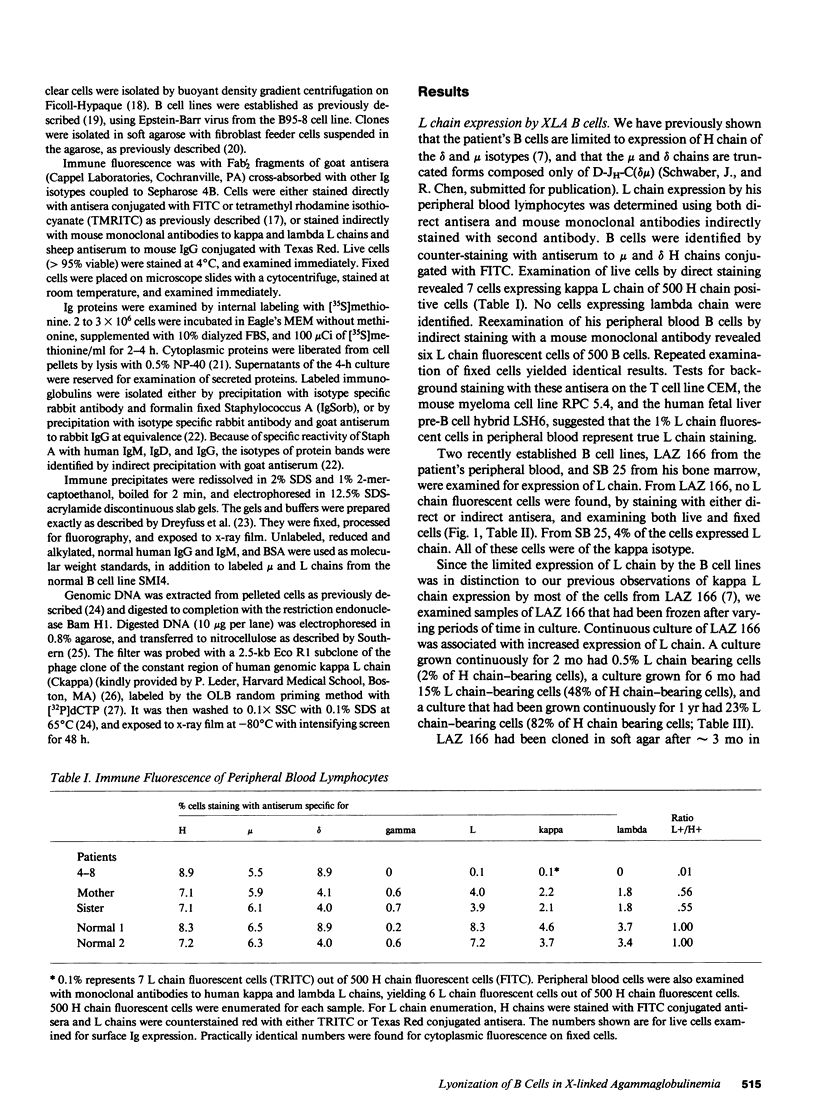
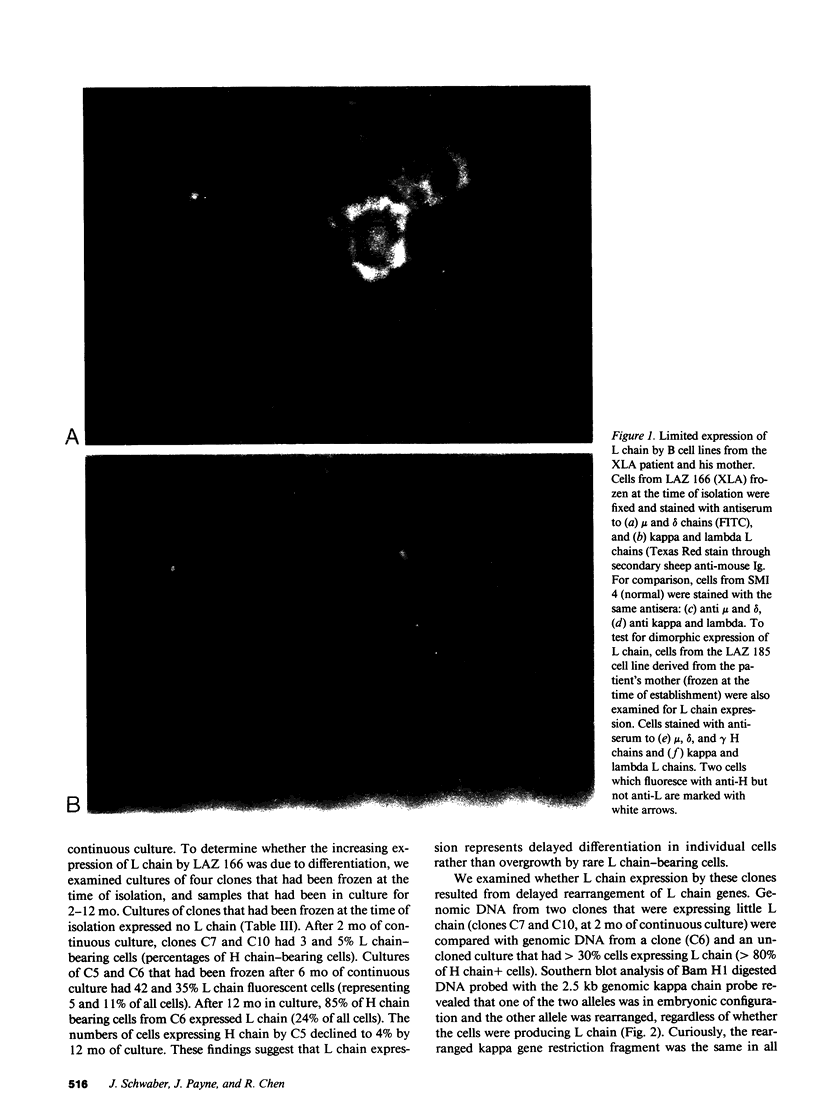
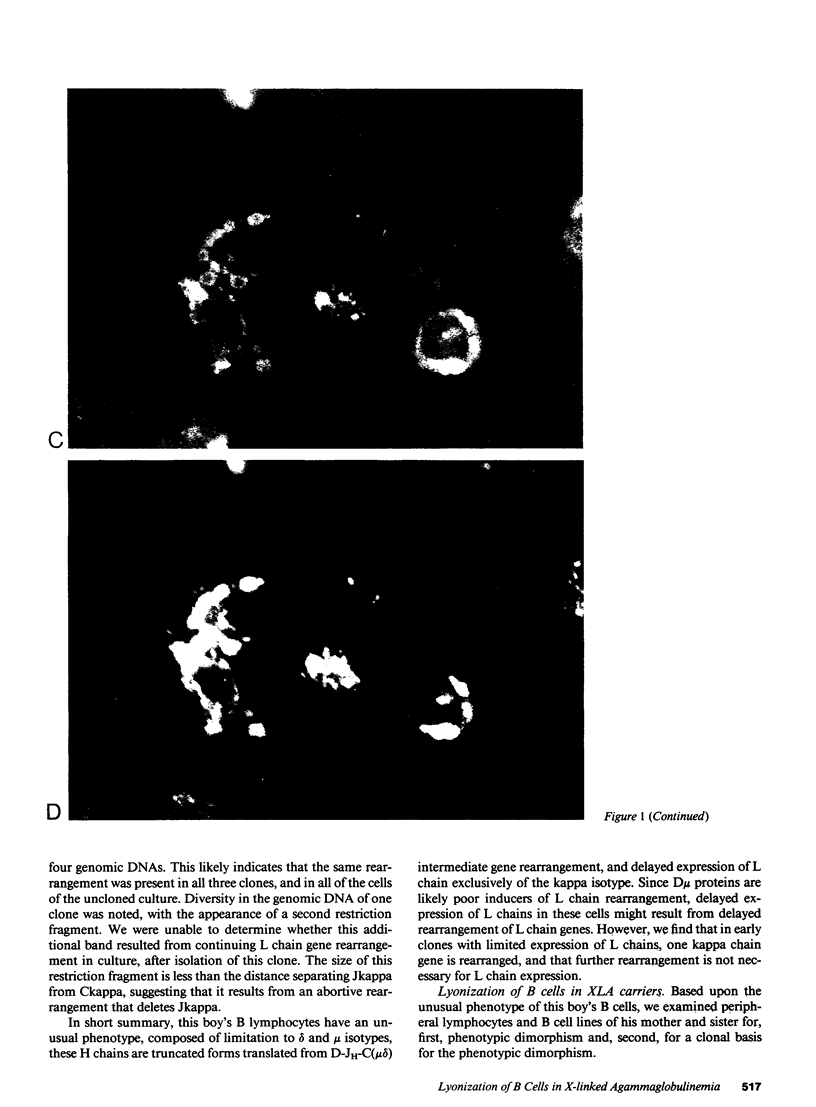
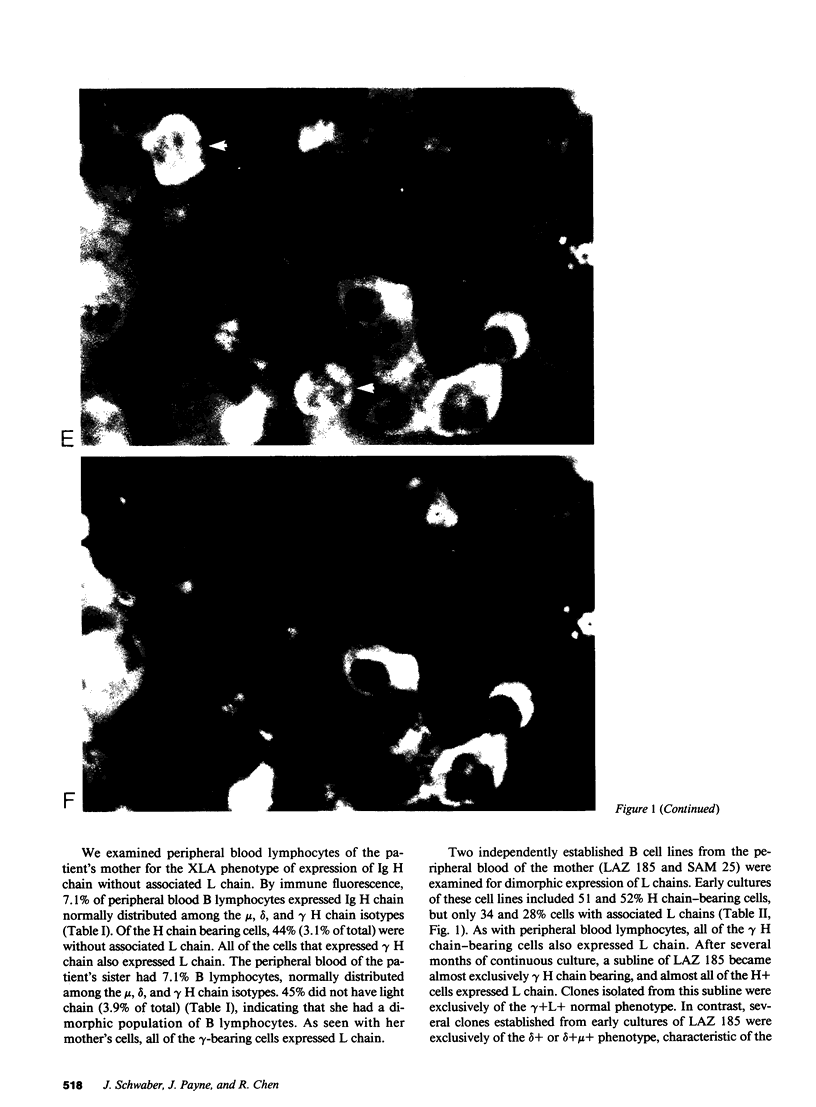



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRUTON O. C. Agammaglobulinemia (congenital absence of gamma globulin); report of a case. Med Ann Dist Columbia. 1953 Dec;22(12):648–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Moore M. W., Yancopoulos G. D., Suh H., Lutzker S., Selsing E., Alt F. W. Recombination between immunoglobulin variable region gene segments is enhanced by transcription. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):585–589. doi: 10.1038/324585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøyum A. Isolation of lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Brown P., Pickard A. R., Buckley R. H., Miller D. S., Raskind W. H., Singer J. W., Fialkow P. J. Expression of the gene defect in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):564–567. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Adam S. A., Choi Y. D. Physical change in cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoproteins in cells treated with inhibitors of mRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):415–423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Winkelstein J. A., Civin C. I., Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B. Carrier detection in X-linked agammaglobulinemia by analysis of X-chromosome inactivation. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 19;316(8):427–431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702193160802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Rocha B., Coutinho A. A. Life span of B lymphocytes: the experimental basis for conflicting results. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):470–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., HITZIG W. H., JANEWAY C. A. Multiple serum protein deficiencies in congenital and acquired agammaglobulinemia. J Clin Invest. 1956 Nov;35(11):1199–1204. doi: 10.1172/JCI103374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavras H., Lever A. F., Brown J. J., Macadam R. F., Robertson J. I. Acute renal failure, tubular necrosis, and myocardial infarction induced in the rabbit by intravenous angiotensin II. Lancet. 1971 Jul 3;2(7714):19–22. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gealy W. J., Dwyer J. M., Harley J. B. Allelic exclusion of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in platelets and T lymphocytes from a Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome carrier. Lancet. 1980 Jan 12;1(8159):63–65. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90492-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Rosen F. S., Merler E. Identification and characterization of subpopulations of lymphocytes in human peripheral blood after fractionation on discontinuous gradients of albumin. The cellular defect in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1726–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI107354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P., Banting G., Sheer D., Ropers H. H., Caine A., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Povey S., Voss R. Genetic evidence that a Y-linked gene in man is homologous to a gene on the X chromosome. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):346–349. doi: 10.1038/302346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. A. Studies on nonidet P40 lysis of murine lymphoid cells. I. Use of cholera toxin and cell surface Ig to determine degree of dissociation of the plasma membrane. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):871–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. Cloned human and mouse kappa immunoglobulin constant and J region genes conserve homology in functional segments. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch S., Schur P. H., Schwaber J. Improved method for cloning human B-cell lines. Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 15;72(2):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keitges E., Rivest M., Siniscalco M., Gartler S. M. X-linkage of steroid sulphatase in the mouse is evidence for a functional Y-linked allele. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):226–227. doi: 10.1038/315226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. P., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Wedgwood R. J., Latt S., Rosen F. S. Mapping of the X-linked agammaglobulinemia locus by use of restriction fragment-length polymorphism. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):649–652. doi: 10.1172/JCI112351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:372–373. doi: 10.1038/190372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. A., Kelley W. N. Lesch-Nyhan syndrome: absence of the mutant enzyme in erythrocytes of a heterozygote for both normal and mutant hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase. Biochem Genet. 1972 Feb;6(1):21–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00485961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl E. R., Vogler L. B., Okos A. J., Crist W. M., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Cooper M. D. B lymphocyte precursors in human bone marrow: an analysis of normal individuals and patients with antibody-deficiency states. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1169–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prchal J. T., Carroll A. J., Prchal J. F., Crist W. M., Skalka H. W., Gealy W. J., Harley J., Malluh A. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: cellular impairments and their implication for carrier detection. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1048–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. G., Alt F. W. Novel immunoglobulin heavy chains are produced from DJH gene segment rearrangements in lymphoid cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):418–423. doi: 10.1038/312418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. G., Ammirati P., Jackson S., Alt F. W. Regulated progression of a cultured pre-B-cell line to the B-cell stage. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):353–355. doi: 10.1038/317353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Cooper M. D., Wedgwood R. J. The primary immunodeficiencies (1). N Engl J Med. 1984 Jul 26;311(4):235–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198407263110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Hutchison G. B., Allen F. H., Jr The Xg blood groups and congenital hypogammaglobulinemia. Vox Sang. 1965 Nov-Dec;10(6):729–730. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1965.tb05185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANGER R., RACE R. R. The Xg blood groups and familial hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1963 Apr 20;1(7286):859–860. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91629-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzmann J., DeMars R., Benke P. Single-allele expression at an X-linked hyperuricemia locus in heterozygous human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):545–552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaber J. F., Rosen F. S. Induction of human immunoglobulin synthesis and secretion in somatic cell hybrids of mouse myeloma and human B lymphocytes from patients with agammaglobulinemia. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):974–986. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaber J. F., Rosen F. S. Isotypes of surface immunoglobulin on B lymphocytes from patients with immune deficiency. J Clin Immunol. 1982 Jan;2(1):30–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00915975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaber J., Lazarus H., Rosen F. S. Bone marrow-derived lymphoid cell lines from patients with agammaglobulinemia. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):302–310. doi: 10.1172/JCI109130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaber J., Lazarus H., Rosen F. S. Restricted classes of immunoglobulin produced by a lymphoid cell line from a patient with agammaglobulinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2421–2423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]