Abstract
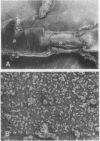
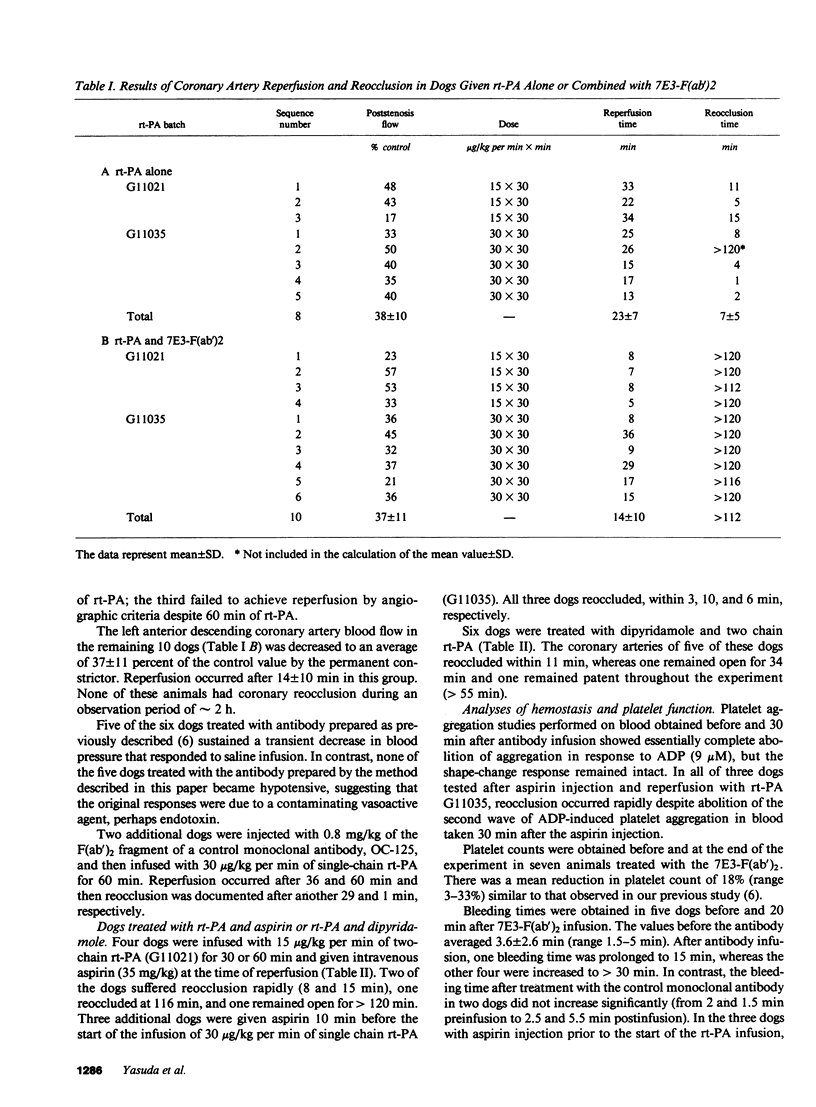
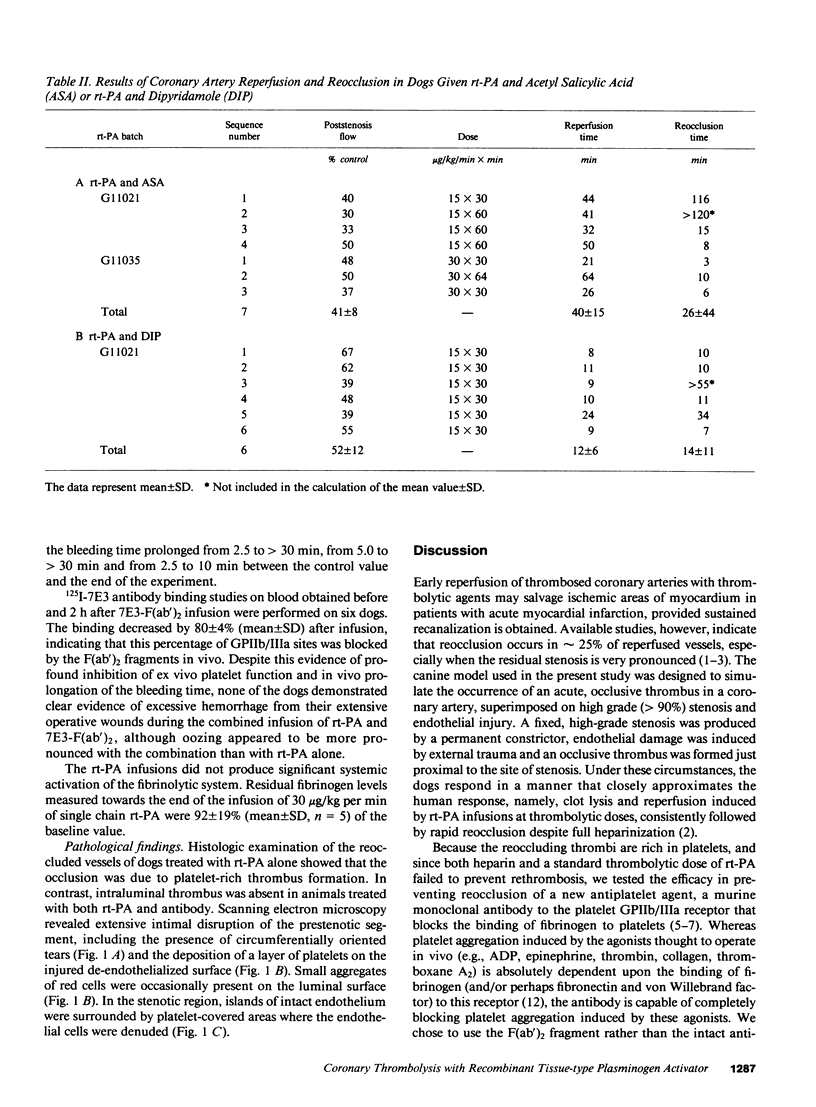
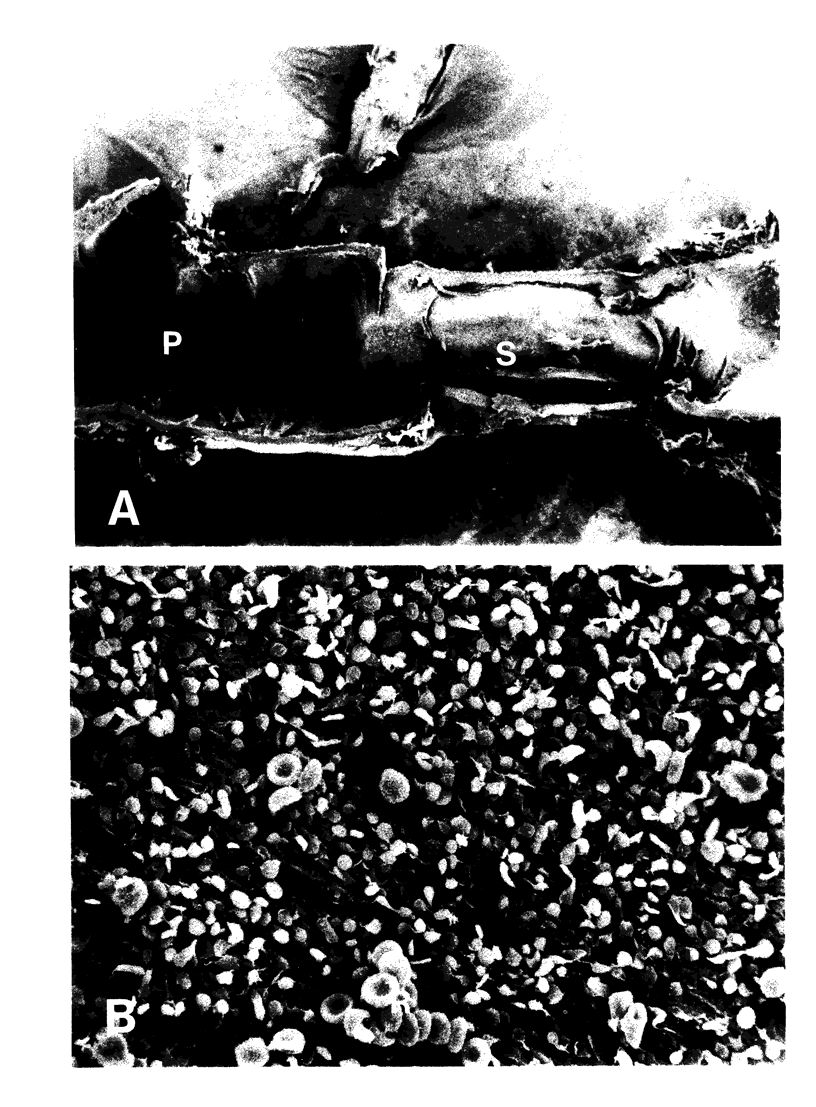
Localized thrombosis was produced in the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery of open chest dogs by constricting a segment so as to produce greater than 90% stenosis (reducing blood flow to 40 +/- 10% of baseline), and placing a thrombus in the segment immediately proximal to the stenosis by inducing endothelial cell injury and instilling a mixture of blood and thrombin. Intravenous infusion of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rt-PA) at a rate of 15-30 micrograms/kg per min for 30 or 60 min in eight dogs induced coronary artery reperfusion within 23 +/- 7 min (mean +/- SD), but reocclusion occurred despite heparin anticoagulation in all but one of these dogs within 7 +/- 5 min. Intravenous injection of 0.8 mg/kg of the F(ab')2 fragment of a monoclonal antibody (7E3) directed against the platelet GPIIb/IIIa receptor, prevented reocclusion in 10/10 dogs during an observation period of 2 h (P less than 0.001 vs. rt-PA alone). The antibody abolished ADP-induced platelet aggregation and markedly prolonged the bleeding time. Intravenous aspirin or dipyridamole prevented reocclusion for 1 h or more in only 2/7 and 1/6 dogs, respectively. We conclude that the monoclonal antibody is very effective in preventing reocclusion after successful thrombolysis of occluded coronary arteries with rt-PA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiken J. W., Shebuski R. J., Miller O. V., Gorman R. R. Endogenous prostacyclin contributes to the efficacy of a thromboxane synthetase inhibitor for preventing coronary artery thrombosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Nov;219(2):299–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bast R. C., Jr, Feeney M., Lazarus H., Nadler L. M., Colvin R. B., Knapp R. C. Reactivity of a monoclonal antibody with human ovarian carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1331–1337. doi: 10.1172/JCI110380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Topol E. J., Tiefenbrunn A. J., Gold H. K., Weisfeldt M. L., Sobel B. E., Leinbach R. C., Brinker J. A., Ludbrook P. A., Yasuda I. Coronary thrombolysis with recombinant human tissue-type plasminogen activator: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Circulation. 1984 Dec;70(6):1012–1017. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.6.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S. A new murine monoclonal antibody reports an activation-dependent change in the conformation and/or microenvironment of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):101–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI111931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Folts J. D., Scudder L. E., Smith S. R. Antithrombotic effect of a monoclonal antibody to the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor in an experimental animal model. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):783–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. A murine monoclonal antibody that completely blocks the binding of fibrinogen to platelets produces a thrombasthenic-like state in normal platelets and binds to glycoproteins IIb and/or IIIa. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):325–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI110973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Scudder L. E. Inhibition of dog platelet function by in vivo infusion of F(ab')2 fragments of a monoclonal antibody to the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor. Blood. 1985 Dec;66(6):1456–1459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conard J., Lecrubier C., Scarabin P. Y., Horellou M. H., Samama M., Bousser M. G. Effects of long term administration of ticlopidine on platelet function and hemostatic variables. Thromb Res. 1980 Oct 1;20(1):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. J., Thomas A. C. Plaque fissuring--the cause of acute myocardial infarction, sudden ischaemic death, and crescendo angina. Br Heart J. 1985 Apr;53(4):363–373. doi: 10.1136/hrt.53.4.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Minno G., Cerbone A. M., Mattioli P. L., Turco S., Iovine C., Mancini M. Functionally thrombasthenic state in normal platelets following the administration of ticlopidine. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):328–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI111705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldor A., Vlodavsky I., Martinowicz U., Fuks Z., Coller B. S. Platelet interaction with subendothelial extracellular matrix: platelet-fibrinogen interactions are essential for platelet aggregation but not for the matrix-induced release reaction. Blood. 1985 Jun;65(6):1477–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folts J. D., Crowell E. B., Jr, Rowe G. G. Platelet aggregation in partially obstructed vessels and its elimination with aspirin. Circulation. 1976 Sep;54(3):365–370. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.54.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian H. D., Gold H. K., Leinbach R. C., Johns J. A., Yasuda T., Kanke M., Collen D. Comparative properties of two clinical preparations of recombinant human tissue-type plasminogen activator in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 Mar;9(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold H. K., Fallon J. T., Yasuda T., Leinbach R. C., Khaw B. A., Newell J. B., Guerrero J. L., Vislosky F. M., Hoyng C. F., Grossbard E. Coronary thrombolysis with recombinant human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Circulation. 1984 Oct;70(4):700–707. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.4.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold H. K., Leinbach R. C., Garabedian H. D., Yasuda T., Johns J. A., Grossbard E. B., Palacios I., Collen D. Acute coronary reocclusion after thrombolysis with recombinant human tissue-type plasminogen activator: prevention by a maintenance infusion. Circulation. 1986 Feb;73(2):347–352. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.2.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. G., Ferguson D. W., Collins S. M., Skorton D. J., Ericksen E. E., Kioschos J. M., Marcus M. L., White C. W. Rethrombosis after reperfusion with streptokinase: importance of geometry of residual lesions. Circulation. 1984 May;69(5):991–999. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.69.5.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Gara P. T., Guerrero J. L., Feldman B., Fallon J. T., Block P. C. Effect of dextran and aspirin on platelet adherence after transluminal angioplasty of normal canine coronary arteries. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Jun 1;53(11):1695–1698. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90604-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakariassen K. S., Nievelstein P. F., Coller B. S., Sixma J. J. The role of platelet membrane glycoproteins Ib and IIb-IIIa in platelet adherence to human artery subendothelium. Br J Haematol. 1986 Aug;63(4):681–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb07552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Rososhansky S. A Glanzmann's thrombasthenia cluster among Iraqi Jews in Israel. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Dec 29;52(3):230–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. E., Joist J. H., Sutera S. P. Role of platelet-prostaglandin synthesis in shear-induced platelet alterations. Blood. 1980 Nov;56(5):753–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weselcouch E. O., Humphrey W. R., Aiken J. W. Effects of low doses of aspirin and dipyridamole on platelet aggregation in the dog coronary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jan;240(1):37–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willerson J. T., Hillis L. D., Winniford M., Buja L. M. Speculation regarding mechanisms responsible for acute ischemic heart disease syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1986 Jul;8(1):245–250. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(86)80121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]