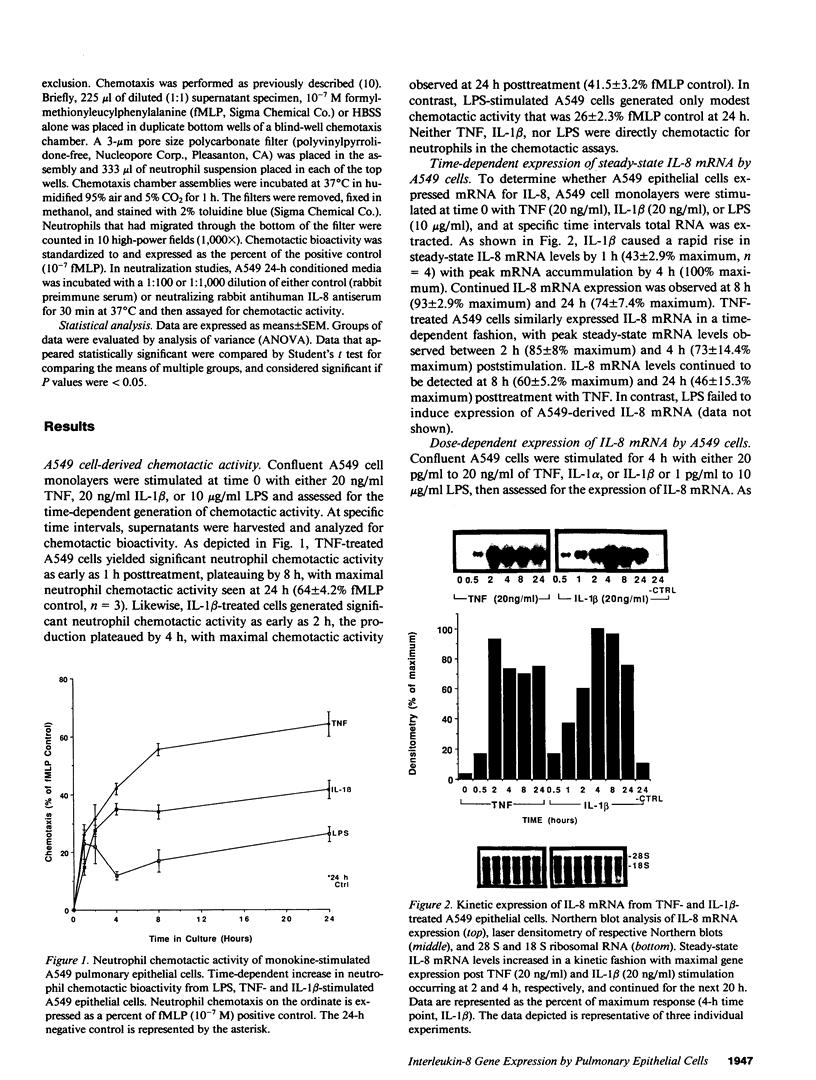
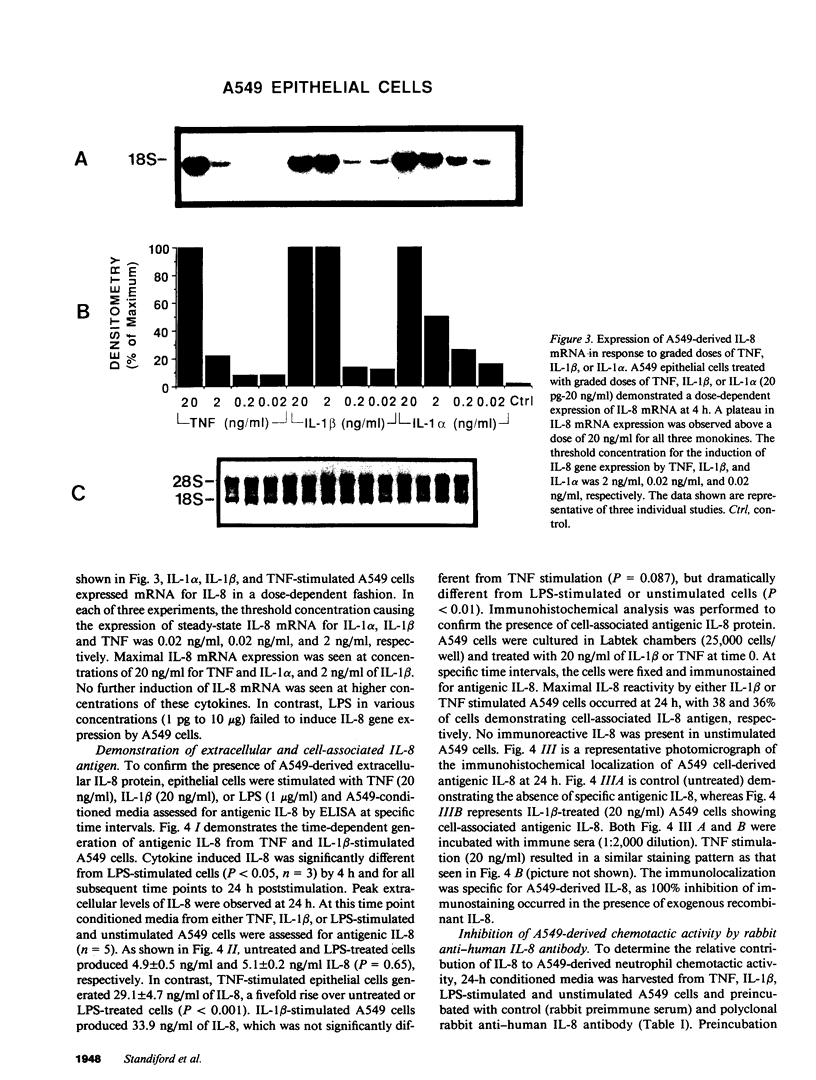
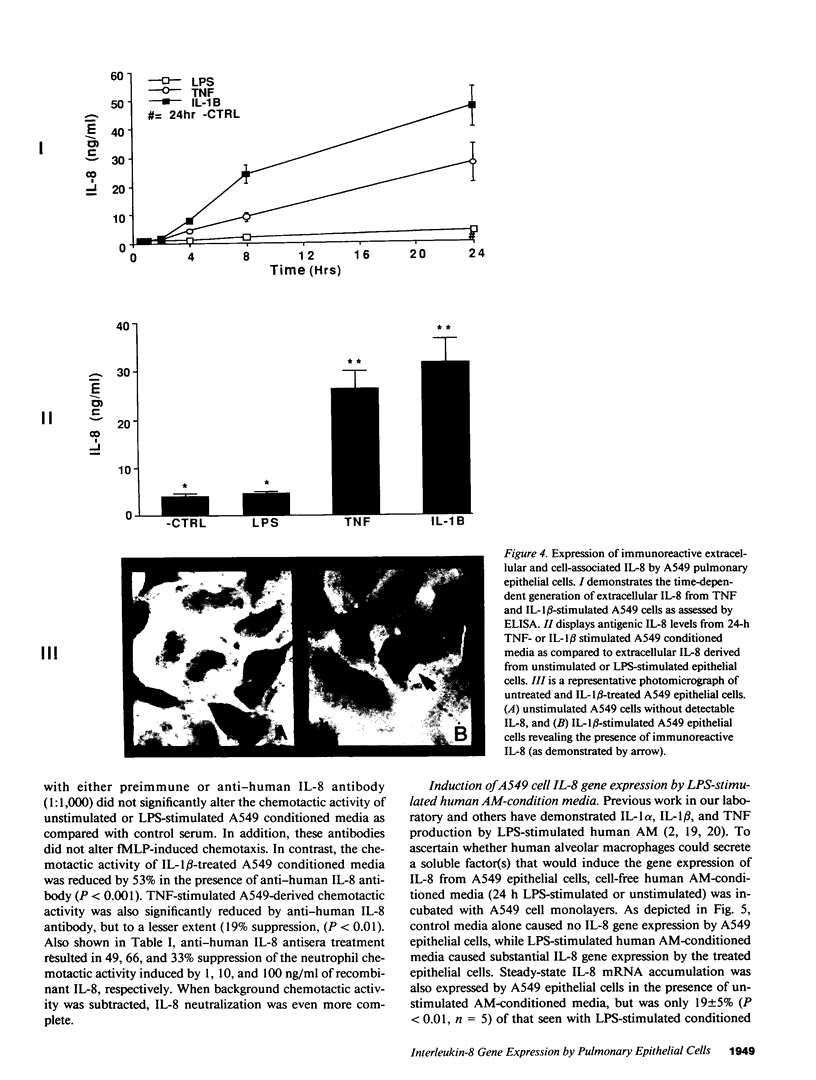
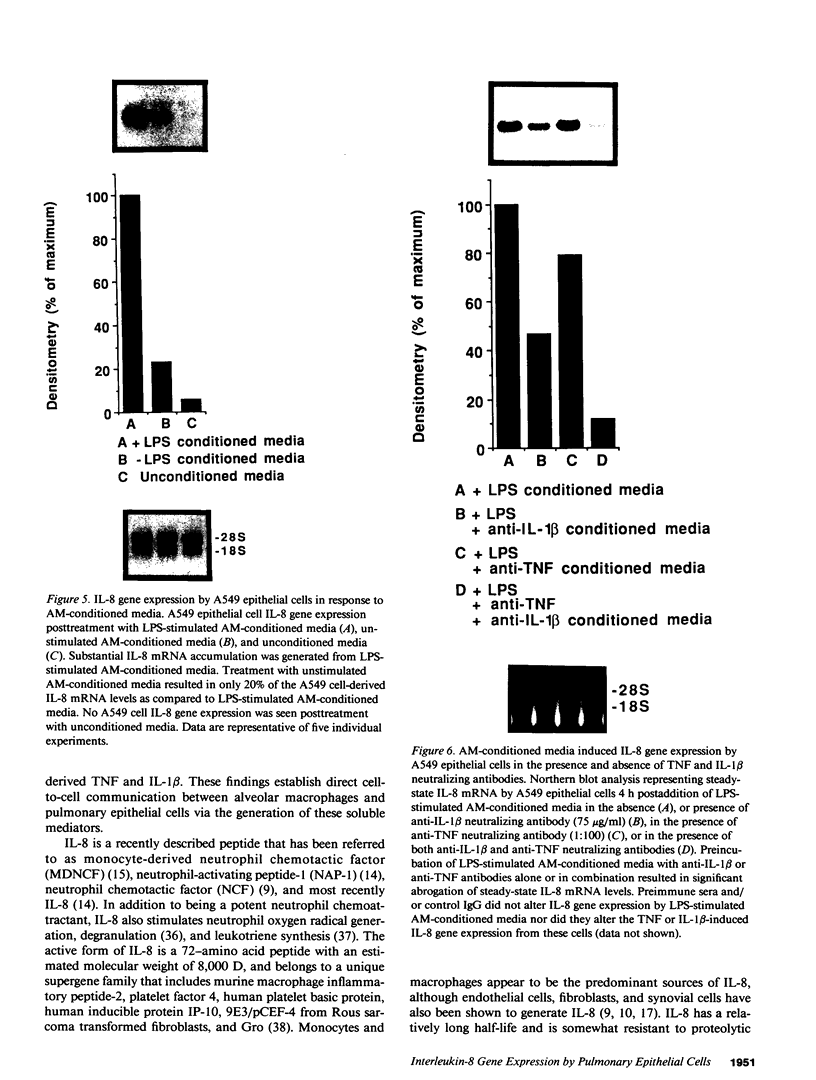
Abstract
Cellular constituents of the alveolar-capillary wall may be key participants in the recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to the lung through the generation of the novel neutrophil chemotactic peptide interleukin-8 (IL-8). This interaction appears to occur via the ability of human alveolar macrophage (AM)-derived monokines, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and interleukin-1 (IL-1) to induce gene expression of IL-8 from pulmonary type II-like epithelial cells (A549). Northern blot analysis demonstrated that steady-state IL-8 mRNA expression, by either TNF- or IL-1 beta-treated A549 cells, occurred in both a dose- and time-dependent fashion. Similarly, extracellular antigenic IL-8, as assessed by specific ELISA, was expressed from TNF- or IL-1 beta-stimulated epithelial cells in a time-dependent fashion with maximal IL-8 antigen detected at 24 h poststimulation. Immunohistochemical staining utilizing rabbit anti-human IL-8 antibody identified immunoreactive, cell-associated IL-8 antigen as early as 8 h post-TNF or IL-1 beta stimulation. A549-generated neutrophil chemotactic bioactivity paralleled IL-8 steady-state mRNA levels. Signal specificity was demonstrated in this system as IL-8 mRNA or protein expression by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated A549 cells was not different from unstimulated cells. Although LPS did not serve as a direct stimulus for the production of IL-8 by type II-like epithelial cells, the condition media from LPS-challenged AM induced a significant expression of IL-8 mRNA by the A549 cells. 24-h conditioned media from LPS-treated cells was as potent as either IL-1 beta or TNF in generating steady-state IL-8 mRNA by A549 cells. Preincubation of LPS-treated AM-conditioned media with anti-human TNF or IL-1 beta neutralizing antibodies resulted in significant abrogation of IL-8 gene expression by A549 pulmonary epithelial cells. These findings demonstrate potential cell-to-cell communication circuits that may be important between AMs and pulmonary epithelial cells during the recruitment phase of acute lung inflammation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayars G. H., Altman L. C., Rosen H., Doyle T. The injurious effect of neutrophils on pneumocytes in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jun;129(6):964–973. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.6.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon K. B., Westwick J., Camp R. D. Potent and specific inhibition of IL-8-, IL-1 alpha- and IL-1 beta-induced in vitro human lymphocyte migration by calcium channel antagonists. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 30;165(1):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauncey J. B., Simon R. H., Peters-Golden M. Rat alveolar macrophages synthesize leukotriene B4 and 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid from alveolar epithelial cell-derived arachidonic acid. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):928–935. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Wikner N. E., Doherty D. E., Norris D. A. Cryptic chemotactic activity of fibronectin for human monocytes resides in the 120-kDa fibroblastic cell-binding fragment. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):12115–12123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E. C., Moxley M. A., Longmore W. Synthesis of collagenous proteins by pulmonary type II epithelial cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 May;135(5):1118–1123. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.5.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin A. B., Stewart P. A. Differential permeability of endothelial and epithelial barriers to albumin flux. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Dec;47(6):1315–1324. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.6.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. A., Rose A. H., Musk A. W., Robinson B. W. Neutrophil chemotactic factor release and neutrophil alveolitis in asbestos-exposed individuals. Chest. 1988 Sep;94(3):521–525. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Fales H. M., Crystal R. G. Human alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor for neutrophils. Stimuli and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):473–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI109878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Garrett K. C., Richerson H. B., Fantone J. C., Ward P. A., Rennard S. I., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Pathogenesis of the granulomatous lung diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Sep;130(3):476–496. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.3.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas E., Sargent T. D., Dawid I. B. Epidermal keratin gene expressed in embryos of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5413–5417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. G., Holland J. F., Foureman G. L., Bend J. R., Fouts J. R. Xenobiotic metabolism in Clara cells and alveolar type II cells isolated from lungs of rats treated with beta-naphthoflavone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 May;225(2):316–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama S., Rennard S. I., Shoji S., Romberger D., Linder J., Ertl R., Robbins R. A. Bronchial epithelial cells release chemoattractant activity for monocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):L130–L136. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.2.L130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskin D. L., Kimura T., Sakakibara S., Riley D. J., Berg R. A. Chemotactic activity of collagen-like polypeptides for human peripheral blood neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 Mar;39(3):255–266. doi: 10.1002/jlb.39.3.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M., Smith B., Szakal A., Nelson-Rees W., Todaro G. A continuous tumor-cell line from a human lung carcinoma with properties of type II alveolar epithelial cells. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):62–70. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. R., Altman L. C., Albert R. K., Henderson W. R. Leukotriene B4 production by the human alveolar macrophage: a potential mechanism for amplifying inflammation in the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jan;129(1):106–111. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Morishita K., Yoshimura T., Lavu S., Kobayashi Y., Lew W., Appella E., Kung H. F., Leonard E. J., Oppenheim J. J. Molecular cloning of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor (MDNCF) and the induction of MDNCF mRNA by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1883–1893. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill W. W., Naegel G. P., Matthay R. A., Reynolds H. Y. Alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor: kinetics of in vitro production and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):268–276. doi: 10.1172/JCI109668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornex J. F., Martinet Y., Yamauchi K., Bitterman P. B., Grotendorst G. R., Chytil-Weir A., Martin G. R., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous expression of the c-sis gene and release of a platelet-derived growth factorlike molecule by human alveolar macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):61–66. doi: 10.1172/JCI112574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons P. E., Fowler A. A., Hyers T. M., Henson P. M. Chemotactic activity in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):490–493. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peveri P., Walz A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1547–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney S. A. The surfactant system and lung phospholipid biochemistry. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):439–460. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Farin F. M., Striker G. E., Fisher A. B. Granular pneumocytes in primary culture secrete several major components of the extracellular matrix. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2148–2155. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M. The monocyte-derived neutrophil activating peptide (NAP/interleukin 8) stimulates human neutrophil arachidonate-5-lipoxygenase, but not the release of cellular arachidonate. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):847–863. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Hinek A., Griffin G. L., Pipoly D. J., Crouch E. C., Mecham R. P. Neutrophils show chemotaxis to type IV collagen and its 7S domain and contain a 67 kD type IV collagen binding protein with lectin properties. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):479–487. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.6.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. H., DeHart P. D., Todd R. F., 3rd Neutrophil-induced injury of rat pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1375–1386. doi: 10.1172/JCI112724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Showell H. J., Remick D. G., Phan S. H., Ward P. A., Marks R. M. Endothelial cell gene expression of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by TNF-alpha, LPS, and IL-1 beta. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1467–1469. doi: 10.1126/science.2648570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Phan S. H., Showell H. J., Remick D. G., Lynch J. P., Genord M., Raiford C., Eskandari M., Marks R. M., Kunkel S. L. Monokine-induced neutrophil chemotactic factor gene expression in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10621–10626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Remick D. G., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Genord M., Raiford C., Spengler R., Kunkel S. L. Differential regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human alveolar macrophages and peripheral blood monocytes: a cellular and molecular analysis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;1(1):57–63. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Remick D. G., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Spengler R. N., Kunkel S. L. Interleukin-2-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) gene expression in human alveolar macrophages and blood monocytes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Feb;139(2):335–342. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.2.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Eidlen D. M., Mason R. J. Pulmonary alveolar type II epithelial cells synthesize and secrete proteins of the classical and alternative complement pathways. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1419–1426. doi: 10.1172/JCI113472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Miyasaka H., Ota H., Yamakawa Y., Tagawa M., Kuramoto A., Mizuno S. Purification and partial primary sequence of a chemotactic protein for polymorphonuclear leukocytes derived from human lung giant cell carcinoma LU65C cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1895–1901. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., DiFlorio R., Hujanen E. S., Lyall R. M., Liotta L. A., Thorgeirsson U., Siegal G. P., Schiffmann E. Laminin promotes rabbit neutrophil motility and attachment. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1180–1186. doi: 10.1172/JCI112419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. L., Lewis G. P., Westwick J. Neutrophil stimulation by recombinant cytokines and a factor produced by IL-1-treated human synovial cell cultures. Immunology. 1988 Dec;65(4):567–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland J. E., Davis W. B., Holter J. F., Mohammed J. R., Dorinsky P. M., Gadek J. E. Lung neutrophils in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clinical and pathophysiologic significance. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Feb;133(2):218–225. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpe S. D., Cerami A. Macrophage inflammatory proteins 1 and 2: members of a novel superfamily of cytokines. FASEB J. 1989 Dec;3(14):2565–2573. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.14.2687068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocytes: partial characterization and separation from interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







