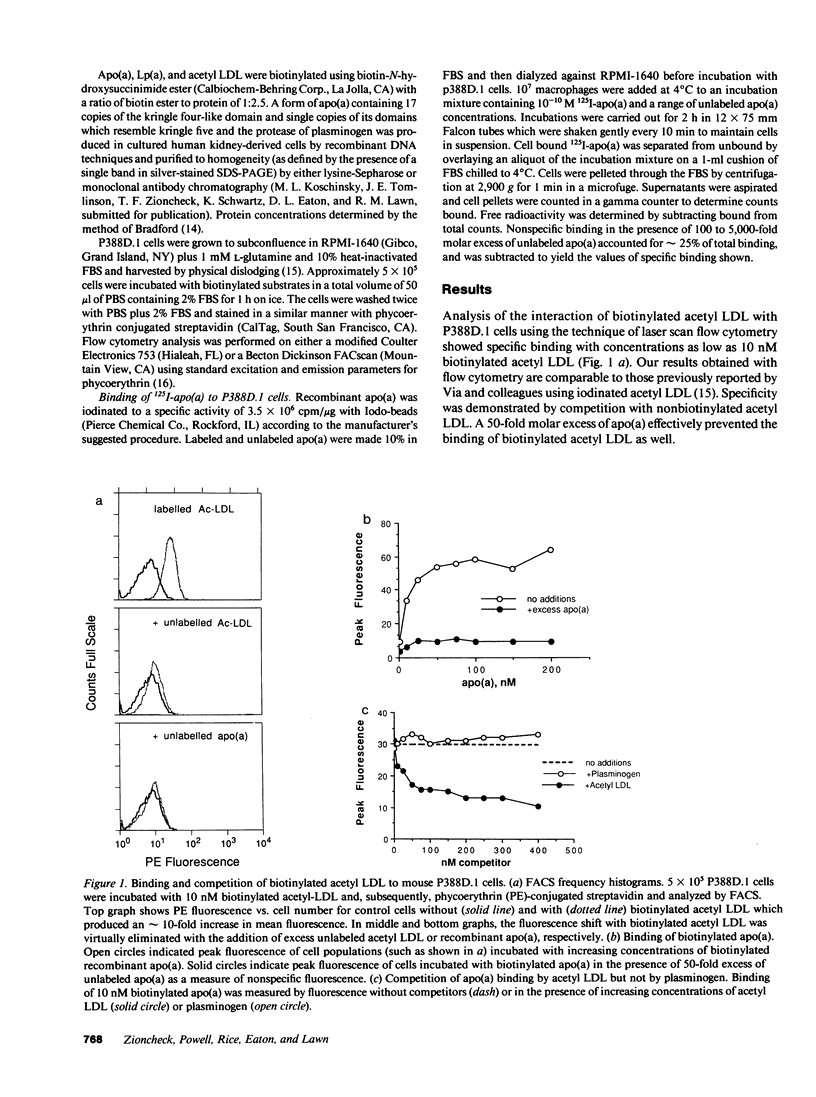
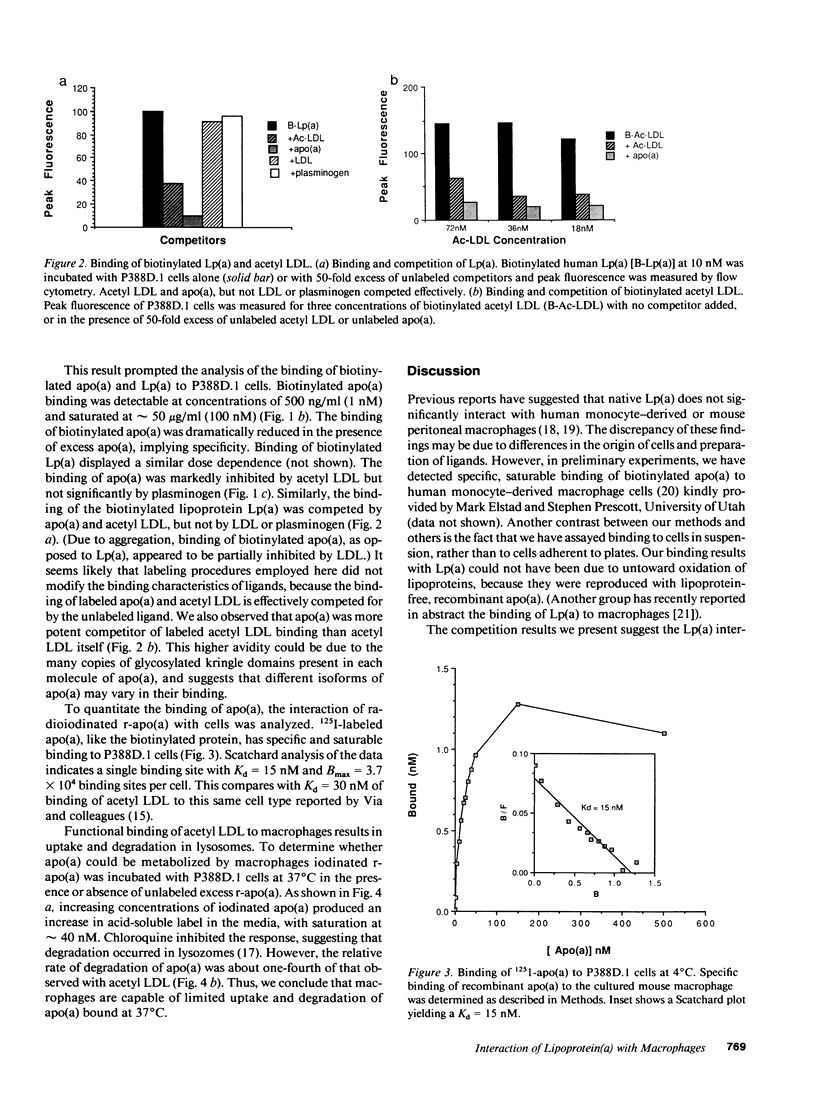
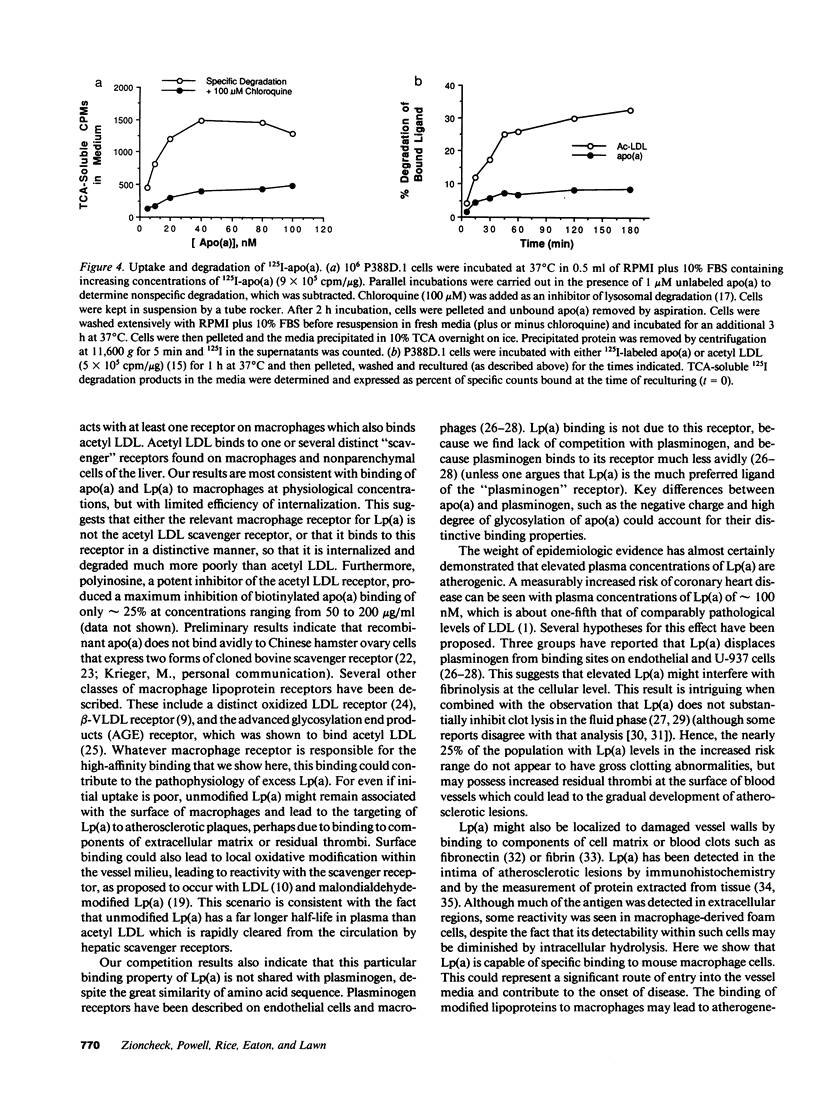
Abstract
Elevated plasma levels of lipoprotein(a), Lp(a), represent a major, inherited risk factor for coronary heart disease, although the mechanism of its action remains unknown. Lp(a) is distinguished from the related LDL particle by the addition of apolipoprotein(a), apo(a). The presence of this large glycoprotein is likely to affect the binding of the particle to the LDL receptor and/or other receptors which may contribute to the atherogenic potential of Lp(a). Here we demonstrate the binding to macrophages of Lp(a) and pure recombinant apo(a) protein, via a specific, high-affinity receptor. This binding could lead to foam cell formation and the localization of Lp(a) to atherosclerotic plaques.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushing G. L., Gaubatz J. W., Nava M. L., Burdick B. J., Bocan T. M., Guyton J. R., Weilbaecher D., DeBakey M. E., Lawrie G. M., Morrisett J. D. Quantitation and localization of apolipoproteins [a] and B in coronary artery bypass vein grafts resected at re-operation. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Sep-Oct;9(5):593–603. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.5.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diez E., Fernandez B., Martin C., Zamorano P., Schuller A. Acetylated low density lipoproteins promote the release and metabolism of arachidonic acid by murine macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):461–467. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92621-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Fless G. M., Kohr W. J., McLean J. W., Xu Q. T., Miller C. G., Lawn R. M., Scanu A. M. Partial amino acid sequence of apolipoprotein(a) shows that it is homologous to plasminogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3224–3228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelberg J. M., Gonzalez-Gronow M., Pizzo S. V. Lipoprotein a inhibits streptokinase-mediated activation of human plasminogen. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2370–2374. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elstad M. R., Stafforini D. M., McIntyre T. M., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase increases during macrophage differentiation. A novel mechanism that regulates accumulation of platelet-activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8467–8470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., Rolih C. A., Scanu A. M. Heterogeneity of human plasma lipoprotein (a). Isolation and characterization of the lipoprotein subspecies and their apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11470–11478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., ZumMallen M. E., Scanu A. M. Physicochemical properties of apolipoprotein(a) and lipoprotein(a-) derived from the dissociation of human plasma lipoprotein (a). J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8712–8718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., Van Lenten B. J., Warden C., Haberland M. E., Edwards P. A. Macrophage lipoprotein receptors. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1988;9:135–149. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1988.supplement_9.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish D., Azrolan N., Breslow J. L. Plasma Ip(a) concentration is inversely correlated with the ratio of Kringle IV/Kringle V encoding domains in the apo(a) gene. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):2021–2027. doi: 10.1172/JCI114395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Inhibition of proteolytic degradation of low density lipoprotein in human fibroblasts by chloroquine, concanavalin A, and Triton WR 1339. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7854–7862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Gronow M., Edelberg J. M., Pizzo S. V. Further characterization of the cellular plasminogen binding site: evidence that plasminogen 2 and lipoprotein a compete for the same site. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2374–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Gavish D., Breslow J. L., Nachman R. L. Lipoprotein(a) modulation of endothelial cell surface fibrinolysis and its potential role in atherosclerosis. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):303–305. doi: 10.1038/339303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Gordon B. R., Parker T. S. Plasmin catalyzes binding of lipoprotein (a) to immobilized fibrinogen and fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3847–3851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Britten M. L., Manis G. S., Rainwater D. L. Apolipoprotein(a) (Apo(a)) glycoprotein isoforms result from size differences in Apo(a) mRNA in baboons. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6013–6016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Freeman M., Rohrer L., Zabrecky J., Matsudaira P., Krieger M. Type I macrophage scavenger receptor contains alpha-helical and collagen-like coiled coils. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):531–535. doi: 10.1038/343531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koschinsky M. L., Beisiegel U., Henne-Bruns D., Eaton D. L., Lawn R. M. Apolipoprotein(a) size heterogeneity is related to variable number of repeat sequences in its mRNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 23;29(3):640–644. doi: 10.1021/bi00455a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H., Armstrong V. W., Niehaus M., Hilschmann N., Seidel D. Structural relationship of an apolipoprotein (a) phenotype (570 kDa) to plasminogen: homologous kringle domains are linked by carbohydrate-rich regions. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Dec;368(12):1533–1544. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krempler F., Kostner G. M., Roscher A., Bolzano K., Sandhofer F. The interaction of human apoB-containing lipoproteins with mouse peritoneal macrophages: a comparison of Lp(a) with LDL. J Lipid Res. 1984 Mar;25(3):283–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loscalzo J., Weinfeld M., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M. Lipoprotein(a), fibrin binding, and plasminogen activation. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Mar-Apr;10(2):240–245. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.2.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Tomlinson J. E., Kuang W. J., Eaton D. L., Chen E. Y., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Lawn R. M. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):132–137. doi: 10.1038/330132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Fless G. M., Levin E. G., Scanu A. M., Plow E. F. A potential basis for the thrombotic risks associated with lipoprotein(a). Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):301–303. doi: 10.1038/339301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Mark D., Banda M. J., Werb Z. Wound macrophages express TGF-alpha and other growth factors in vivo: analysis by mRNA phenotyping. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):708–712. doi: 10.1126/science.3041594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath M., Niendorf A., Reblin T., Dietel M., Krebber H. J., Beisiegel U. Detection and quantification of lipoprotein(a) in the arterial wall of 107 coronary bypass patients. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Sep-Oct;9(5):579–592. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer L., Freeman M., Kodama T., Penman M., Krieger M. Coiled-coil fibrous domains mediate ligand binding by macrophage scavenger receptor type II. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):570–572. doi: 10.1038/343570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Jauhiainen M., Zardi L., Vaheri A., Ehnholm C. Lipoprotein(a) binds to fibronectin and has serine proteinase activity capable of cleaving it. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4035–4040. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Fless G. M. Lipoprotein (a). Heterogeneity and biological relevance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1709–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI114625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow C. P., Parthasarathy S., Steinberg D. A macrophage receptor that recognizes oxidized low density lipoprotein but not acetylated low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2599–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Via D. P., Plant A. L., Craig I. F., Gotto A. M., Jr, Smith L. C. Metabolism of normal and modified low-density lipoproteins by macrophage cell lines of murine and human origin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 6;833(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassara H., Brownlee M., Cerami A. Novel macrophage receptor for glucose-modified proteins is distinct from previously described scavenger receptors. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1301–1309. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N., Smith K. M., Schwartz S. M., Gordon D. Localization of tissue factor in the normal vessel wall and in the atherosclerotic plaque. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woronicz J. D., Rice G. C. Simple modification of a commercial flow cytometer to triple laser excitation. Simultaneous five-color fluorescence detection. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jun 21;120(2):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


