Abstract
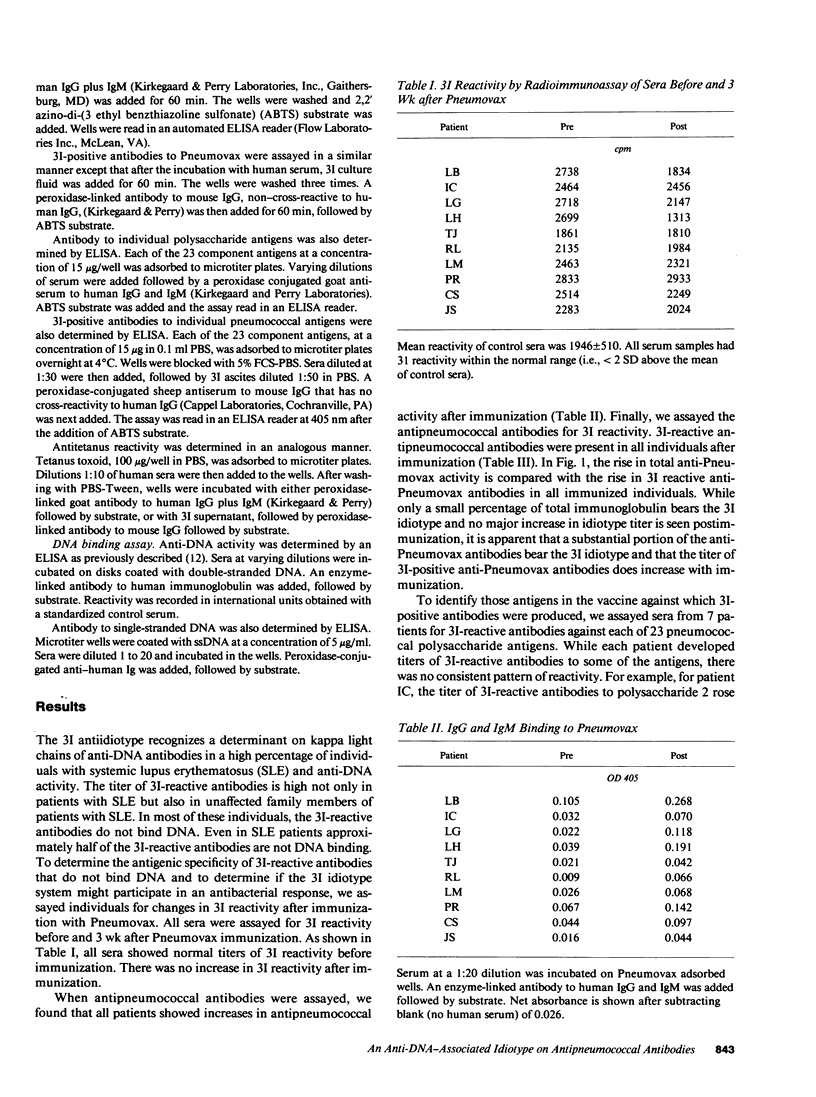
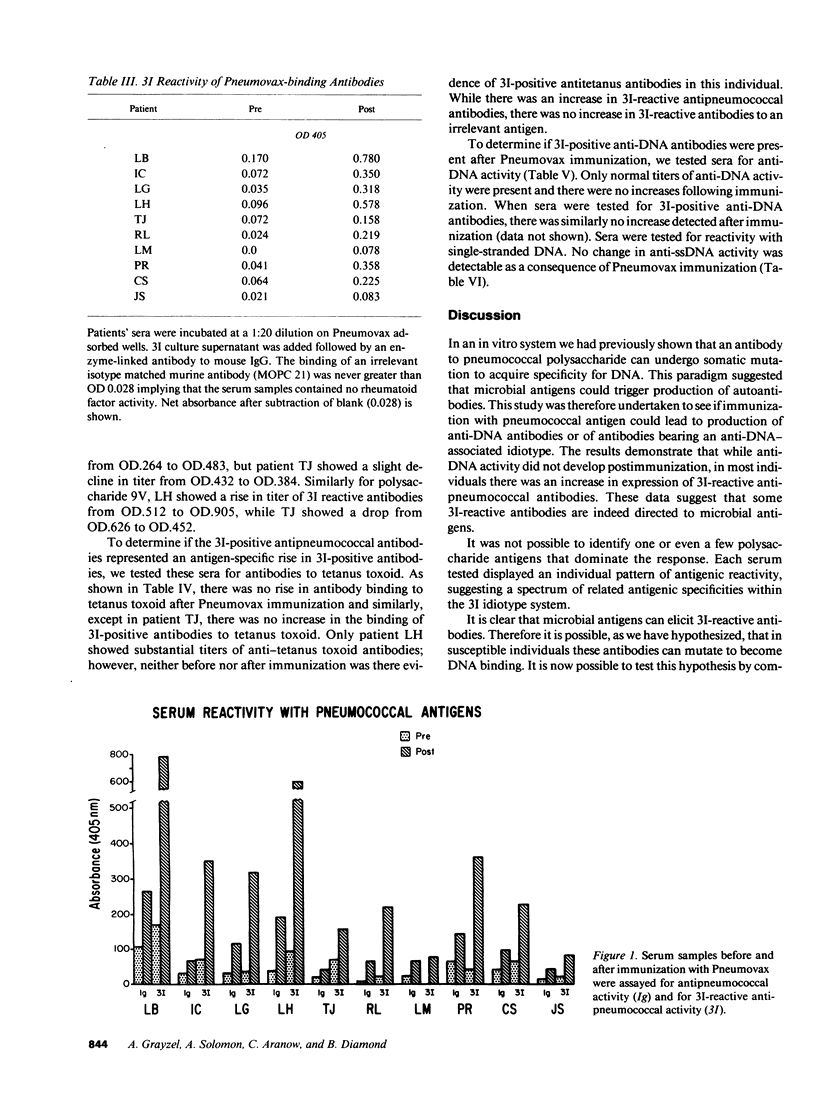
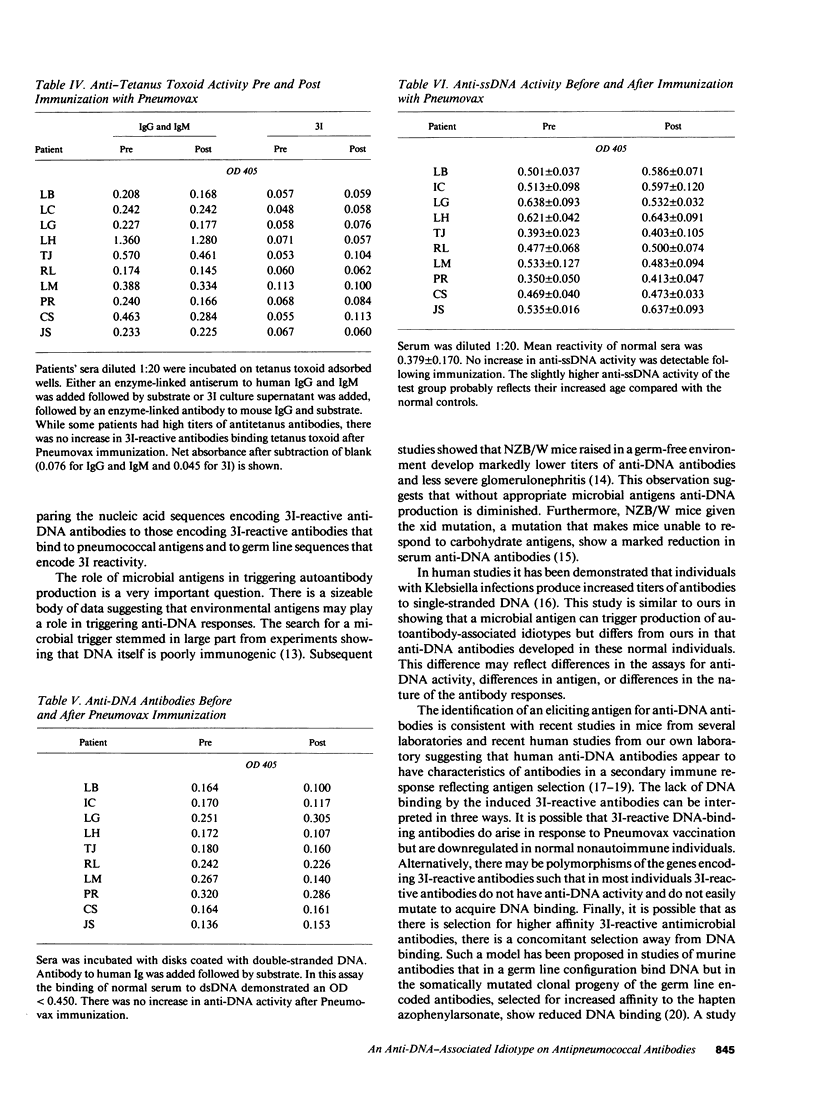
There is evidence in both murine and human lupus that the production of anti-DNA antibodies may be triggered by environmental antigens. To explore this further, we studied the serum of 10 nonautoimmune individuals immunized with a polyvalent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. All 10 patients showed a rise in the titer of antipneumococcal antibodies bearing an anti-DNA-associated idiotype. The antipneumococcal response was specific as no idiotypic antitetanus antibodies were detected. Furthermore, no anti-DNA antibodies were present in postvaccination sera. The molecular analysis of antipneumococcal and anti-DNA antibodies bearing a common idiotype will help elucidate how foreign antigen might lead to the production of anti-DNA antibodies in susceptible individuals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behar S. M., Scharff M. D. Somatic diversification of the S107 (T15) VH11 germ-line gene that encodes the heavy-chain variable region of antibodies to double-stranded DNA in (NZB x NZW)F1 mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3970–3974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll P., Stafford D., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Murine monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibodies bind to endogenous bacteria. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1086–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson A., Preud'homme J. L., Solomon A., Chang M. D., Beede S., Diamond B. Idiotypic analysis of myeloma proteins: anti-DNA activity of monoclonal immunoglobulins bearing an SLE idiotype is more common in IgG than IgM antibodies. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1515–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson A., Smith A., Katz J., Preud'Homme J. L., Solomon A., Diamond B. A cross-reactive idiotype on anti-DNA antibodies defines a H chain determinant present almost exclusively on IgG antibodies. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation of the T15 heavy chain gives rise to an antibody with autoantibody specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5841–5844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D., Hochberg M., Pumphrey J., Rudikoff S. Monoclonal antibodies to DNA and RNA from NZB/NZW F1 mice: antigenic specificities and NH2 terminal amino acid sequences. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):489–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A., Greenberg M., Diamond B., Grayzel A. I. Suppression of anti-DNA antibody synthesis in vitro by a cross-reactive antiidiotypic antibody. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):997–1000. doi: 10.1172/JCI112912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern R., Davidson A., Lazo A., Solomon G., Lahita R., Diamond B. Familial systemic lupus erythematosus. Presence of a cross-reactive idiotype in healthy family members. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):731–736. doi: 10.1172/JCI112028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Nickerson K. G., Liao J., Grossbard L., Osserman E. F., Glickman E., Chess L., Robbins J. B., Schneerson R., Yang Y. H. A human monoclonal macroglobulin with specificity for alpha(2----8)-linked poly-N-acetyl neuraminic acid, the capsular polysaccharide of group B meningococci and Escherichia coli K1, which crossreacts with polynucleotides and with denatured DNA. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):642–654. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofler R., Noonan D. J., Levy D. E., Wilson M. C., Møller N. P., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Genetic elements used for a murine lupus anti-DNA autoantibody are closely related to those for antibodies to exogenous antigens. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):805–815. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackworth-Young C., Sabbaga J., Schwartz R. S. Idiotypic markers of polyclonal B cell activation. Public idiotypes shared by monoclonal antibodies derived from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus or leprosy. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):572–581. doi: 10.1172/JCI112849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naparstek Y., André-Schwartz J., Manser T., Wysocki L. J., Breitman L., Stollar B. D., Gefter M., Schwartz R. S. A single germline VH gene segment of normal A/J mice encodes autoantibodies characteristic of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):614–626. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naparstek Y., Duggan D., Schattner A., Madaio M. P., Goni F., Frangione B., Stollar B. D., Kabat E. A., Schwartz R. S. Immunochemical similarities between monoclonal antibacterial Waldenstrom's macroglobulins and monoclonal anti-DNA lupus autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1525–1538. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M. J., Aucoin A. H., Pisetsky D. S., Weigert M. G. Structure and function of anti-DNA autoantibodies derived from a single autoimmune mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9150–9154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Vilner Y., Coates A. R., Rauch J., Lavie G., Shaul D., Pinkhas J. Monoclonal anti-tuberculosis antibodies react with DNA, and monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibodies react with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Nov;66(2):255–261. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon G., Schiffenbauer J., Keiser H. D., Diamond B. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify shared idiotypes on human antibodies to native DNA from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):850–854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg B. J., Smathers P. A., Frederiksen K., Steinberg A. D. Ability of the xid gene to prevent autoimmunity in (NZB X NZW)F1 mice during the course of their natural history, after polyclonal stimulation, or following immunization with DNA. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):587–597. doi: 10.1172/JCI110651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. Antibodies to DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(1):1–36. doi: 10.3109/10409238609115899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unni K. K., Holley K. E., McDuffie F. C., Titus J. L. Comparative study of NZB mice under germfree and conventional conditions. J Rheumatol. 1975 Mar;2(1):36–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Roiey A., Sela O., Isenberg D. A., Feldman R., Colaco B. C., Kennedy R. C., Shoenfeld Y. The sera of patients with Klebsiella infections contain a common anti-DNA idiotype (16/6) Id and anti-polynucleotide activity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Mar;67(3):507–515. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


