Abstract
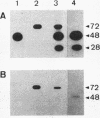
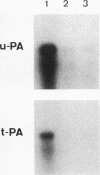
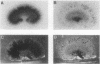
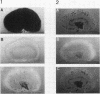
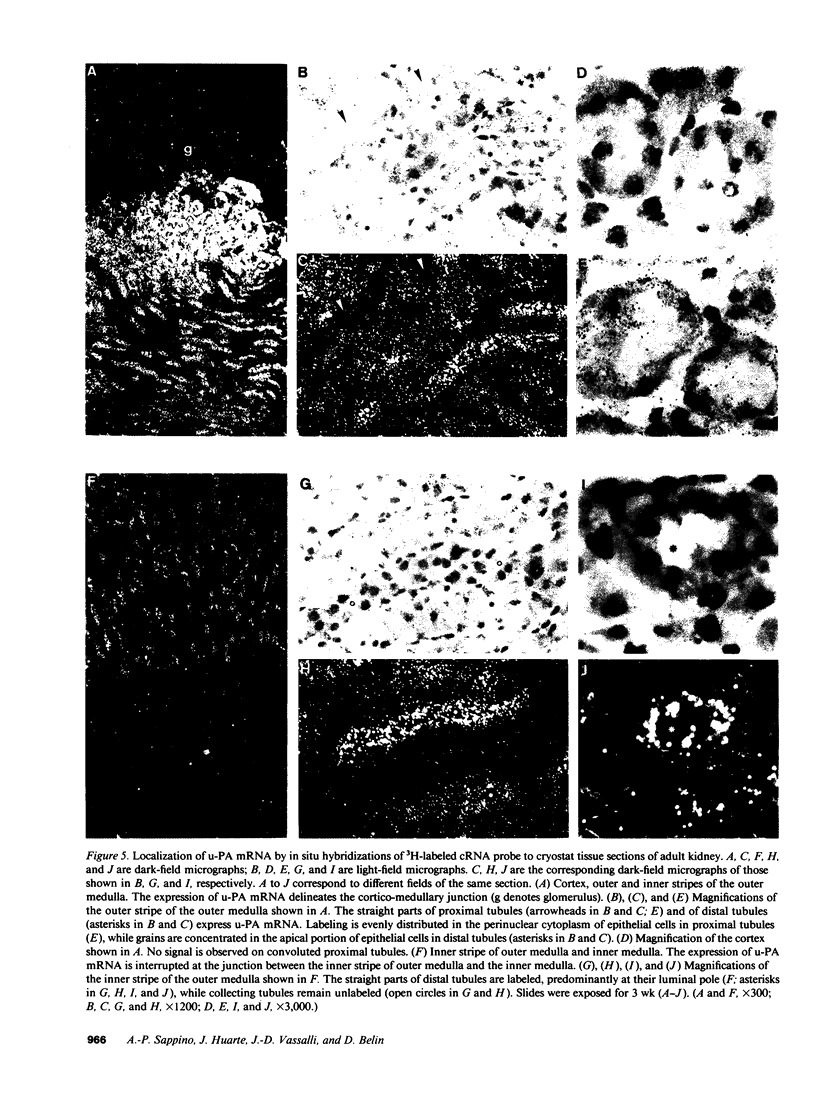
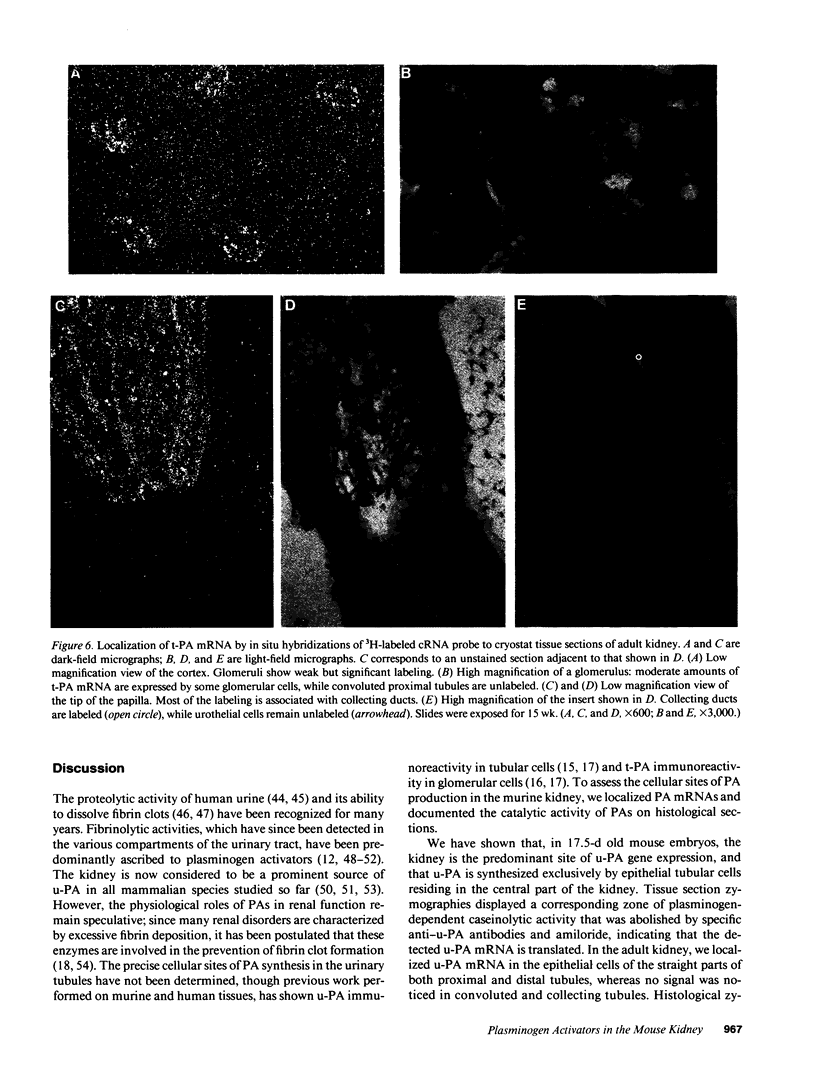
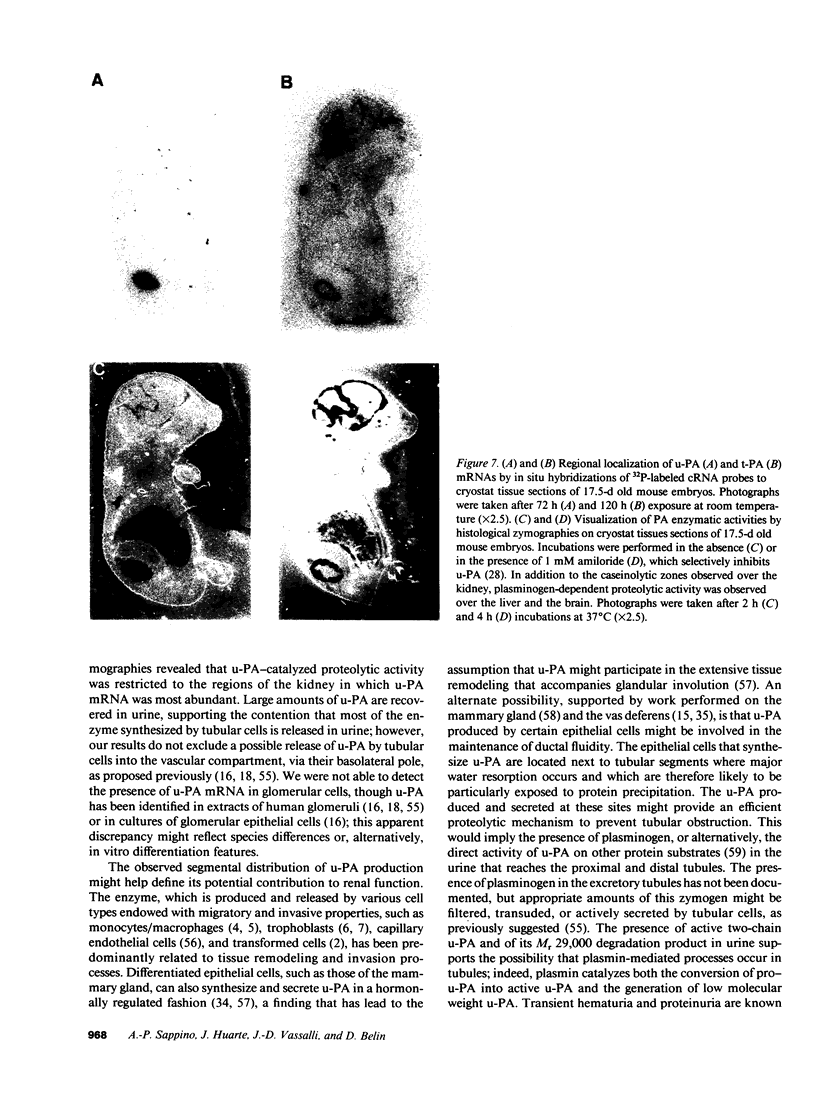
Kidneys have long been recognized as a major source of plasminogen activators (PAs). However, neither the sites of synthesis of the enzymes nor their role in renal function have been elucidated. By the combined use of zymographies on tissue sections and in situ hybridizations, we have explored the cellular distribution of urokinase-type (u-PA) and tissue-type (t-PA) plasminogen activators and of their mRNAs in developing and adult mouse kidneys. In 17.5-d old embryos, renal tubules synthesize u-PA, while S-shaped bodies produce t-PA. In the adult kidney, u-PA is synthesized and released in urine by the epithelial cells lining the straight parts of both proximal and distal tubules. In contrast, t-PA is produced by glomerular cells and by epithelial cells lining the distal part of collecting ducts. The precise segmental distribution of PAs suggests that both enzymes may be implicated in the maintenance of tubular patency, by catalyzing extracellular proteolysis to prevent or circumvent protein precipitation.
Full text
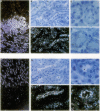
PDF

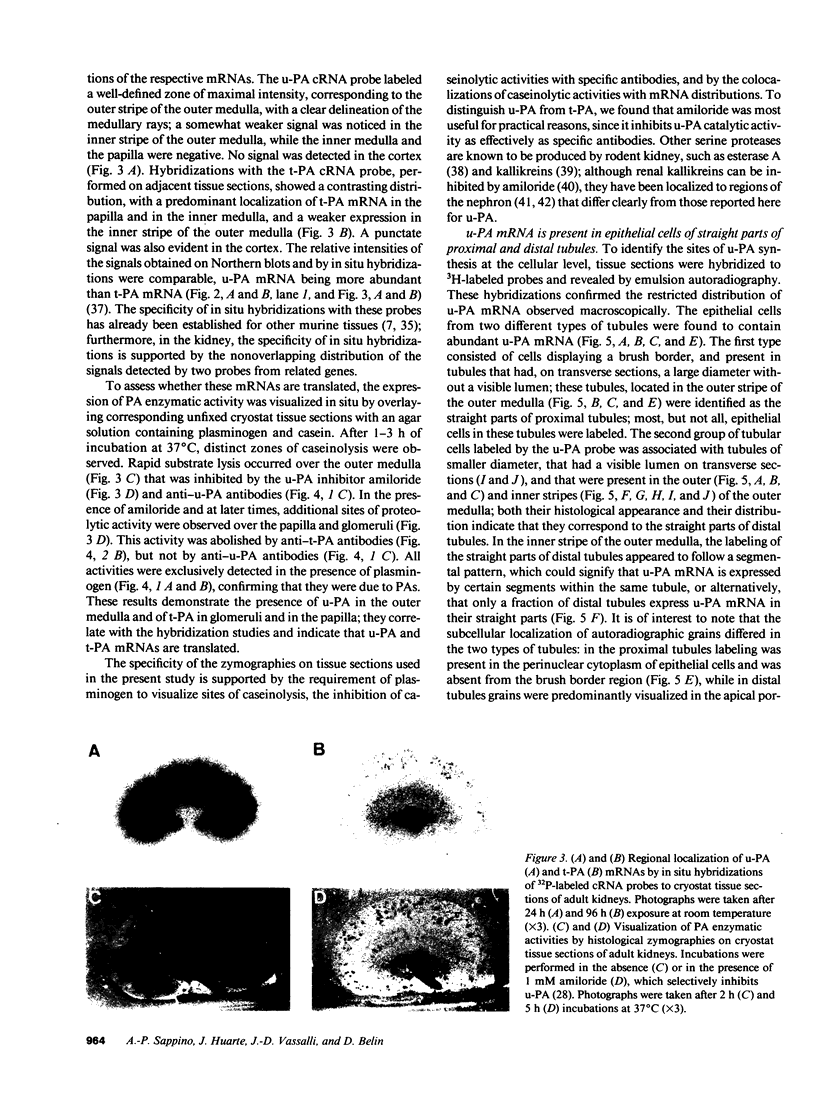



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angles-Cano E., Rondeau E., Delarue F., Hagege J., Sultan Y., Sraer J. D. Identification and cellular localization of plasminogen activators from human glomeruli. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):688–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. B., Low D. A., Simmer R. L., Cunningham D. D. Protease-nexin: a cellular component that links thrombin and plasminogen activator and mediates their binding to cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Godeau F., Vassalli J. D. Tumor promoter PMA stimulates the synthesis and secretion of mouse pro-urokinase in MSV-transformed 3T3 cells: this is mediated by an increase in urokinase mRNA content. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1901–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02065.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Vassalli J. D., Combépine C., Godeau F., Nagamine Y., Reich E., Kocher H. P., Duvoisin R. M. Cloning, nucleotide sequencing and expression of cDNAs encoding mouse urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):225–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergstein J. M., Riley M., Bang N. U. Analysis of the plasminogen activator activity of the human glomerulus. Kidney Int. 1988 Apr;33(4):868–874. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F., Vassalli J. D., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator: proenzyme, receptor, and inhibitors. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):801–804. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busso N., Belin D., Failly-Crépin C., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in a human mammary cell line (HBL-100). Modulation by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9309–9315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busso N., Huarte J., Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. Plasminogen activators in the mouse mammary gland. Decreased expression during lactation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7455–7457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J. Purification and characterization of rat urinary esterase A, a plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4434–4439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa C. D., Caorsi I., Subiabre J., Vío C. P. Immunoreactive kallikrein localization in the rat kidney: an immuno-electron-microscopic study. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Jan;32(1):117–121. doi: 10.1177/32.1.6558105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller P. J., Funder J. W. The cellular physiology of glandular kallikrein. Kidney Int. 1986 May;29(5):953–964. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. I., Schwimmer R., Quigley J. P. Human plasma fibronectin as a substrate for human urokinase. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):529–534. doi: 10.1042/bj2620529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. A., Rehemtulla A., Babins E. M. Species differences in the detection of high molecular weight urinary plasminogen activators. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1986;84(3):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(86)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Bosco D., Sappino A. P., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activator and mouse spermatozoa: urokinase synthesis in the male genital tract and binding of the enzyme to the sperm cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1281–1289. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activator in mouse and rat oocytes: induction during meiotic maturation. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. N., Cherry W. R., Weaver G. W. The origin and characteristics of a pig kidney cell strain, LLC-PK. In Vitro. 1976 Oct;12(10):670–677. doi: 10.1007/BF02797469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielberg V., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L., Danø K. Proenzyme to urokinase-type plasminogen activator in the mouse in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 25;182(2):441–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80350-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen P., Larsson L. I., Nielsen L. S., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Andreasen P. A., Danø K. Human endothelial cells contain one type of plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett. 1984 Mar 12;168(1):33–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper J., Otter M., Rijken D. C., van Berkel T. J. Characterization of the interaction in vivo of tissue-type plasminogen activator with liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18220–18224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LADEHOFF A. A. The content of plasminogen activator in the human urinary tract. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1960;12:136–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Skriver L., Nielsen L. S., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Danø K. Distribution of urokinase-type plasminogen activator immunoreactivity in the mouse. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):894–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecander I., Astedt B. Isolation of a new specific plasminogen activator inhibitor from pregnancy plasma. Br J Haematol. 1986 Feb;62(2):221–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb02925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., van Mourik J. A., Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. Detection of an unusually stable fibrinolytic inhibitor produced by bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOHLER S. R., CELANDER D. R., GUEST M. M. Distribution of urokinase among the common mammals. Am J Physiol. 1958 Jan;192(1):186–190. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.192.1.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Chao J. Amiloride inhibits mammalian renal kallikrein and a kallikrein-like enzyme from toad bladder and skin. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1343–1350. doi: 10.1172/JCI109798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotti K. R., Belin D., Strickland S. The production of distinct forms of plasminogen activator by mouse embryonic cells. Dev Biol. 1982 Mar;90(1):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell D., Johnson J. G., Young I., Holemans R. Localization of plasminogen activator in kidney tissue. Lab Invest. 1966 Jun;15(6):980–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muellbacher W., Maier M., Binder B. R. Regulation of plasminogen activation in isolated perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):F787–F793. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.5.F787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Biegel D., Reich E. Mammary plasminogen activator: correlation with involution, hormonal modulation and comparison between normal and neoplastic tissue. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):929–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Vassalli J. D., Montesano R., Orci L. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is induced in migrating capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2535–2541. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles R. J., Darrow A. L., Strickland S. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA to mouse tissue plasminogen activator mRNA and its expression during F9 teratocarcinoma cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1563–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles R. J., Strickland S. Tissue plasminogen activator mRNA in murine tissues. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Binnema D. J., Los P. Specific fibrinolytic properties of different molecular forms of pro-urokinase from a monkey kidney cell culture. Thromb Res. 1986 Jun 15;42(6):761–768. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90112-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Wijngaards G., Welbergen J. Immunological characterization of plasminogen activator activities in human tissues and body fluids. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Apr;97(4):477–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Holthöfer H. Plasminogen activators during differentiation of the human kidney. Differentiation. 1987;34(2):131–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Zitting A., Vaheri A. Laminin interacts with plasminogen and its tissue-type activator. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jun 25;172(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80866-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Busso N., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Increase of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression in human lung and breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):4043–4046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activators in tissue remodeling and invasion: mRNA localization in mouse ovaries and implanting embryos. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2471–2479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Soffientini A., Cassani G., Blasi F., Assoian R. K. Differentiation-enhanced binding of the amino-terminal fragment of human urokinase plasminogen activator to a specific receptor on U937 monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suenson E., Lützen O., Thorsen S. Initial plasmin-degradation of fibrin as the basis of a positive feed-back mechanism in fibrinolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):513–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD A. S. LOCALIZATION OF FIBRINOLYTIC ACTIVITY IN TISSUES. Br Med Bull. 1964 Sep;20:210–212. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada A., Sakakibara K., Nagase M., Shizume K., Takada Y. Determination of urokinase in the urine of healthy volunteers and patients with renal diseases. Thromb Res. 1986 Dec 15;44(6):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Gordon S., Reich E. Secretion of plasminogen activator by stimulated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):834–850. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Baccino D., Belin D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):86–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Amiloride selectively inhibits the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Dayer J. M., Wohlwend A., Belin D. Concomitant secretion of prourokinase and of a plasminogen activator-specific inhibitor by cultured human monocytes-macrophages. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1653–1668. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Hamilton J., Reich E. Macrophage plasminogen activator: induction by concanavalin A and phorbol myristate acetate. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):695–705. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli P., McCluskey R. T. The pathogenetic role of the coagulation process in glomerular diseases of immunologic origin. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1971;1:47–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J. R. B. The fibrinolytic activity of urine. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Dec;32(6):530–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong W., Chao L., Chao J. Renal kallikrein mRNA localization by in situ hybridization. Kidney Int. 1989 Jun;35(6):1324–1329. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]