Abstract
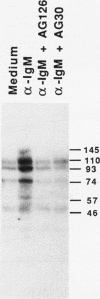
Cross-linking of the surface antigen receptor on B lymphocytes has been demonstrated to lead to activation of phospholipase C (PLC) with subsequent increases in production of inositol phosphates and diacylglycerol. In turn, these second messengers increase cytosolic free calcium [( Ca2+]i) and activate the serine threonine phosphotransferase protein kinase C (PKC). These processes are thought to play a major role in B cell activation and proliferation. However, the mechanism linking the B lymphocyte antigen receptor to phospholipase C remains to be identified. We demonstrate herein that activation of the antigen receptor on human lymphocytes, in addition to activation of PLC, increases tyrosine phosphorylation of specific substrates. Tyrphostins, a new class of tyrosine kinase inhibitors which compete for substrate binding site of specific tyrosine kinases have recently been synthesized. Preincubation of B lymphocytes with two different tyrphostins blocked anti-IgM-induced proliferation, oncogene expression, tyrosine phosphorylation, increases in [Ca2+]i, and production of inositol phosphates. The same inhibitors were without effect on B cell proliferation induced by phorbol esters and cation ionophores which directly activate PKC and increase [Ca2+]i thus bypassing PLC. These findings strongly indicate that tyrphostins do not exhibit significant nonspecific toxicity and suggest that they act proximal to PLC. The ability of the tyrphostins to block increases in [Ca2+]i and inositol phosphate production, after activation of the B cell antigen receptor, indicates that a tyrosine kinase acts as an essential link between the B cell antigen receptor and PLC.
Full text
PDF

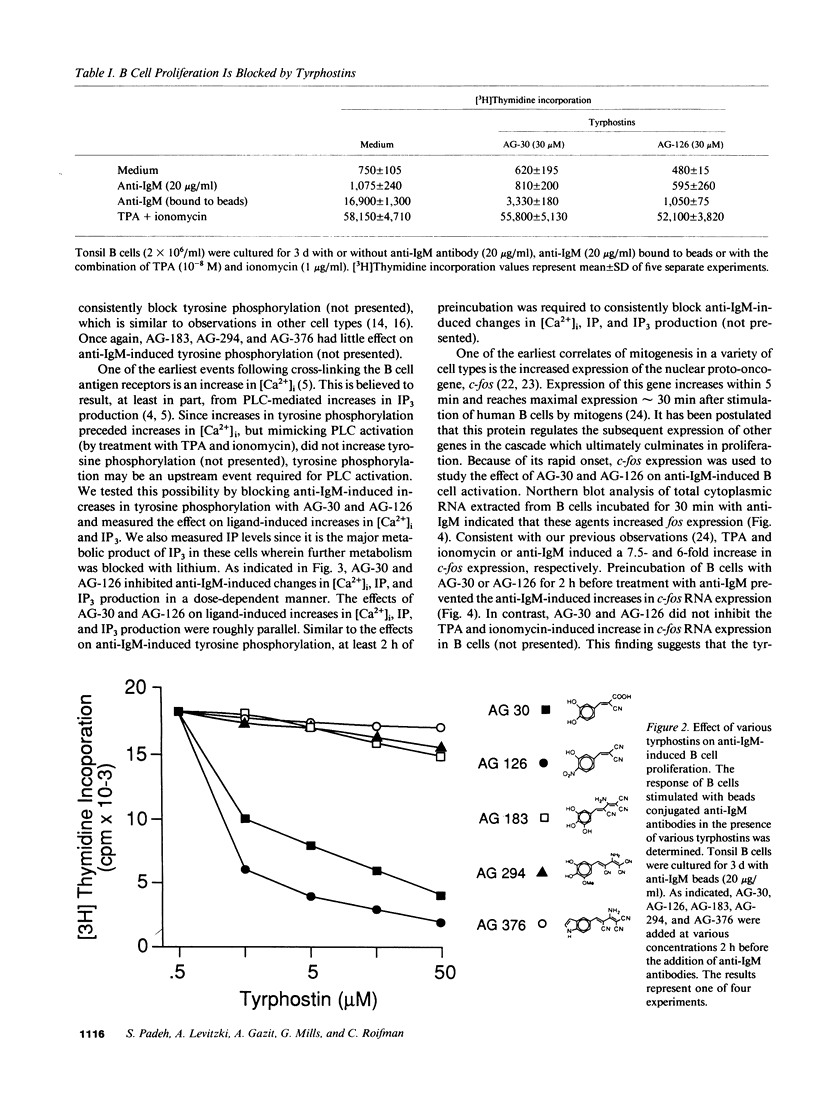
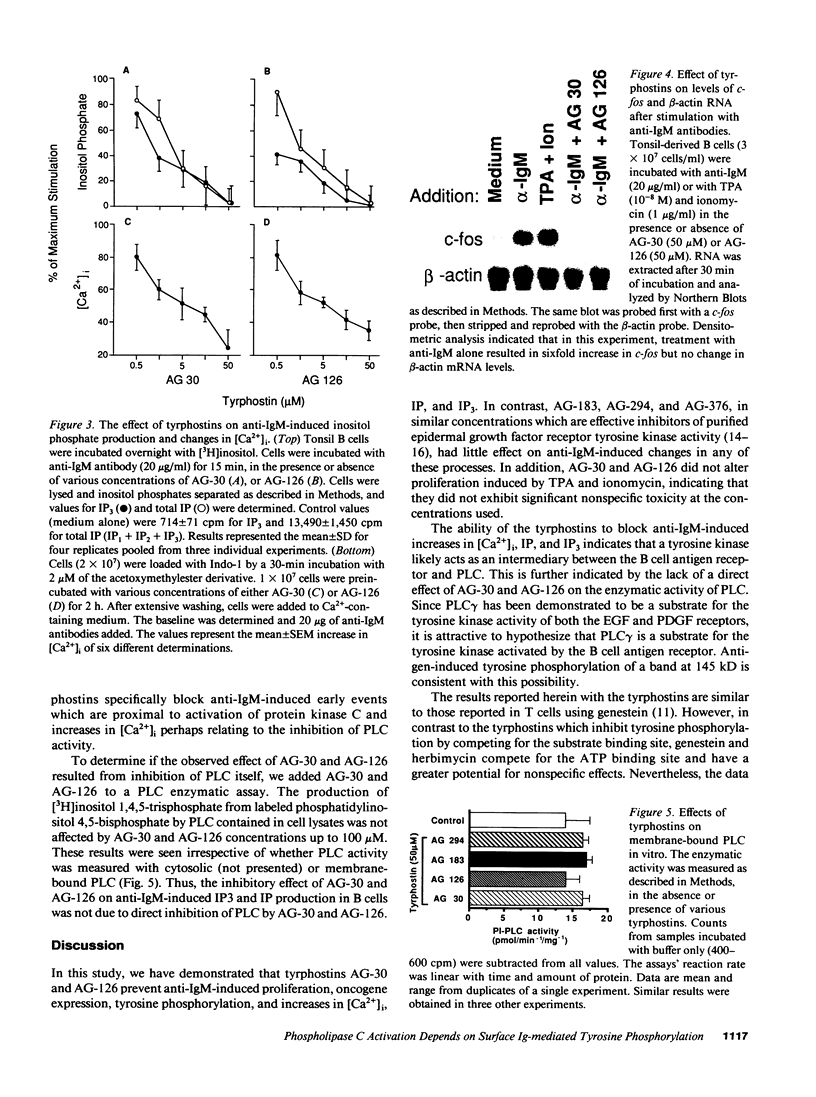

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Heusser C. H., Julius M. H. Abortive activation of B lymphocytes by monoclonal anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3140–3146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is induced in murine B lymphocytes in response to stimulation with anti-immunoglobulin. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2125–2131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit A., Yaish P., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Tyrphostins I: synthesis and biological activity of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1989 Oct;32(10):2344–2352. doi: 10.1021/jm00130a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Law D. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):810–813. doi: 10.1038/345810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani Y., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. The effect of quercetin on the phosphorylation activity of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):583–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackowski S., Rettenmier C. W., Sherr C. J., Rock C. O. A guanine nucleotide-dependent phosphatidylinositol 4,5-diphosphate phospholipase C in cells transformed by the v-fms and v-fes oncogenes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4978–4985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P. J., McConnell F. M., Schieven G. L., Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. The role of class II molecules in human B cell activation. Association with phosphatidyl inositol turnover, protein tyrosine phosphorylation, and proliferation. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3684–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama S., Kubagawa H., Cooper M. D. Activation of human B cells and inhibition of their terminal differentiation by monoclonal anti-mu antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills G. B., May C., McGill M., Fung M., Baker M., Sutherland R., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Interleukin 2 receptor beta is tyrosine phosphorylated. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3561–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nel A. E., Landreth G. E., Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Tung H. E., Galbraith R. M. Enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation in B lymphocytes upon complexing of membrane immunoglobulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):859–866. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roifman C. M., Benedict S. H., Cheung R. K., Gelfand E. W. Induction of human B cell proliferation and differentiation by the combination of phorbol ester and ionomycin. Eur J Immunol. 1987 May;17(5):701–706. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roifman C. M., Hummel D., Martinez-Valdez H., Thorner P., Doherty P. J., Pan S., Cohen F., Cohen A. Depletion of CD8+ cells in human thymic medulla results in selective immune deficiency. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2177–2182. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roifman C. M., Mills G. B., Stewart D., Cheung R. K., Grinstein S., Gelfand E. W. Response of human B cells to different anti-immunoglobulin isotypes: absence of a correlation between early activation events and cell proliferation. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1737–1742. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudich S. M., Winchester R., Mongini P. K. Human B cell activation. Evidence for diverse signals provided by various monoclonal anti-IgM antibodies. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1236–1255. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Yaish P., Chorev M., Gilon C., Braun S., Levitzki A. Inhibition of insulin-dependent lipogenesis and anti-lipolysis by protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1671–1676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splawski J. B., Lipsky P. E. Antigen-induced proliferation and immunoglobulin A secretion by a human-human hybridoma. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1432–1437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaish P., Gazit A., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Blocking of EGF-dependent cell proliferation by EGF receptor kinase inhibitors. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):933–935. doi: 10.1126/science.3263702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]