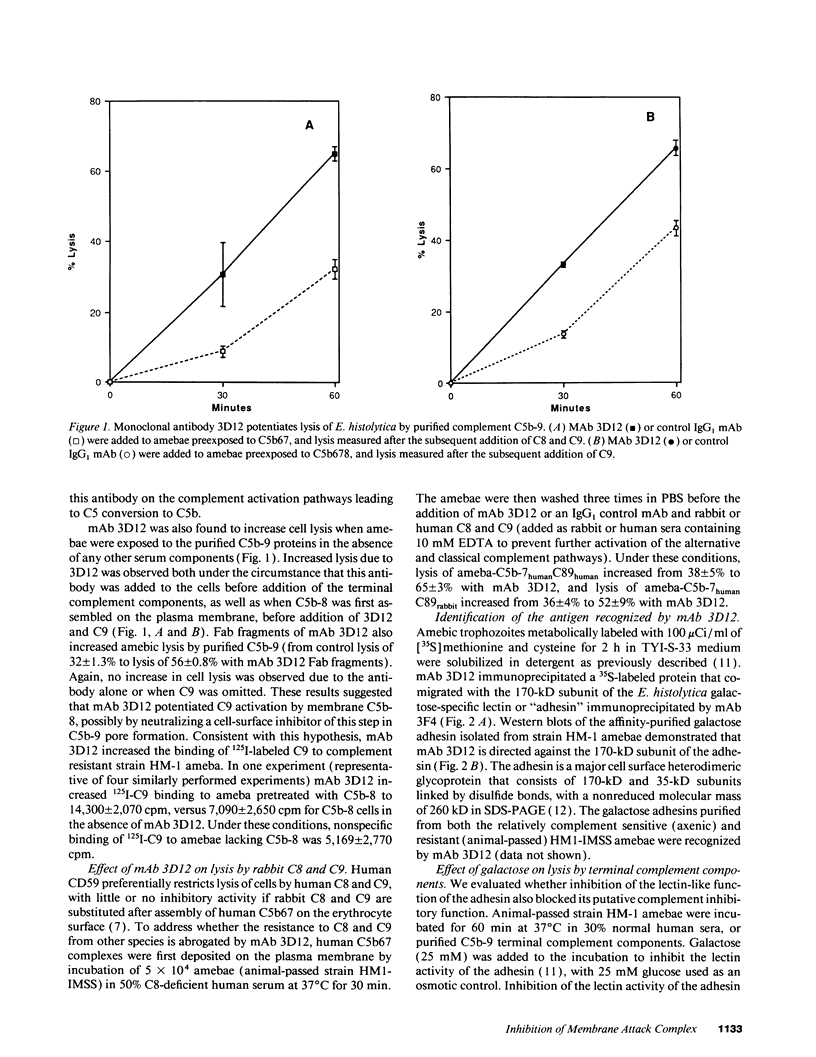
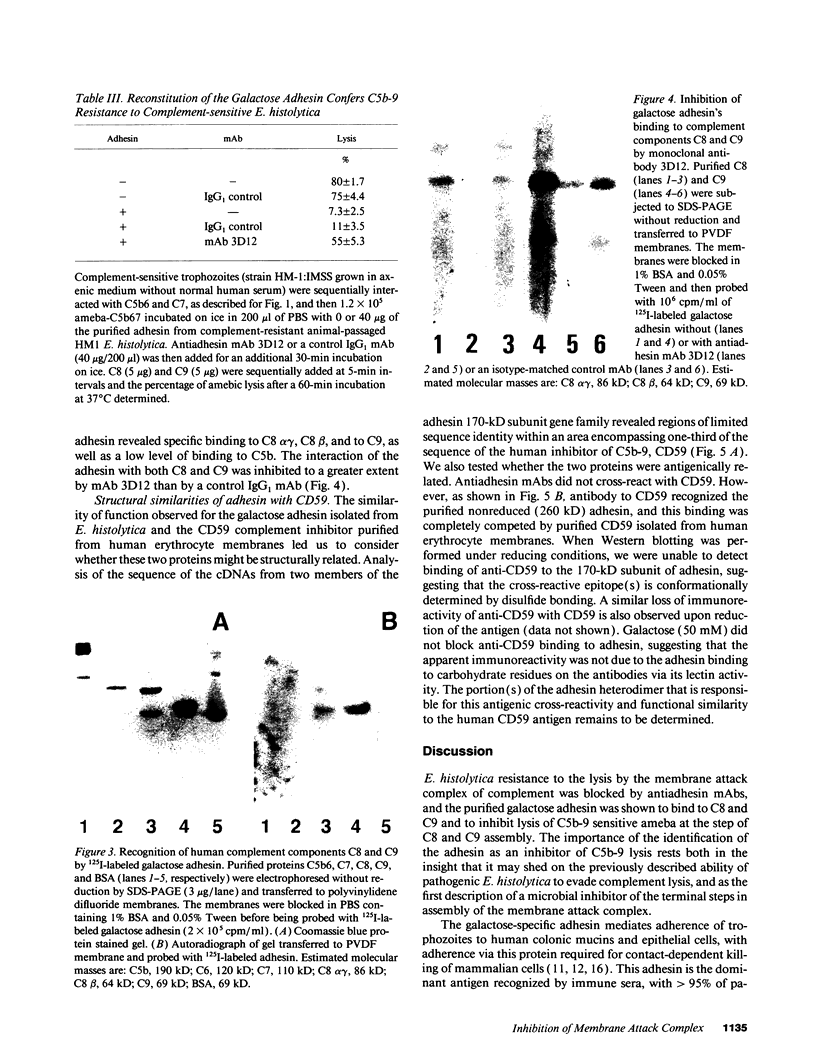
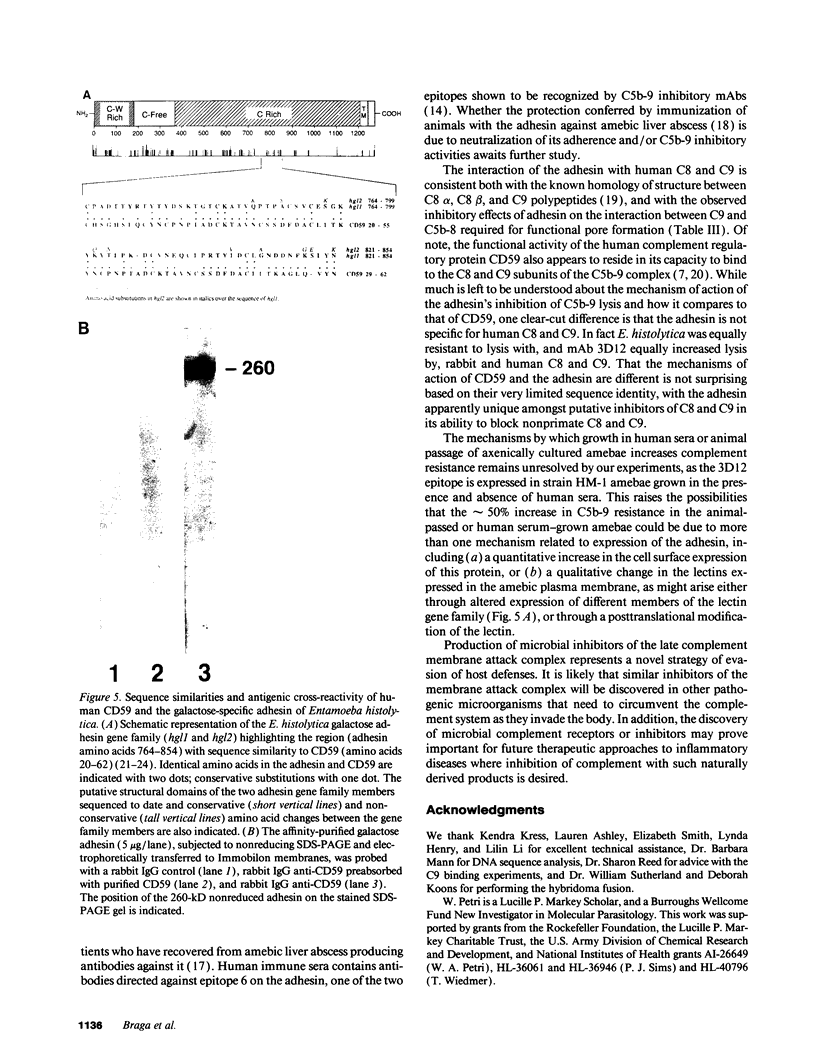
Abstract
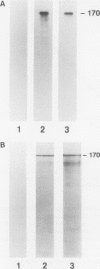
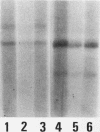
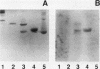
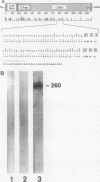
The human complement system is an important early host defense against infection. Entamoeba histolytica activates the complement system but is resistant to killing by complement C5b-9 complexes deposited on the membrane surface. Our aim was to identify components of the amebic plasma membrane that mediate resistance to human complement C5b-9 by screening for neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. A monoclonal antibody was identified that abrogated amebic resistance to C5b-9, and the mAb was shown to recognize the parasite's galactose-specific adhesin. The purified adhesin bound to C8 and C9 and conferred C5b-9 resistance to sensitive ameba upon reconstitution; these activities of the adhesin were inhibited by the antiadhesin mAb. The E. histolytica adhesin shared sequence similarities and antigenic cross-reactivity with CD59, a membrane inhibitor of C5b-9 in human blood cells, suggesting both molecular mimicry and shared complement-inhibitory functions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blakely P., Sargeaunt P. G., Reed S. L. An immunogenic 30-kDa surface antigen of pathogenic clinical isolates of Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):949–954. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderon J., Tovar R. Loss of susceptibility to complement lysis in Entamoeba histolytica HM1 by treatment with human serum. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):467–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R. Complement evasion strategies of microorganisms. Immunol Today. 1991 Sep;12(9):327–331. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90010-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitler C., Mogyoros M., Calef E., Rosenberg I. Lethal recognition between Entamoeba histolytica and the host tissues. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1985;79(5):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(85)90162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haefliger J. A., Peitsch M. C., Jenne D. E., Tschopp J. Structural and functional characterization of complement C8 gamma, a member of the lipocalin protein family. Mol Immunol. 1991 Jan-Feb;28(1-2):123–131. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamelmann C., Foerster B., Burchard G. D., Horstmann R. D. Lysis of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica by human complement: methodological analysis. Parasite Immunol. 1992 Jan;14(1):23–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1992.tb00003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann B. J., Petri W. A., Jr Cell surface proteins of Entamoeba histolytica. Parasitol Today. 1991 Jul;7(7):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90125-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann B. J., Torian B. E., Vedvick T. S., Petri W. A., Jr Sequence of a cysteine-rich galactose-specific lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3248–3252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H., Nagami Y., Takahashi K., Okada N., Hideshima T., Takizawa H., Kondo J. 20 KDa homologous restriction factor of complement resembles T cell activating protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1553–1559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90852-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Harada R., Fujita T., Okada H. Monoclonal antibodies capable of causing hemolysis of neuraminidase-treated human erythrocytes by homologous complement. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2262–2266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Chapman M. D., Snodgrass T., Mann B. J., Broman J., Ravdin J. I. Subunit structure of the galactose and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):3007–3012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Ravdin J. I. Protection of gerbils from amebic liver abscess by immunization with the galactose-specific adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.97-101.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Smith R. D., Schlesinger P. H., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Isolation of the galactose-binding lectin that mediates the in vitro adherence of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1238–1244. doi: 10.1172/JCI113198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Snodgrass T. L., Jackson T. F., Gathiram V., Simjee A. E., Chadee K., Chapman M. D. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the galactose-binding lectin of Entamoeba histolytica enhance adherence. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4803–4809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Guerrant R. L. Role of adherence in cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. Study with mammalian tissue culture cells and human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Jackson T. F., Petri W. A., Jr, Murphy C. F., Ungar B. L., Gathiram V., Skilogiannis J., Simjee A. E. Association of serum antibodies to adherence lectin with invasive amebiasis and asymptomatic infection with pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):768–772. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. L., Gigli I. Lysis of complement-sensitive Entamoeba histolytica by activated terminal complement components. Initiation of complement activation by an extracellular neutral cysteine proteinase. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1815–1822. doi: 10.1172/JCI114911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins S. A., Zhao J., Ninomiya H., Sims P. J. Inhibition of homologous complement by CD59 is mediated by a species-selective recognition conferred through binding to C8 within C5b-8 or C9 within C5b-9. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2345–2351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Ebert F., Horstmann R. D. Primary structure of the 170-kDa surface lectin of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Wood L. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane protein capable of inhibiting expression of homologous complement transmembrane channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6975–6979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J., Rollins S. A., Maher S. E., Bothwell A. L., Sims P. J. Amplified gene expression in CD59-transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells confers protection against the membrane attack complex of human complement. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13418–13422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]