Abstract
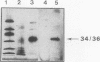
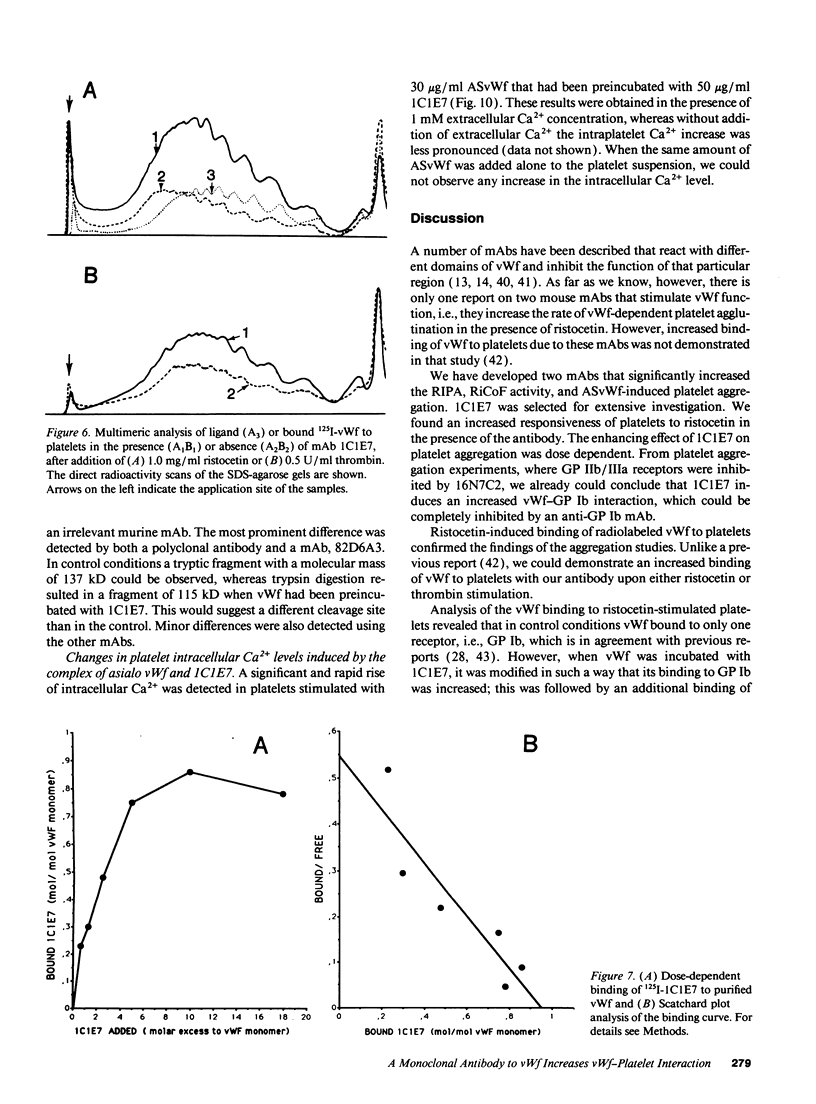
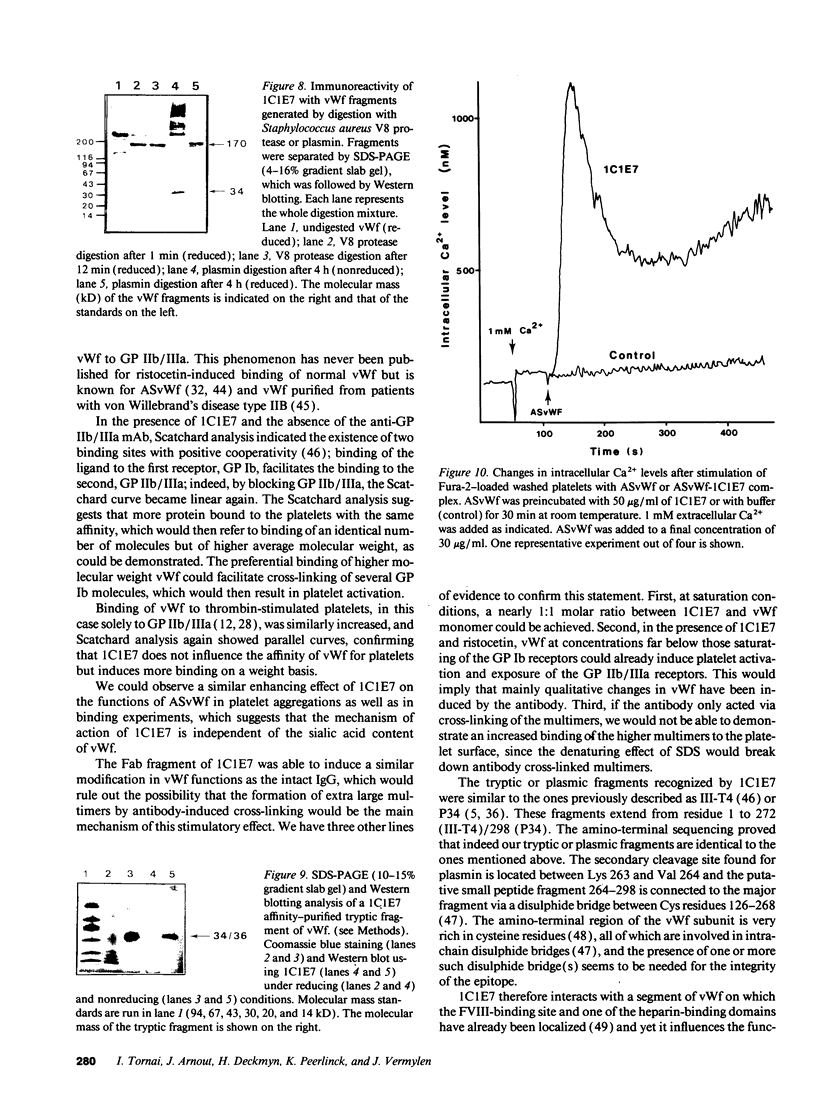
We developed a monoclonal antibody, 1C1E7, against vWf that increases ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation in a dose-dependent manner and lowers the threshold concentration of ristocetin needed to obtain a full aggregatory response. The platelet aggregatory effect of asialo vWf (ASvWf) also is enhanced by 1C1E7, in the presence or absence of glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa receptor antagonism. In the presence of ristocetin, both intact 1C1E7 and its Fab fragments enhance specific binding of 125I-vWf to platelets. With 1C1E7, the intermediate and higher molecular weight multimers of vWf are preferentially bound to both GP Ib and GP IIb/IIIa. Thrombin-induced 125I-vWf binding to GP IIb/IIIa also is increased by 1C1E7. Maximal binding of 1C1E7 to vWf corresponds to 0.97 mol/mol vWf monomer with a Kd of 4.7 x 10(-10) M. 1C1E7 reacts with a 34/36-kD tryptic fragment (III-T4) and a 34-kD plasmic fragment (P34), which localizes the epitope between amino acid residues 1 and 272; this was confirmed by NH2-terminal amino acid sequencing. Finally, platelet aggregation by ASvWf was associated with a sharp rise in intracellular Ca2+ only in the presence of 1C1E7. An antibody-mediated conformational change of vWf may result in an improved presentation of the GP Ib- and GP IIb/IIIa-binding domains of mainly the larger multimers; the increased density of vWf on the platelet surface leads to platelet activation. The antibody may thus recognize a domain of relevance for vWf physiology.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma H., Dent J. A., Sugimoto M., Ruggeri Z. M., Ware J. Independent assembly and secretion of a dimeric adhesive domain of von Willebrand factor containing the glycoprotein Ib-binding site. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12342–12347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baruch D., Bahnak B., Girma J. P., Meyer D. von Willebrand factor and platelet function. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1989 Jul;2(3):627–672. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3536(89)80037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berndt M. C., Du X. P., Booth W. J. Ristocetin-dependent reconstitution of binding of von Willebrand factor to purified human platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):633–640. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolhuis P. A., Sakariassen K. S., Sander H. J., Bouma B. N., Sixma J. J. Binding of factor VIII-von Willebrand factor to human arterial subendothelium precedes increased platelet adhesion and enhances platelet spreading. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Apr;97(4):568–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo M., Mustard J. F., Canciani M. T., Richardson M., Federici A. B., Mannucci P. M. Conditions influencing the interaction of asialo von Willebrand factor with human platelets--the effects of external ionized calcium concentration and the role of arachidonate pathway. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Oct 31;60(2):280–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopek M. W., Girma J. P., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W., Titani K. Human von Willebrand factor: a multivalent protein composed of identical subunits. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3146–3155. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Girolami A., Russell S., Ruggeri Z. M. Interaction of asialo von Willebrand factor with glycoprotein Ib induces fibrinogen binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex and mediates platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1198–1203. doi: 10.1172/JCI111816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Mazzuccato M., Grazia Del Ben M., Budde U., Federici A. B., Girolami A., Ruggeri Z. M. Type IIB von Willebrand factor with normal sialic acid content induces platelet aggregation in the absence of ristocetin. Role of platelet activation, fibrinogen, and two distinct membrane receptors. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):475–482. doi: 10.1172/JCI113095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federici A. B., Bader R., Pagani S., Colibretti M. L., De Marco L., Mannucci P. M. Binding of von Willebrand factor to glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa complex: affinity is related to multimeric size. Br J Haematol. 1989 Sep;73(1):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb00226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
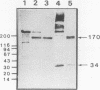
- Foster P. A., Fulcher C. A., Marti T., Titani K., Zimmerman T. S. A major factor VIII binding domain resides within the amino-terminal 272 amino acid residues of von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8443–8446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fretto L. J., Fowler W. E., McCaslin D. R., Erickson H. P., McKee P. A. Substructure of human von Willebrand factor. Proteolysis by V8 and characterization of two functional domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15679–15689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Roberts J. R., Kostel P., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. A heparin-binding domain of human von Willebrand factor. Characterization and localization to a tryptic fragment extending from amino acid residue Val-449 to Lys-728. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1734–1739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Russell S. R., Roberts J. R., Elder J. H., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor. A reduced and alkylated 52/48-kDa fragment beginning at amino acid residue 449 contains the domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):381–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Usami Y., Titani K., Niinomi K., Nishio K., Takase T., Yoshioka A., Fukui H. Studies on anti-von Willebrand factor (vWF) monoclonal antibody NMC-4, which inhibits both ristocetin- and botrocetin-induced vWF binding to platelet glycoprotein Ib. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):113–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girma J. P., Kalafatis M., Piétu G., Lavergne J. M., Chopek M. W., Edgington T. S., Meyer D. Mapping of distinct von Willebrand factor domains interacting with platelet GPIb and GPIIb/IIIa and with collagen using monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1356–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girma J. P., Meyer D., Verweij C. L., Pannekoek H., Sixma J. J. Structure-function relationship of human von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):605–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainick H. R., Williams S. B., Coller B. S. Asialo von Willebrand factor interactions with platelets. Interdependence of glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa for binding and aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):19–25. doi: 10.1172/JCI111673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton K. K., Fretto L. J., Grierson D. S., McKee P. A. Effects of plasmin on von Willebrand factor multimers. Degradation in vitro and stimulation of release in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):261–270. doi: 10.1172/JCI111956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornsey V., Micklem L. R., McCann M. C., James K., Dawes J., McClelland D. B., Prowse C. V. Enhancement of factor VIII-von Willebrand factor ristocetin cofactor activity by monoclonal antibodies. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Aug 30;54(2):510–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. J., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Demonstration and characterization of specific binding sites for factor VIII/von Willebrand factor on human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):656–664. doi: 10.1172/JCI109348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Harris T. S., Moake J. L., Handin R. I., Schafer A. I. von Willebrand factor binding to platelet GpIb initiates signals for platelet activation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1568–1573. doi: 10.1172/JCI115468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrie A. S., Harrison P., Armstrong A. L., Wilbourn B. R., Dalton R. G., Savidge G. F. Comparison of the in vitro characteristics of von Willebrand factor in British and commercial factor VIII concentrates. Br J Haematol. 1989 Sep;73(1):100–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb00227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane D. E., Stibbe J., Kirby E. P., Zucker M. B., Grant R. A., McPherson J. Letter: A method for assaying von Willebrand factor (ristocetin cofactor). Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Sep 30;34(1):306–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti T., Rösselet S. J., Titani K., Walsh K. A. Identification of disulfide-bridged substructures within human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8099–8109. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Baumgartner H. R., Edginton T. S. Hybridoma antibodies to human von Willebrand factor. II. Relative role of intramolecular loci in mediation of platelet adhesion to the subendothelium. Br J Haematol. 1984 Aug;57(4):609–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb02938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri H., Fujimura Y., Shima M., Yoshioka A., Houghten R. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Structure of the von Willebrand factor domain interacting with glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17901–17904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery R. R., Kunicki T. J., Taves C., Pidard D., Corcoran M. Diagnosis of Bernard-Soulier syndrome and Glanzmann's thrombasthenia with a monoclonal assay on whole blood. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):385–389. doi: 10.1172/JCI110780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand J. H., Patel N. D., Schwartz E., Zhou S. L., Potter B. J. 150-kD von Willebrand factor binding protein extracted from human vascular subendothelium is type VI collagen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):253–259. doi: 10.1172/JCI115285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sage S. O. Stimulated calcium efflux from fura-2-loaded human platelets. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:513–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., De Marco L., Gatti L., Bader R., Montgomery R. R. Platelets have more than one binding site for von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):1–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI110946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. The complex multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1140–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. E. von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22777–22780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixma J. J., Sakariassen K. S., Beeser-Visser N. H., Ottenhof-Rovers M., Bolhuis P. A. Adhesion of platelets to human artery subendothelium: effect of factor VIII-von Willebrand factor of various multimeric composition. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):128–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixma J. J., Sakariassen K. S., Stel H. V., Houdijk W. P., In der Maur D. W., Hamer R. J., de Groot P. G., van Mourik J. A. Functional domains on von Willebrand factor. Recognition of discrete tryptic fragments by monoclonal antibodies that inhibit interaction of von Willebrand factor with platelets and with collagen. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):736–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI111489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stel H. V., Sakariassen K. S., Scholte B. J., Veerman E. C., van der Kwast T. H., de Groot P. G., Sixma J. J., van Mourik J. A. Characterization of 25 monoclonal antibodies to factor VIII-von Willebrand factor: relationship between ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation and platelet adherence to subendothelium. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1408–1415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangen O., Berman H. J. Gel filtration of blood platelets: a methodological report. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1972;34:235–243. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3231-2_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons S., Hawiger J. Isolation of human platelets by albumin gradient and gel filtration. Methods Enzymol. 1989;169:11–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)69046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Kumar S., Takio K., Ericsson L. H., Wade R. D., Ashida K., Walsh K. A., Chopek M. W., Sadler J. E., Fujikawa K. Amino acid sequence of human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3171–3184. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornai I., Declerck P. J., Smets L., Arnout J., Deckmyn H., Caekebeke-Peerlinck K. M., Vermylen J. Measurement of von Willebrand factor antigen in plasma and platelets with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on two murine monoclonal antibodies. Haemostasis. 1991;21(3):125–134. doi: 10.1159/000216216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermylen J., Donati M. B., De Gaetano G., Verstraete M. Aggregation of human platelets by bovine or human factor VIII: role of carbohydrate side chains. Nature. 1973 Jul 20;244(5412):167–168. doi: 10.1038/244167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot P. G., Ottenhof-Rovers M., van Mourik J. A., Sixma J. J. Evidence that the primary binding site of von Willebrand factor that mediates platelet adhesion on subendothelium is not collagen. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):65–73. doi: 10.1172/JCI113602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]