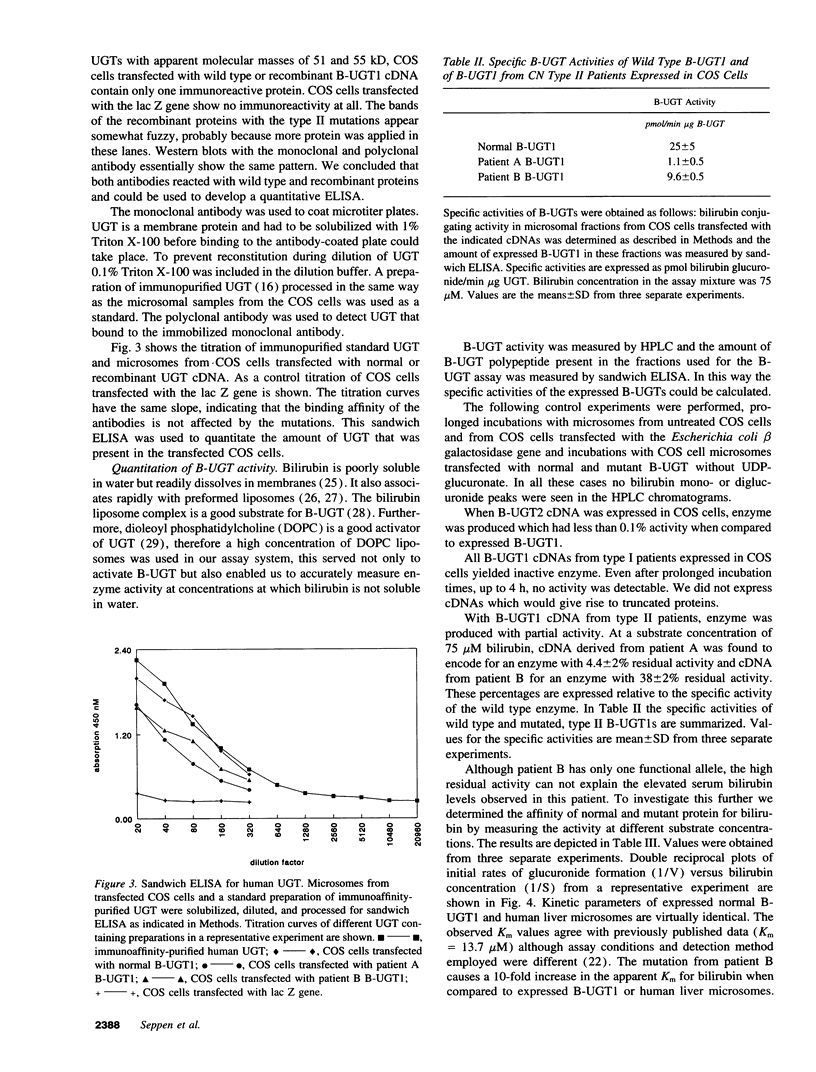
Abstract
Crigler-Najjar (CN) disease is classified into two subtypes, type I and II. The molecular basis for the difference between these types is not well understood. Several mutations in the bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyl-transferase (B-UGT) gene of six CN type I and two CN type II patients were identified. Recombinant cDNAs containing these mutations were expressed in COS cells. B-UGT activity was measured using HPLC and the amount of expressed protein was quantitated using a sandwich ELISA. This enabled us to determine the specific activities of the expressed enzymes. All type I patients examined had mutations in the B-UGT1 gene that lead to completely inactive enzymes. The mutations in the B-UGT1 gene of patients with CN type II only partially inactivated the enzyme. At saturating concentrations of bilirubin (75 microM) CN type II patient A had 4.4 +/- 2% residual activity and CN type II patient B had 38 +/- 2% residual activity. Kinetic constants for the glucuronidation of bilirubin were determined. The affinities for bilirubin of B-UGT1 expressed in COS cells and B-UGT from human liver microsomes were similar with Km of 5.1 +/- 0.9 microM and 7.9 +/- 5.3 microM, respectively. B-UGT1 from patient B had a tenfold decreased affinity for bilirubin, Km = 56 +/- 23 microM. At physiological concentrations of bilirubin both type II patients will have a strongly reduced conjugation capacity, whereas type I patients have no B-UGT activity. We conclude that CN type I is caused by a complete absence of functional B-UGT and that in CN type II B-UGT activity is reduced.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias I. M., Gartner L. M., Cohen M., Ezzer J. B., Levi A. J. Chronic nonhemolytic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia with glucuronyl transferase deficiency. Clinical, biochemical, pharmacologic and genetic evidence for heterogeneity. Am J Med. 1969 Sep;47(3):395–409. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock K. W., Bock-Hennig B. S. Differential induction of human liver UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activities by phenobarbital-type inducers. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 1;36(23):4137–4143. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90572-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma P. J., Chowdhury J. R., Huang T. J., Lahiri P., Elferink R. P., Van Es H. H., Lederstein M., Whitington P. F., Jansen P. L., Chowdhury N. R. Mechanisms of inherited deficiencies of multiple UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoforms in two patients with Crigler-Najjar syndrome, type I. FASEB J. 1992 Jul;6(10):2859–2863. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.10.1634050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma P. J., Chowdhury N. R., Goldhoorn B. G., Hofker M. H., Oude Elferink R. P., Jansen P. L., Chowdhury J. R. Sequence of exons and the flanking regions of human bilirubin-UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene complex and identification of a genetic mutation in a patient with Crigler-Najjar syndrome, type I. Hepatology. 1992 May;15(5):941–947. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma P. J., Goldhoorn B., Oude Elferink R. P., Sinaasappel M., Oostra B. A., Jansen P. L. A mutation in bilirubin uridine 5'-diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase isoform 1 causing Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jul;105(1):216–220. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90029-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma P. J., Seppen J., Goldhoorn B., Bakker C., Oude Elferink R. P., Chowdhury J. R., Chowdhury N. R., Jansen P. L. Bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 is the only relevant bilirubin glucuronidating isoform in man. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):17960–17964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRIGLER J. F., Jr, NAJJAR V. A. Congenital familial nonhemolytic jaundice with kernicterus. Pediatrics. 1952 Aug;10(2):169–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Cervera M., Marco R. A convenient micromethod for the assay of primary amines and proteins with fluorescamine. A reexamination of the conditions of reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. N., Kapitulnik J., Ostrow J. D., Zenone E. A., Cochrane C., Celic L., Cheney H. Effects of phenobarbital on bilirubin metabolism and its response to phototherapy in the jaundiced Gunn rat. Hepatology. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):310–316. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. M., Ransil B. J., Narciso J. P., Gollan J. L. Hepatic microsomal bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase. The kinetics of bilirubin mono- and diglucuronide synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16943–16950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng W. P., Nickoloff J. A. Site-directed mutagenesis of virtually any plasmid by eliminating a unique site. Anal Biochem. 1992 Jan;200(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90280-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doostdar H., Grant M. H., Melvin W. T., Wolf C. R., Burke M. D. The effects of inducing agents on cytochrome P450 and UDP-glucuronyltransferase activities in human HEPG2 hepatoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 17;46(4):629–635. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90548-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel G., Blanckaert N., Metreau J. M., Préaux A. M., Bouvry M., Fevery J., Berthelot P. An unusual case of Crigler-Najjar disease in the adult. Classification into types I and II revisited. J Hepatol. 1985;1(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erps L. T., Ritter J. K., Hersh J. H., Blossom D., Martin N. C., Owens I. S. Identification of two single base substitutions in the UGT1 gene locus which abolish bilirubin uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase activity in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):564–570. doi: 10.1172/JCI117008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevery J., Blanckaert N., Heirwegh K. P., Préaux A. M., Berthelot P. Unconjugated bilirubin and an increased proportion of bilirubin monoconjugates in the bile of patients with Gilbert's syndrome and Crigler-Najjar disease. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):970–979. doi: 10.1172/JCI108877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevery J., Blanckaert N., Leroy P., Michiels R., Heirwegh K. P. Analysis of bilirubins in biological fluids by extraction and thin-layer chromatography of the intact tetrapyrroles: application to bile of patients with Gilbert's syndrome, hemolysis, or cholelithiasis. Hepatology. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):177–183. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentile S., Del Vecchio Blanco C., Persico M., Marmo R., Coltorti M. Familial clustering of heterogeneous chronic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Hepatogastroenterology. 1986 Aug;33(4):155–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollan J. L., Huang S. N., Billing B., Sherlock S. Prolonged survival in three brothers with severe type 2 Crigler-Najjar syndrome. Ultrastructural and metabolic studies. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jun;68(6):1543–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter J. O., Thompson R. P., Dunn P. M., Williams R. Inheritance of type 2 Crigler-Najjar hyperbilirubinaemia. Gut. 1973 Jan;14(1):46–49. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyanagi T. Molecular basis of multiple UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoenzyme deficiencies in the hyperbilirubinemic rat (Gunn rat). J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24048–24052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen P. L., Mulder G. J., Burchell B., Bock K. W. New developments in glucuronidation research: report of a workshop on "glucuronidation, its role in health and disease". Hepatology. 1992 Mar;15(3):532–544. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrune P., Myara A., Hennion C., Gout J. P., Trivin F., Odievre M. Crigler-Najjar type II disease inheritance: a family study. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1989;12(3):302–306. doi: 10.1007/BF01799221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinekugel P., Michel S., Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. Quantitative correlation between the residual activity of beta-hexosaminidase A and arylsulfatase A and the severity of the resulting lysosomal storage disease. Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;88(5):513–523. doi: 10.1007/BF00219337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magdalou J., Hochman Y., Zakim D. Factors modulating the catalytic specificity of a pure form of UDP-glucuronyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13624–13629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moghrabi N., Clarke D. J., Boxer M., Burchell B. Identification of an A-to-G missense mutation in exon 2 of the UGT1 gene complex that causes Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 2. Genomics. 1993 Oct;18(1):171–173. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noy N., Leonard M., Zakim D. The kinetics of interactions of bilirubin with lipid bilayers and with serum albumin. Biophys Chem. 1992 Feb;42(2):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(92)85007-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura T. Cytochrome P-450 linked mixed function oxidase turnover of microsomal components and effects of inducers on the turnover phospholipids, proteins and specific enzymes. Pharmacol Ther. 1980;8(3):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W. H., Allebes W. A., Jansen P. L., Poels L. G., Capel P. J. Characterization and tissue specificity of a monoclonal antibody against human uridine 5'-diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jul;93(1):162–169. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pett S., Mowat A. P. Crigler-Najjar syndrome types I and II. Clinical experience--King's College Hospital 1972-1978. Phenobarbitone, phototherapy and liver transplantation. Mol Aspects Med. 1987;9(5):473–482. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(87)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter J. K., Chen F., Sheen Y. Y., Tran H. M., Kimura S., Yeatman M. T., Owens I. S. A novel complex locus UGT1 encodes human bilirubin, phenol, and other UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isozymes with identical carboxyl termini. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3257–3261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter J. K., Crawford J. M., Owens I. S. Cloning of two human liver bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase cDNAs with expression in COS-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1043–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson K. J., Clarke D., Sutherland L., Wooster R., Coughtrie M. W., Burchell B. Investigation of the molecular basis of the genetic deficiency of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase in Crigler-Najjar syndrome. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1991;14(4):563–579. doi: 10.1007/BF01797927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinaasappel M., Jansen P. L. The differential diagnosis of Crigler-Najjar disease, types 1 and 2, by bile pigment analysis. Gastroenterology. 1991 Mar;100(3):783–789. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)80026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak W., Carey M. C. Reverse-phase h.p.l.c. separation, quantification and preparation of bilirubin and its conjugates from native bile. Quantitative analysis of the intact tetrapyrroles based on h.p.l.c. of their ethyl anthranilate azo derivatives. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 1;225(3):787–805. doi: 10.1042/bj2250787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland L., Ebner T., Burchell B. The expression of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases of the UGT1 family in human liver and kidney and in response to drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 26;45(2):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thapa B. R., Yachha S. K., Mehta S. Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II with kernicterus. Indian Pediatr. 1987 Aug;24(8):680–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiribelli C., Ostrow J. D. New concepts in bilirubin chemistry, transport and metabolism: report of the Second International Bilirubin Workshop, April 9-11, 1992, Trieste, Italy. Hepatology. 1993 Apr;17(4):715–736. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840170428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmer D. I., Russell P. E., Gollan J. L. Membrane-membrane interactions associated with rapid transfer of liposomal bilirubin to microsomal UDP-glucuronyltransferase. Relevance for hepatocellular transport and biotransformation of hydrophobic substrates. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):41–47. doi: 10.1042/bj2440041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff H., Otto G., Giest H. Liver transplantation in Crigler-Najjar syndrome. A case report. Transplantation. 1986 Jul;42(1):84–84. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198607000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker S. D., Storch J., Zeidel M. L., Gollan J. L. Mechanism of the spontaneous transfer of unconjugated bilirubin between small unilamellar phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 31;31(12):3184–3192. doi: 10.1021/bi00127a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Es H. H., Goldhoorn B. G., Paul-Abrahamse M., Elferink R. P., Jansen P. L. Immunochemical analysis of uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase in four patients with the Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1199–1205. doi: 10.1172/JCI114553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]