Abstract
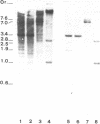
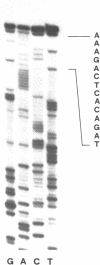
A cDNA library from the protist Euglena gracilis was used to isolate and sequence an ORF coding for the elongation factor protein EF-1 alpha. The decoded amino acid sequence (MW, 48'515) is to 75-80% identical with other eukaryotic EF-1 alpha sequences but only to 24% identical with the Euglena chloroplast EF-Tu. Homologous DNA probes interact with multiple fragments of Euglena nuclear restricted DNA typical for a multimembered gene family. We present the restriction sites map of four tef nuclear gene loci and postulate that the nuclear genome also contains tef related sequences (e.g. pseudogenes). Expression of tef gene(s) is monitored by Northern hybridization and the 5' end of a stable transcript (1.5 kb) is sequenced and shown to precede the start codon by 29 positions only. The steady state concentration of the 1.5 kb mRNA is not influenced by switching cell growth conditions from dark to light (chloroplast development).
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G., Friesen J. D. The nucleotide sequence of tufB and four nearby tRNA structural genes of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. M., Spremulli L. L. Purification of Euglena EF-1l: a cytoplasmic factor that also functions on procaryotic and organellar ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 May;215(2):414–424. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis S. E., Rawson J. R. Characterization of the nuclear ribosomal DNA of Euglena gracilis. Gene. 1981 Nov;15(2-3):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg C. J., Hauser S. D. Accurate and efficient in vitro splicing of purified precursor RNAs specified by early region 2 of the adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1337–1348. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNINGSEN K. A new deleted Rh-chromosome. Nature. 1958 Feb 15;181(4607):502–502. doi: 10.1038/181502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlne G., Schantz R. Molecular analysis of the transcripts encoding the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein in Euglena gracilis: unusual size of the mRNA. Curr Genet. 1987;12(8):611–616. doi: 10.1007/BF00368064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlné G., Schantz R. Characterization of cDNA sequences for LHCI apoproteins in Euglena gracilis: the mRNA encodes a large precursor containing several consecutive divergent polypeptides. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):479–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00339619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovemann B., Richter S., Walldorf U., Cziepluch C. Two genes encode related cytoplasmic elongation factors 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) in Drosophila melanogaster with continuous and stage specific expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3175–3194. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenstra J. A., Van Vliet A., Arnberg A. C., Van Hemert F. J., Möller W. Genes coding for the elongation factor EF-1 alpha in Artemia. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Mar 17;155(3):475–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linz J. E., Sypherd P. S. Expression of three genes for elongation factor 1 alpha during morphogenesis of Mucor racemosus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1925–1932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Man Y. M., Delius H., Leader D. P. Molecular analysis of elements inserted into mouse gamma-actin processed pseudogenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3291–3304. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Knuchel-Aegerter C., Stutz E. Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA: the untranslated leader of tufA-ORF206 gene contains an intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7809–7822. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Stutz E. Nucleotide sequence of a Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome region coding for the elongation factor Tu; evidence for a spliced mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5877–5892. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Slamon D. J., Tremblay J. M., Cline M. J., Verma I. M. Differential expression of cellular oncogenes during pre- and postnatal development of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):640–644. doi: 10.1038/299640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima K., Kasai M., Nagata S., Kaziro Y. Structure of the two genes coding for polypeptide chain elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1986;45(3):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Nagashima K., Tsunetsugu-Yokota Y., Fujimura K., Miyazaki M., Kaziro Y. Polypeptide chain elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) from yeast: nucleotide sequence of one of the two genes for EF-1 alpha from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1825–1830. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz W., Reardon E. M., Price C. A. Preparation of chloroplasts from euglena highly active in protein synthesis. Plant Physiol. 1980 Aug;66(2):291–294. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokalsky A. R., Hiatt W. R., Ridge N., Rasmussen R., Houck C. M., Shewmaker C. K. Structure and expression of elongation factor 1 alpha in tomato. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4661–4673. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawson J. R., Eckenrode V. K., Boerma C. L., Curtis S. DNA sequence organization in the alga Euglena gracilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 20;563(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawson J. R. The characterization of Euglena gracilis DNA by its reassociation kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 21;402(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz M. L., Schantz R. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding beta tubulin from Euglena gracilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6727–6727. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos A., Pollack M., Mendiola L. R., Hoffmann H. P., Brown D. H., Price C. A. Isolation of Intact Chloroplasts from Euglena gracilis by Zonal Centrifugation. Plant Physiol. 1971 Feb;47(2):217–221. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]