Abstract
Sequence analysis of a substantial part of the polymerase gene of the murine coronavirus MHV-A59 revealed the 3' end of an open reading frame (ORF1a) overlapping with a large ORF (ORF1b; 2733 amino acids) which covers the 3' half of the polymerase gene. The expression of ORF1b occurs by a ribosomal frameshifting mechanism since the ORF1a/ORF1b overlapping nucleotide sequence is capable of inducing ribosomal frameshifting in vitro as well as in vivo. A stem-loop structure and a pseudoknot are predicted in the nucleotide sequence involved in ribosomal frameshifting. Comparison of the predicted amino acid sequence of MHV ORF1b with the amino acid sequence deduced from the corresponding gene of the avian coronavirus IBV demonstrated that in contrast to the other viral genes this ORF is extremely conserved. Detailed analysis of the predicted amino acid sequence revealed sequence elements which are conserved in many DNA and RNA polymerases.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P. A sequence motif in many polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9909–9916. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J., Niemann H., Smeekens S., Rottier P., Warren G. Sequence and topology of a model intracellular membrane protein, E1 glycoprotein, from a coronavirus. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):751–752. doi: 10.1038/308751a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boursnell M. E., Brown T. D., Foulds I. J., Green P. F., Tomley F. M., Binns M. M. Completion of the sequence of the genome of the coronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):57–77. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayton P. R., Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Stohlman S. A. Characterization of two RNA polymerase activities induced by mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):847–853. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.847-853.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayton P. R., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Further characterization of mouse hepatitis virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90439-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Boursnell M. E., Binns M. M., Bilimoria B., Blok V. C., Brown T. D., Inglis S. C. An efficient ribosomal frame-shifting signal in the polymerase-encoding region of the coronavirus IBV. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3779–3785. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coia G., Parker M. D., Speight G., Byrne M. E., Westaway E. G. Nucleotide and complete amino acid sequences of Kunjin virus: definitive gene order and characteristics of the virus-specified proteins. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton S. R., Rogers D. B., Holmes K. V., Fertsch D., Remenick J., McGowan J. J. In vitro replication of mouse hepatitis virus strain A59. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1814–1820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1814-1820.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. R., Perlman S. Translation and processing of mouse hepatitis virus virion RNA in a cell-free system. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.12-18.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M., Perlman S. Identification of putative polymerase gene product in cells infected with murine coronavirus A59. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):565–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90303-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Stohlman S. A., Harmon R. C., Lai M. M., Frelinger J. A., Weiner L. P. Antigenic relationships of murine coronaviruses: analysis using monoclonal antibodies to JHM (MHV-4) virus. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):296–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90498-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbach R., Wellink J. Evolution of plus-strand RNA viruses. Intervirology. 1988;29(5):260–267. doi: 10.1159/000150054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V. Birnavirus RNA polymerase is related to polymerases of positive strand RNA viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7735–7735. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. A novel superfamily of nucleoside triphosphate-binding motif containing proteins which are probably involved in duplex unwinding in DNA and RNA replication and recombination. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81226-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C. A new superfamily of replicative proteins. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–23. doi: 10.1038/333022b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Madhani H. D., Masiarz F. R., Varmus H. E. Signals for ribosomal frameshifting in the Rous sarcoma virus gag-pol region. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90031-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the Rous sarcoma virus pol gene by ribosomal frameshifting. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1237–1242. doi: 10.1126/science.2416054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A. Presence of leader sequences in the mRNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1027-1033.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Stohlman S. A. Further characterization of mRNA's of mouse hepatitis virus: presence of common 5'-end nucleotides. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):557–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.557-565.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Stohlman S. A. Replication of mouse hepatitis virus: negative-stranded RNA and replicative form RNA are of genome length. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):487–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.487-492.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., DeVries J. R., Haspel M. V. Genetic analysis of murine hepatitis virus strain JHM. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1080–1087. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1080-1087.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., DeVries J. R. Synthesis of virus-specific RNA in permeabilized murine coronavirus-infected cells. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90147-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenstra J. A., de Groot R. J., Jacobs L., Kusters J. G., Niesters H. G., van der Zeijst B. A. Synthesis of long cDNA from viral RNA template. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 May-Jun;5(3):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90017-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Bredenbeek P. J., Noten A. F., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Sequence of mouse hepatitis virus A59 mRNA 2: indications for RNA recombination between coronaviruses and influenza C virus. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90512-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahy B. W., Siddell S., Wege H., ter Meulen V. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in murine coronavirus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):103–111. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niesters H. G., Lenstra J. A., Spaan W. J., Zijderveld A. J., Bleumink-Pluym N. M., Hong F., van Scharrenburg G. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. The peplomer protein sequence of the M41 strain of coronavirus IBV and its comparison with Beaudette strains. Virus Res. 1986 Aug;5(2-3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90022-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
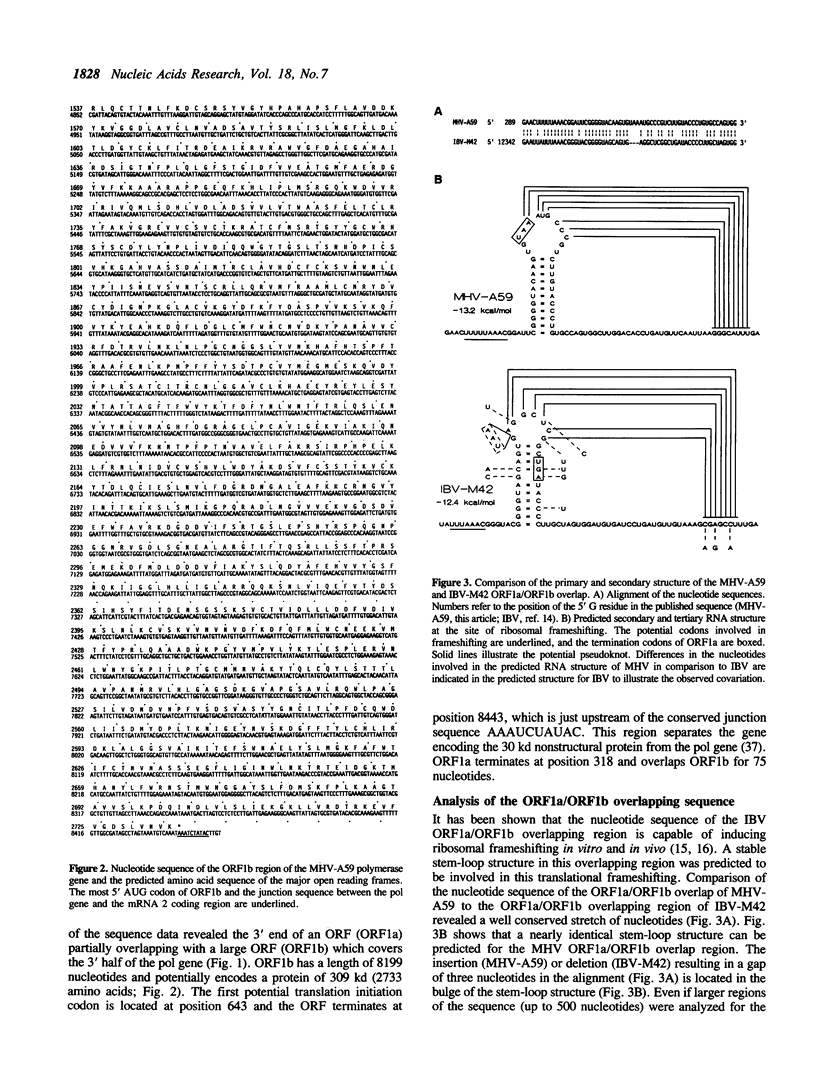
- Pachuk C. J., Bredenbeek P. J., Zoltick P. W., Spaan W. J., Weiss S. R. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the putative polymerase of mouse hepatitis coronavirus, strain A59. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90520-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottier P. J., Rose J. K. Coronavirus E1 glycoprotein expressed from cloned cDNA localizes in the Golgi region. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2042–2045. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2042-2045.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki S. G., Sawicki D. L. Coronavirus minus-strand RNA synthesis and effect of cycloheximide on coronavirus RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):328–334. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.328-334.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soe L. H., Shieh C. K., Baker S. C., Chang M. F., Lai M. M. Sequence and translation of the murine coronavirus 5'-end genomic RNA reveals the N-terminal structure of the putative RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3968–3976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3968-3976.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Isolation and identification of virus-specific mRNAs in cells infected with mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-A59). Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90449-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
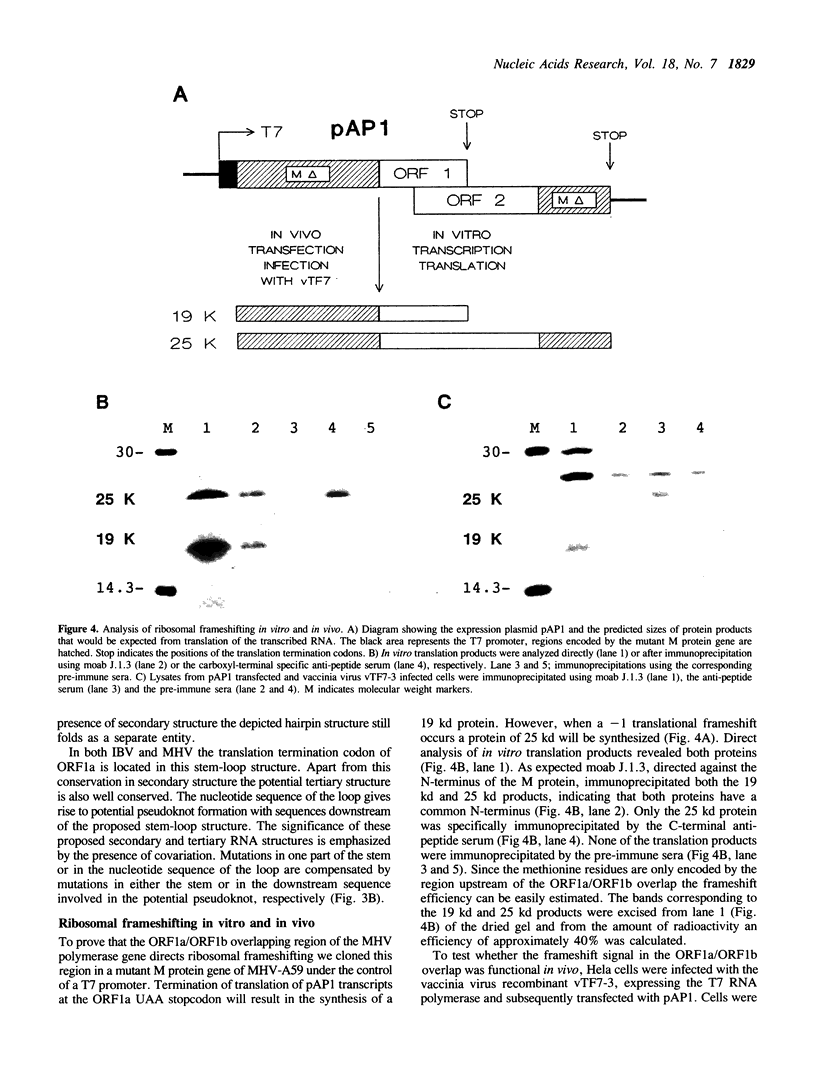
- Spaan W., Cavanagh D., Horzinek M. C. Coronaviruses: structure and genome expression. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):2939–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. The current status and portability of our sequence handling software. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):217–231. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Levinson R., Rice C. M., Dalrymple J., Strauss J. H. Nonstructural proteins nsP3 and nsP4 of Ross River and O'Nyong-nyong viruses: sequence and comparison with those of other alphaviruses. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90644-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. H., Strauss E. G. Evolution of RNA viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:657–683. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tordo N., Poch O., Ermine A., Keith G., Rougeon F. Completion of the rabies virus genome sequence determination: highly conserved domains among the L (polymerase) proteins of unsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90600-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., ter Haar R. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Intracellular RNAs of the feline infectious peritonitis coronavirus strain 79-1146. J Gen Virol. 1987 Apr;68(Pt 4):995–1002. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-4-995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]