Abstract
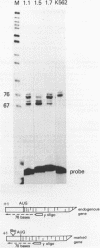
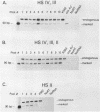
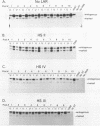
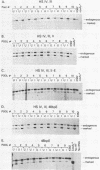
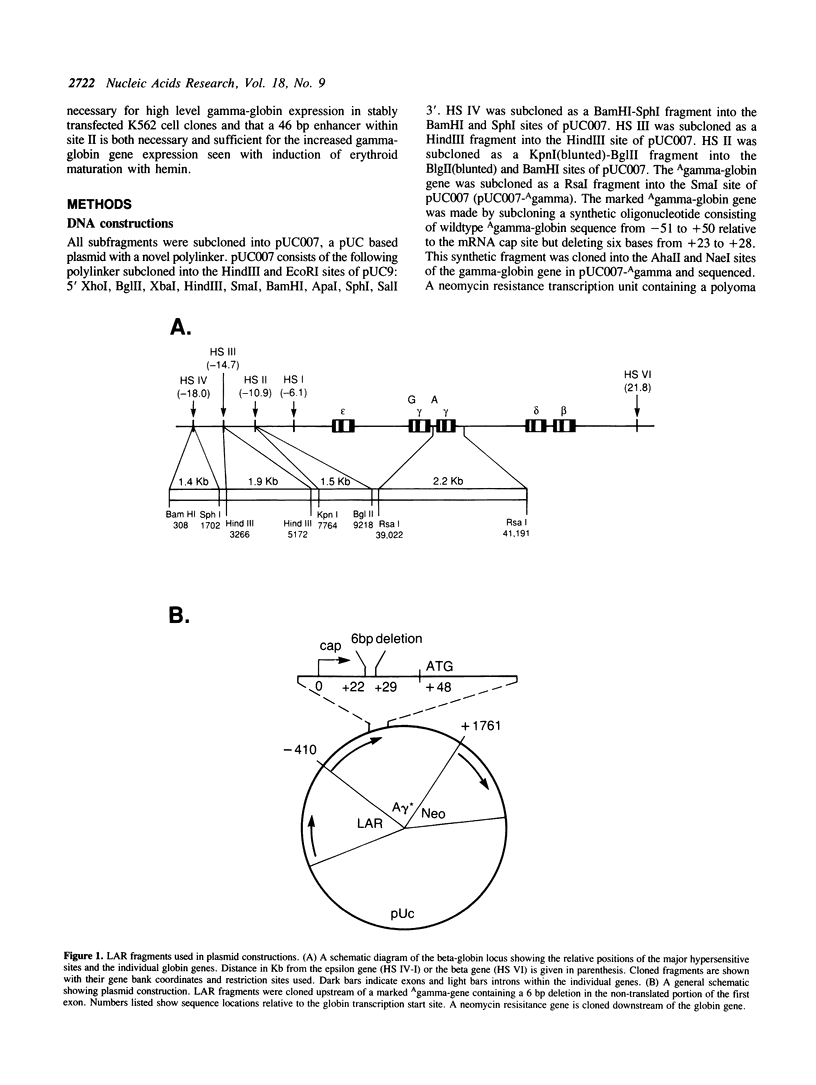
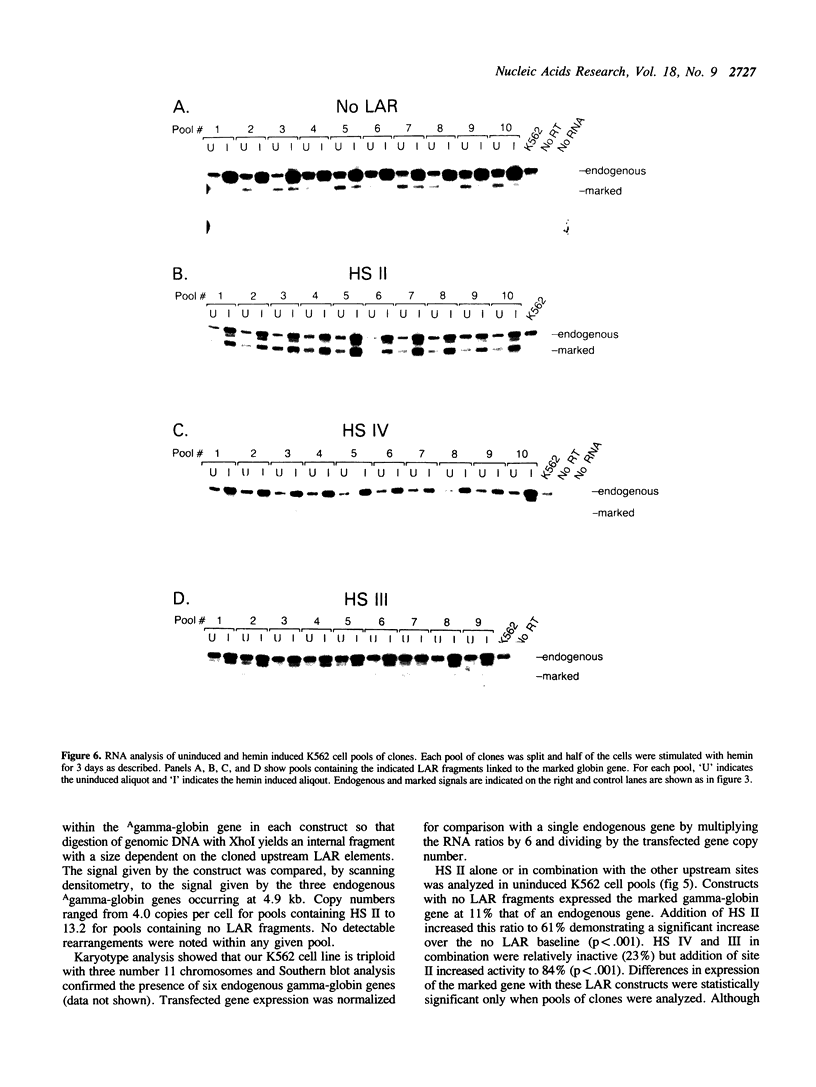
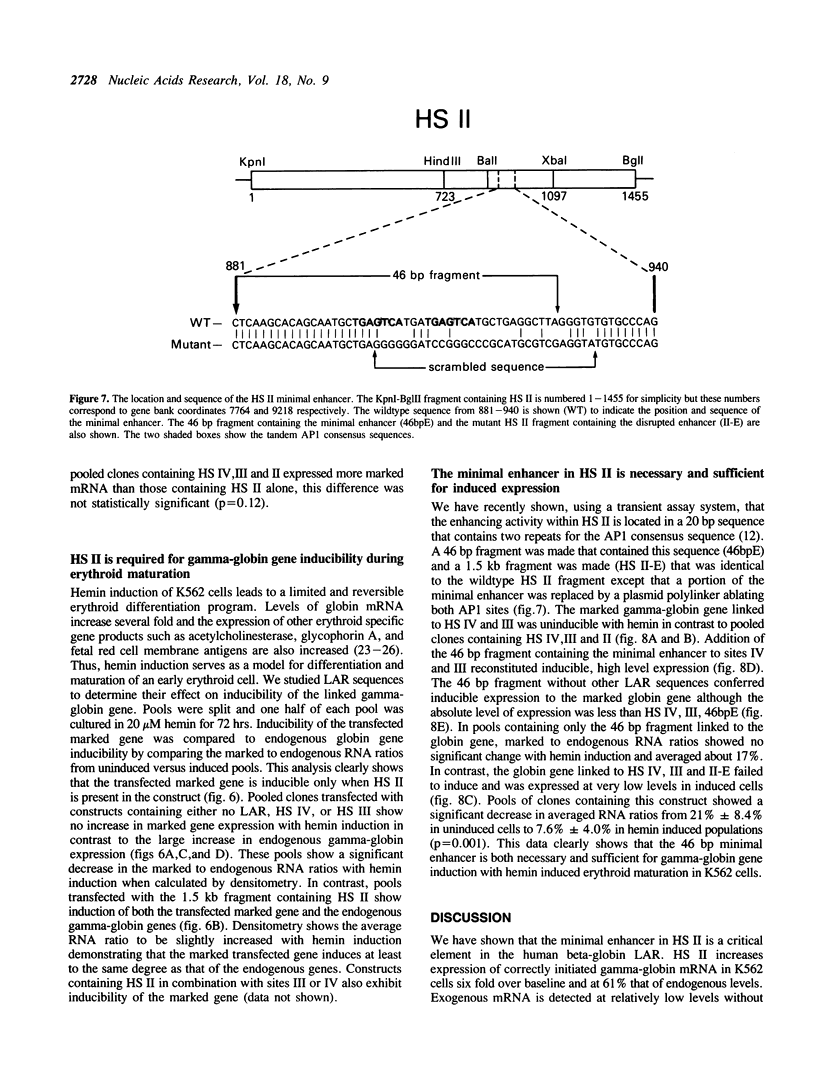
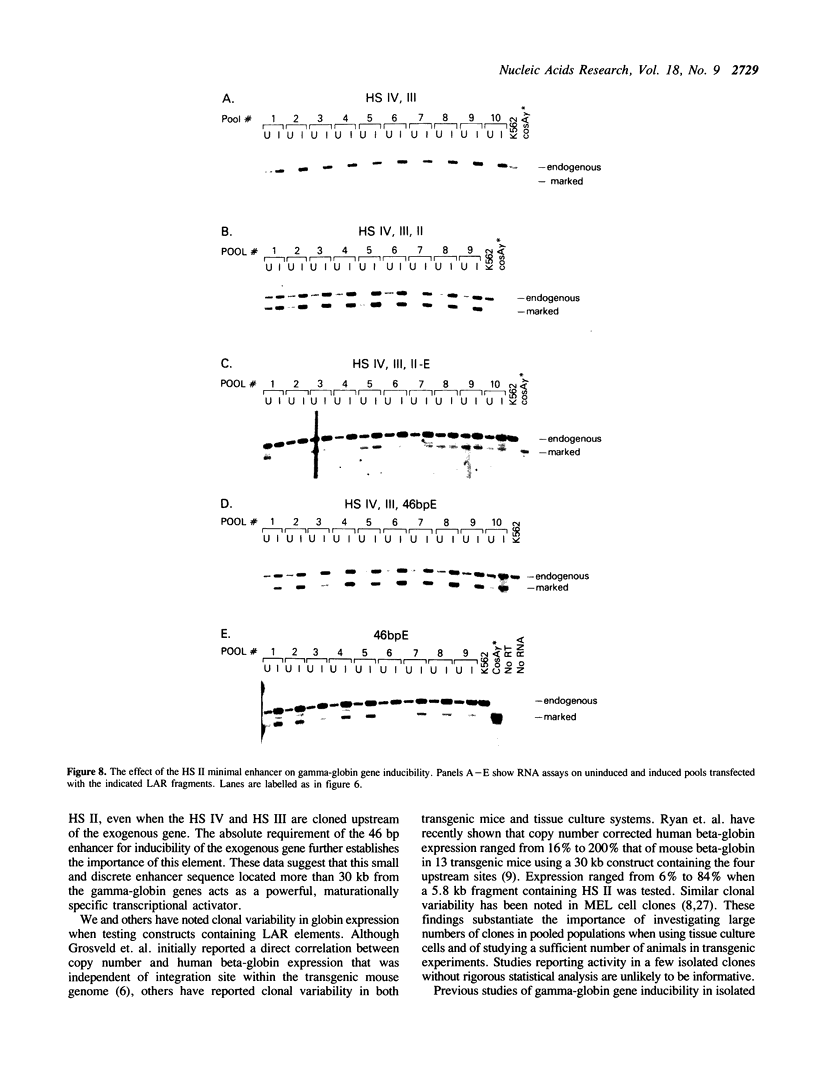
The locus activating region (LAR), contained within 30 kb of chromatin flanking the human beta-globin gene cluster, has recently been shown to be essential for high level beta-globin gene expression. To determine the effect of fragments containing LAR sequences on globin gene expression, mRNA from a marked gamma-globin gene linked to LAR fragments was assayed in stably transfected K562 erythroleukemia cells. DNaseI hypersensitive site II (HS II), located 10.9 kb upstream of the epsilon-globin gene, was required for high level gamma-globin gene expression. We also showed that a 46 bp enhancer element within HS II was necessary and sufficient for the increased gamma-globin gene expression observed with hemin induced erythroid maturation of K562 cells. These results localize a distant regulatory element important for activation of globin genes during human erythroid cell maturation.
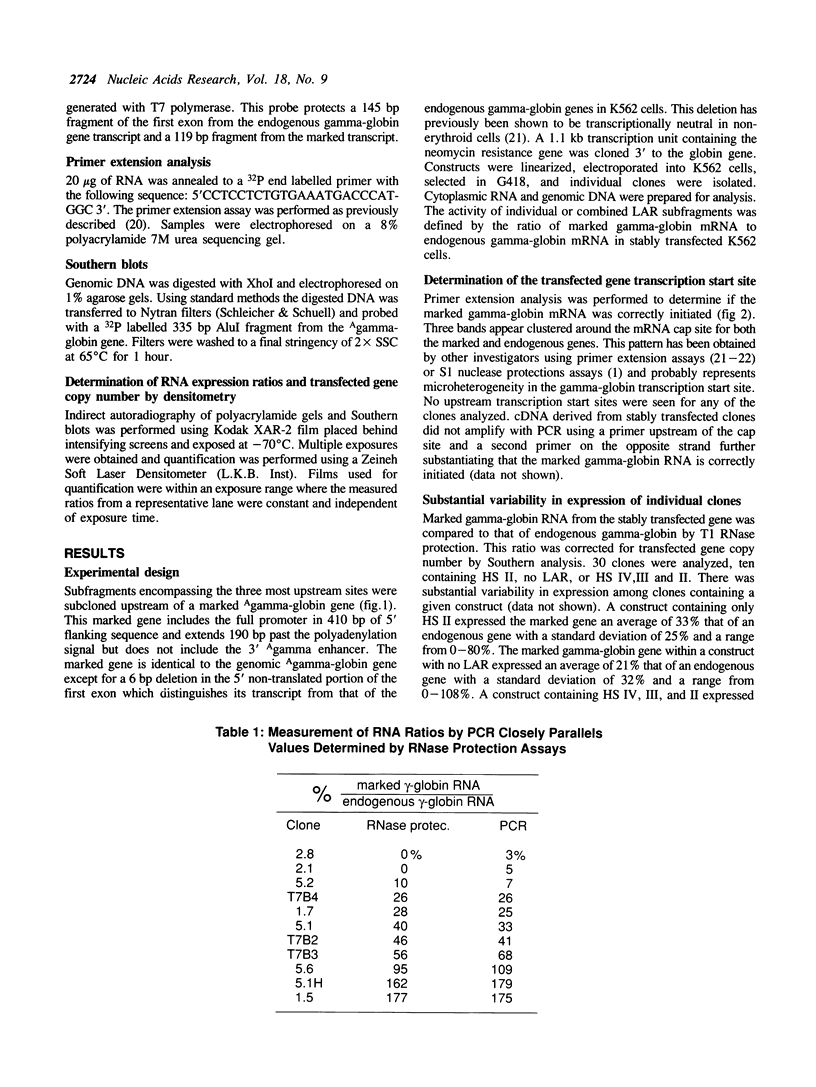
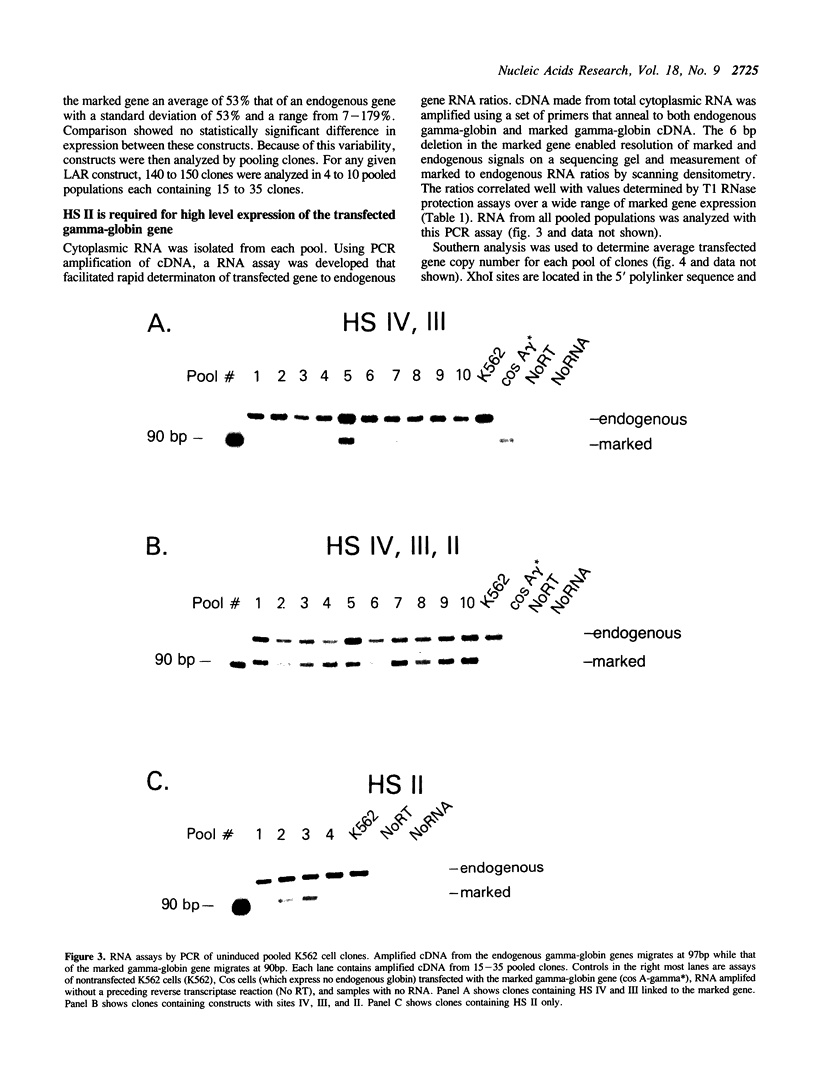
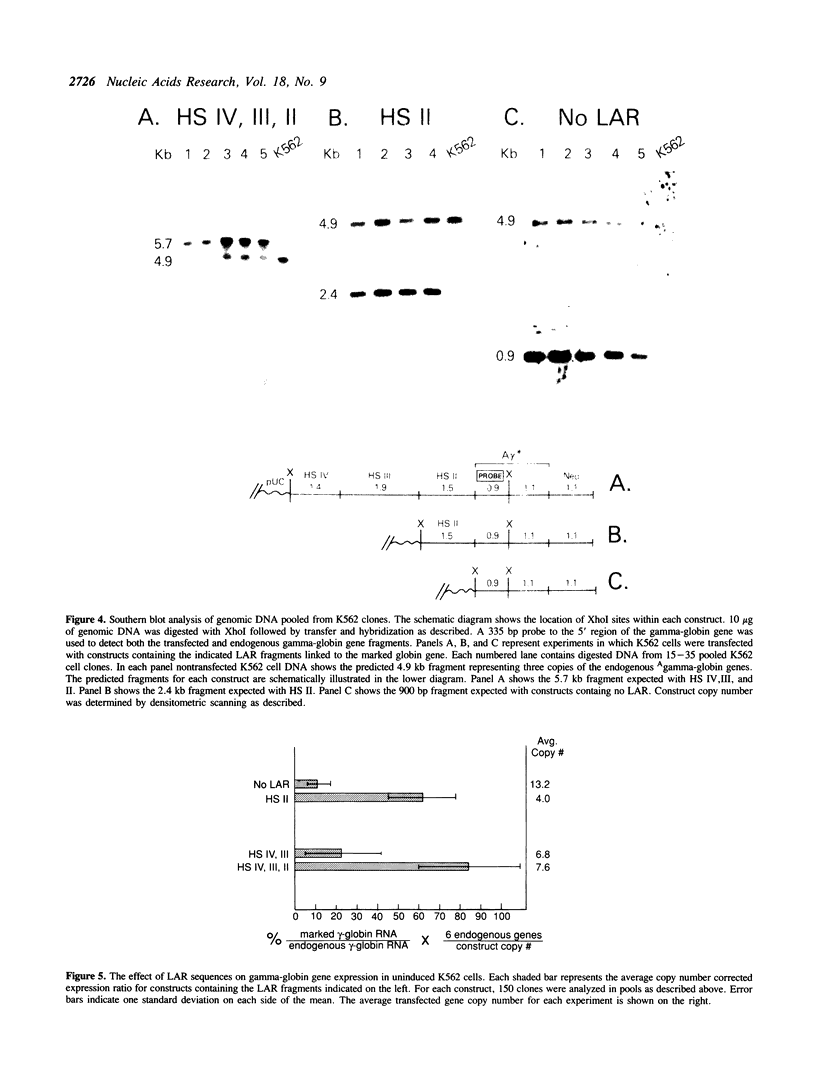
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnou N. P., Karlsson S., Moulton A. D., Keller G., Nienhuis A. W. Promoter sequences required for function of the human gamma globin gene in erythroid cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):121–126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniou M., deBoer E., Habets G., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene contains multiple regulatory regions: identification of one promoter and two downstream enhancers. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):377–384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02824.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartha E., Oláh E., Szelényi J. G., Hollan S. R. Characterization of "fetal-type" acetylcholinesterase in hemin-treated K562 cell culture. Blood Cells. 1987;12(3):647–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behringer R. R., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D., Townes T. M. Two 3' sequences direct adult erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7056–7060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom van Assendelft G., Hanscombe O., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. The beta-globin dominant control region activates homologous and heterologous promoters in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90630-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catala F., deBoer E., Habets G., Grosveld F. Nuclear protein factors and erythroid transcription of the human A gamma-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3811–3827. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Henry L. Regulated expression of cloned human fetal A gamma-globin genes introduced into murine erythroleukemia cells. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):475–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin P. T., Liu D. P., Liu W., Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. Human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice is enhanced by a distant DNase I hypersensitive site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7082–7086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A., Ley T. J., Humphries R. K., Fordis M., Schechter A. N. Inducible transcription of five globin genes in K562 human leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5515–5519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan-Peluso M., Acuto S., Swanson M., Dobkin C., Bank A. Expression of human gamma-globin genes in human erythroleukemia (K562) cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17051–17057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll M. C., Dobkin C. S., Alter B. P. Gamma delta beta-thalassemia due to a de novo mutation deleting the 5' beta-globin gene activation-region hypersensitive sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7470–7474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzierzak E. A., Papayannopoulou T., Mulligan R. C. Lineage-specific expression of a human beta-globin gene in murine bone marrow transplant recipients reconstituted with retrovirus-transduced stem cells. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):35–41. doi: 10.1038/331035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Coen D. M., McKnight S. L. Promoter domains required for expression of plasmid-borne copies of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in virus-infected mouse fibroblasts and microinjected frog oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1940–1947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Novak U., Gelinas R., Groudine M. Molecular analysis of the human beta-globin locus activation region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5439–5443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R., Ibrahim N., Murnane M. J., Diamond A., Forget B. G., Levere R. D. Hemin control of heme biosynthesis and catabolism in a human leukemia cell line. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):567–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson S., Bodine D. M., Perry L., Papayannopoulou T., Nienhuis A. W. Expression of the human beta-globin gene following retroviral-mediated transfer into multipotential hematopoietic progenitors of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6062–6066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Vanin E., deLange T., Flavell R. A., Grosveld F. G. Beta-globin gene inactivation by DNA translocation in gamma beta-thalassaemia. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):662–666. doi: 10.1038/306662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Wilson F., Khazaie K., Grosveld F. Differential expression of human globin genes introduced in K562 cells. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):927–931. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. J., Anagnou N. P., Rutherford T. R., Shimada T., Nienhuis A. W. Activation of the human beta-globin promoter in K562 cells by DNA sequences 5' to the fetal gamma- or embryonic zeta-globin genes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):374–380. doi: 10.1172/JCI113082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinniss M. H., Dean A. Expression of red cell antigens by K562 human leukemia cells before and after induction of hemoglobin synthesis by hemin. Transfusion. 1985 Mar-Apr;25(2):105–109. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1985.25285169197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte V., Eleouet J. F., Raich N., Romeo P. H. Cis- and trans-acting elements involved in the regulation of the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6548–6552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte V., Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F., Romeo P. H. Two tissue-specific factors bind the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):37–54. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Weir L., Leder P. Enhancer-dependent expression of human kappa immunoglobulin genes introduced into mouse pre-B lymphocytes by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7161–7165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon M. W., Gelinas R. E. A fetal globin gene mutation in A gamma nondeletion hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin increases promoter strength in a nonerythroid cell. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):713–721. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Martin N. C., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A single erythroid-specific DNase I super-hypersensitive site activates high levels of human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):314–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. High-level erythroid expression of human alpha-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):37–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Collis P., Antoniou M., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring integration site-independent gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):352–355. doi: 10.1038/338352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taramelli R., Kioussis D., Vanin E., Bartram K., Groffen J., Hurst J., Grosveld F. G. Gamma delta beta-thalassaemias 1 and 2 are the result of a 100 kbp deletion in the human beta-globin cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7017–7029. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D. Y., Solomon W. B., London I. M., Lee D. P. An erythroid-specific, developmental-stage-independent enhancer far upstream of the human "beta-like globin" genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., Rosenthal A., Flavell R., Grosveld F. DNA sequences required for regulated expression of beta-globin genes in murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90548-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., deBoer E., Grosveld F. G., Flavell R. A. Regulated expression of the human beta-globin gene family in murine erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):333–336. doi: 10.1038/305333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBoer E., Antoniou M., Mignotte V., Wall L., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin promoter; nuclear protein factors and erythroid specific induction of transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4203–4212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03317.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]