Abstract
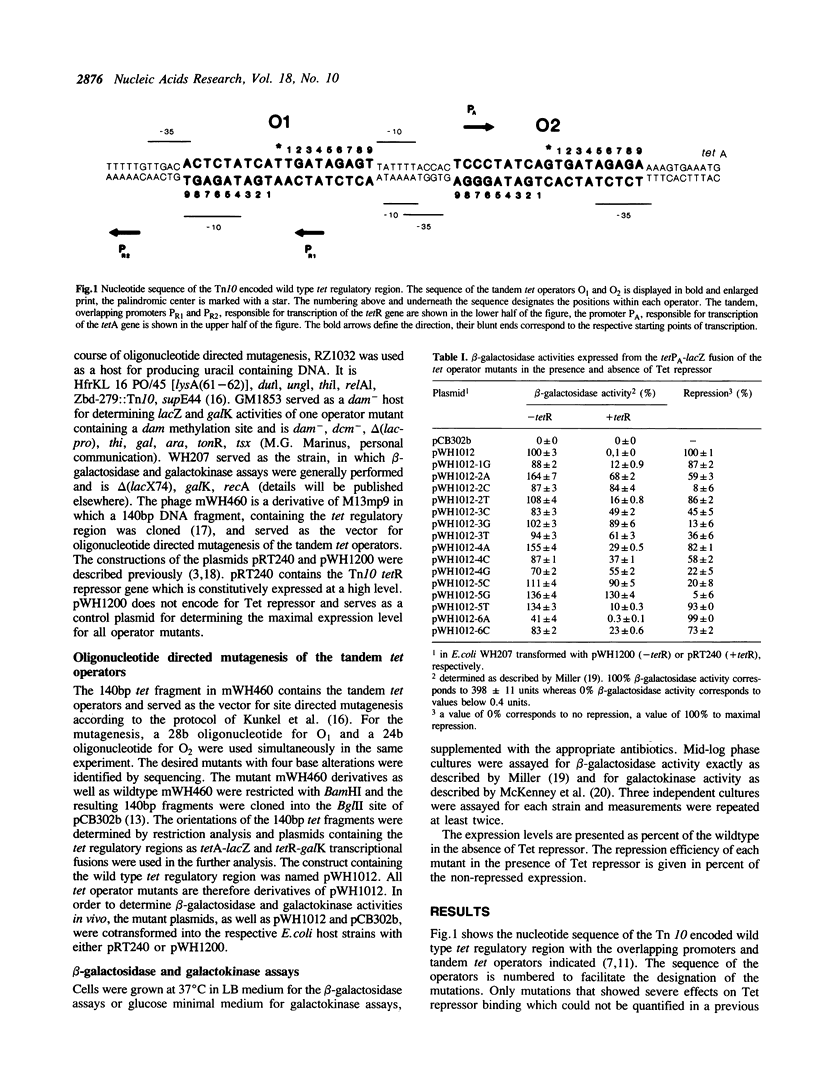
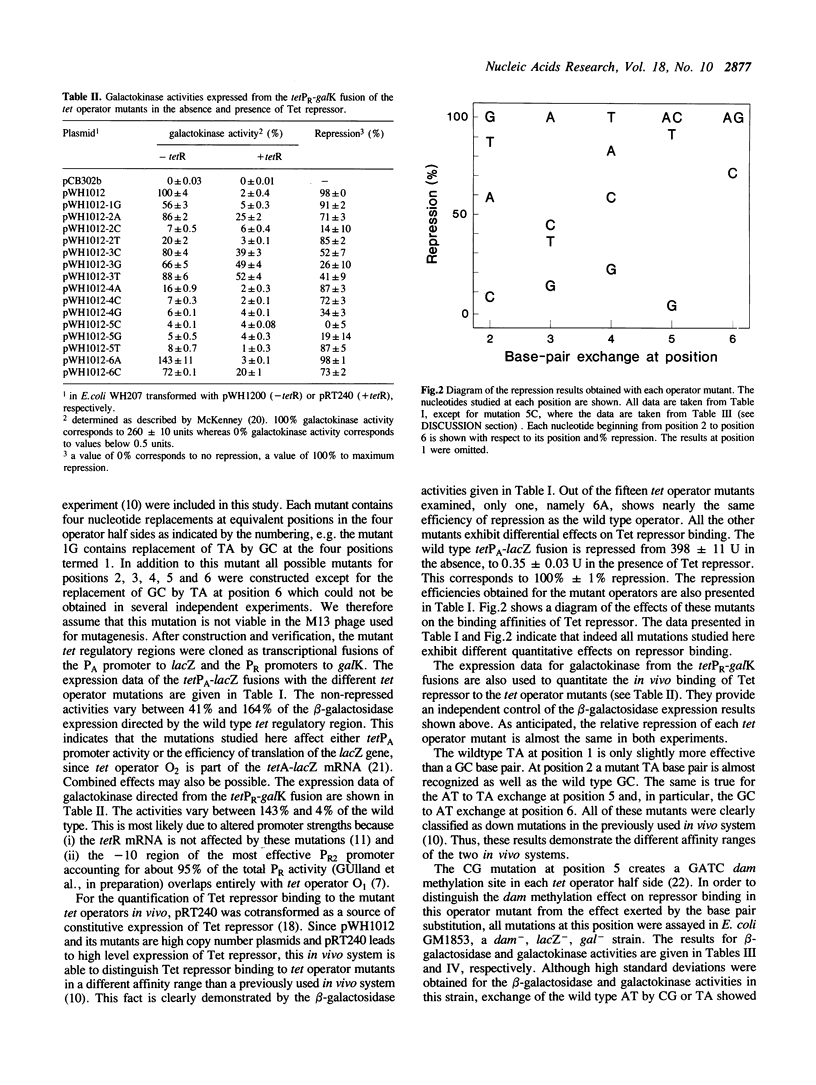
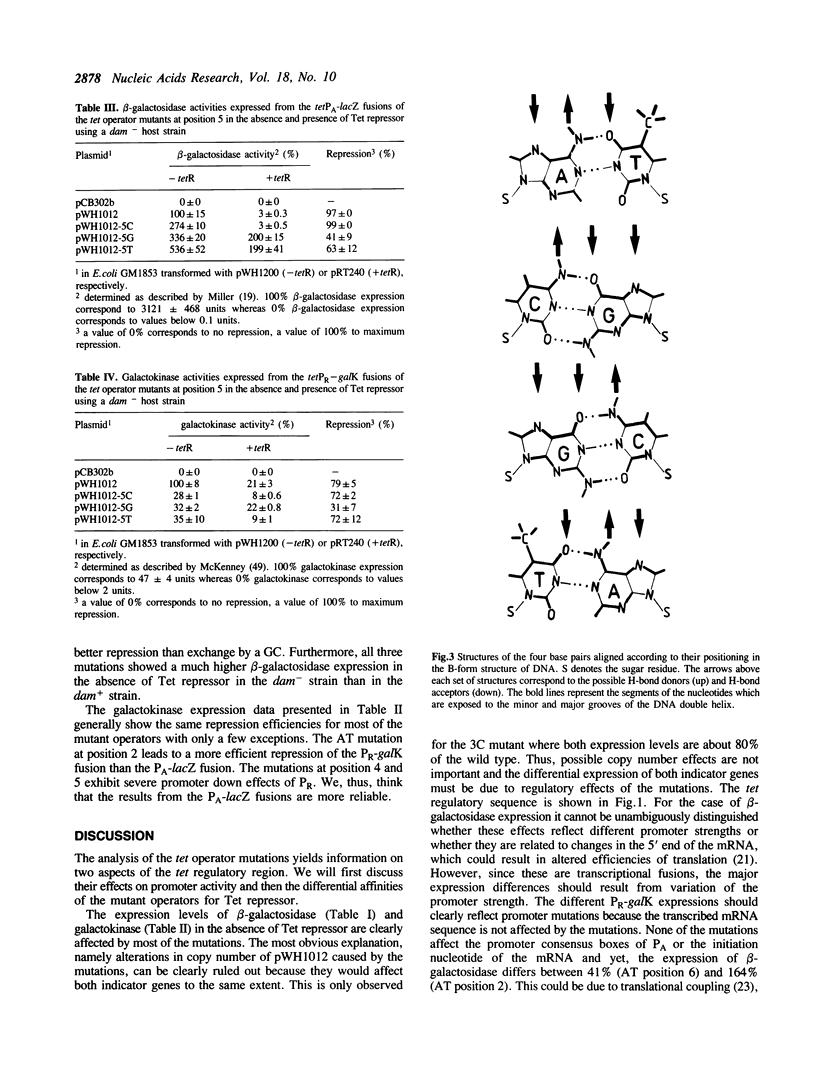
A saturating oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of both tet operators in the tet regulatory sequence was performed yielding mutants with four identical base pair exchanges at equivalent positions in the four tet operator half sides. The mutants were cloned between bipolar lacZ and galK indicator genes on a multicopy plasmid allowing the quantitative analysis of their effects in vivo. In the absence of Tet repressor the mutations lead to considerably different expression levels of both genes. They are discussed with respect to the promoter consensus sequences. In particular, the -10 region of the in vivo active tetPR2 promoter is unambiguously defined by these results. In the presence of Tet repressor most of the mutants exhibit a lower affinity for that protein as determined quantitatively by their reduced expression levels. In general, tet operator recognition is most strongly affected by alterations of base pairs near the center of the palindromic sequence. The most important position is the third base pair, followed by base pairs two, four, five and six, the latter showing similar effects as base pair one. At each position, the four possible base pairs show different affinities for Tet repressor. They are discussed according to their exposure of H-bond donors and -acceptors in the major and minor grooves of the B-DNA. The results are in agreement with major groove contacts at positions two, three and five. At position four a low potential correlation of efficiencies with the H-bonding in the minor groove is found, while mutations at position six seem to influence repressor binding by other mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschmied L., Baumeister R., Pfleiderer K., Hillen W. A threonine to alanine exchange at position 40 of Tet repressor alters the recognition of the sixth base pair of tet operator from GC to AT. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):4011–4017. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand K. P., Postle K., Wray L. V., Jr, Reznikoff W. S. Overlapping divergent promoters control expression of Tn10 tetracycline resistance. Gene. 1983 Aug;23(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D. W., Bertrand K. P. Promoter mutations affecting divergent transcription in the Tn10 tetracycline resistance determinant. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen D., Altschmied L., Hillen W. Engineered Tet repressor mutants with single tryptophan residues as fluorescent probes. Solvent accessibilities of DNA and inducer binding sites and interaction with tetracycline. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14030–14035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen D., Hillen W. Tryptophan in alpha-helix 3 of Tet repressor forms a sequence-specific contact with tet operator in solution. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12269–12274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillen W., Gatz C., Altschmied L., Schollmeier K., Meier I. Control of expression of the Tn10-encoded tetracycline resistance genes. Equilibrium and kinetic investigation of the regulatory reactions. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 25;169(3):707–721. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillen W., Schollmeier K., Gatz C. Control of expression of the Tn10-encoded tetracycline resistance operon. II. Interaction of RNA polymerase and TET repressor with the tet operon regulatory region. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 15;172(2):185–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isackson P. J., Bertrand K. P. Dominant negative mutations in the Tn10 tet repressor: evidence for use of the conserved helix-turn-helix motif in DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6226–6230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler C., Höltke H. J. Specificity of restriction endonucleases and methylases--a review. Gene. 1986;47(1):1–153. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90245-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt C., Tovar K., Hillen W., Porschke D. Dynamics of repressor-operator recognition: the Tn10-encoded tetracycline resistance control. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1094–1104. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klock G., Unger B., Gatz C., Hillen W., Altenbuchner J., Schmid K., Schmitt R. Heterologous repressor-operator recognition among four classes of tetracycline resistance determinants. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):326–332. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.326-332.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier I., Wray L. V., Hillen W. Differential regulation of the Tn10-encoded tetracycline resistance genes tetA and tetR by the tandem tet operators O1 and O2. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):567–572. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02846.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postle K., Nguyen T. T., Bertrand K. P. Nucleotide sequence of the repressor gene of the TN10 tetracycline resistance determinant. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4849–4863. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Beck C. F. New expression vectors for identifying and testing signal structures for initiation and termination of transcription. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:452–461. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Beck C. F. Point mutations that affect translation initiation of the transposon Tn10 tetA gene. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):559–563. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Beck C. F. Promoter-probe vectors for the analysis of divergently arranged promoters. Gene. 1986;42(1):37–48. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissmann A., Meier I., Hillen W. Saturation mutagenesis of the Tn10-encoded tet operator O1. Identification of base-pairs involved in Tet repressor recognition. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. V., Jr, Reznikoff W. S. Identification of repressor binding sites controlling expression of tetracycline resistance encoded by Tn10. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1188–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1188-1191.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


