Abstract
The cloning of large DNA fragments of hundreds of kilobases in Yeast artificial chromosomes, has simplified the analysis of regions of the genome previously cloned by cosmid walking. The mapping of expressed sequences within cosmid contigs has relied on the association of genes with sequence motifs defined by rare-cutting endonucleases, and the identification of sequence conservation between species. We reasoned that if the contribution of repetitive sequences to filter hybridizations could be minimised, then the use of large cloned DNAs as hybridisation probes to screen cDNA libraries would greatly simplify the characterisation of hitherto unidentified genes. In this paper we demonstrate the use of this approach by using a YAC, containing 180 kb of human genomic DNA including the aldose reductase gene, as a probe to isolate an aldose reductase cDNA from a lambda gt11 human foetal liver cDNA library.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand R., Riley J. H., Butler R., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. A 3.5 genome equivalent multi access YAC library: construction, characterisation, screening and storage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):1951–1956. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickmore W. A., Sumner A. T. Mammalian chromosome banding--an expression of genome organization. Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
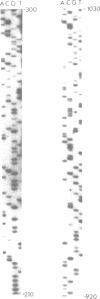
- Graham A., Hedge P. J., Powell S. J., Riley J., Brown L., Gammack A., Carey F., Markham A. F. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA for human aldose reductase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8368–8368. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Olson M. V. Systematic screening of yeast artificial-chromosome libraries by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard E., Davies B., Feo S., Fried M. An improved method for the screening of YAC libraries. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5861–5861. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwu H. R., Roberts J. W., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Insertion and/or deletion of many repeated DNA sequences in human and higher ape evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3875–3879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C. R., Kalsheker N., Graham A., Powell S., Gammack A., Riley J., Markham A. F. Diagnosis of alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency by enzymatic amplification of human genomic DNA and direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8233–8243. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Dunham I., Campbell R. D. Identification of multiple HTF-island associated genes in the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey P. G., Whittaker P. A., Southern E. M. Removal of repeated sequences from hybridisation probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1905–1922. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Anand R., Brown W. R., Fletcher D. S. A model for the separation of large DNA molecules by crossed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5925–5943. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]