Abstract
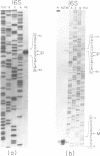
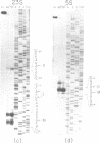
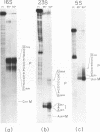
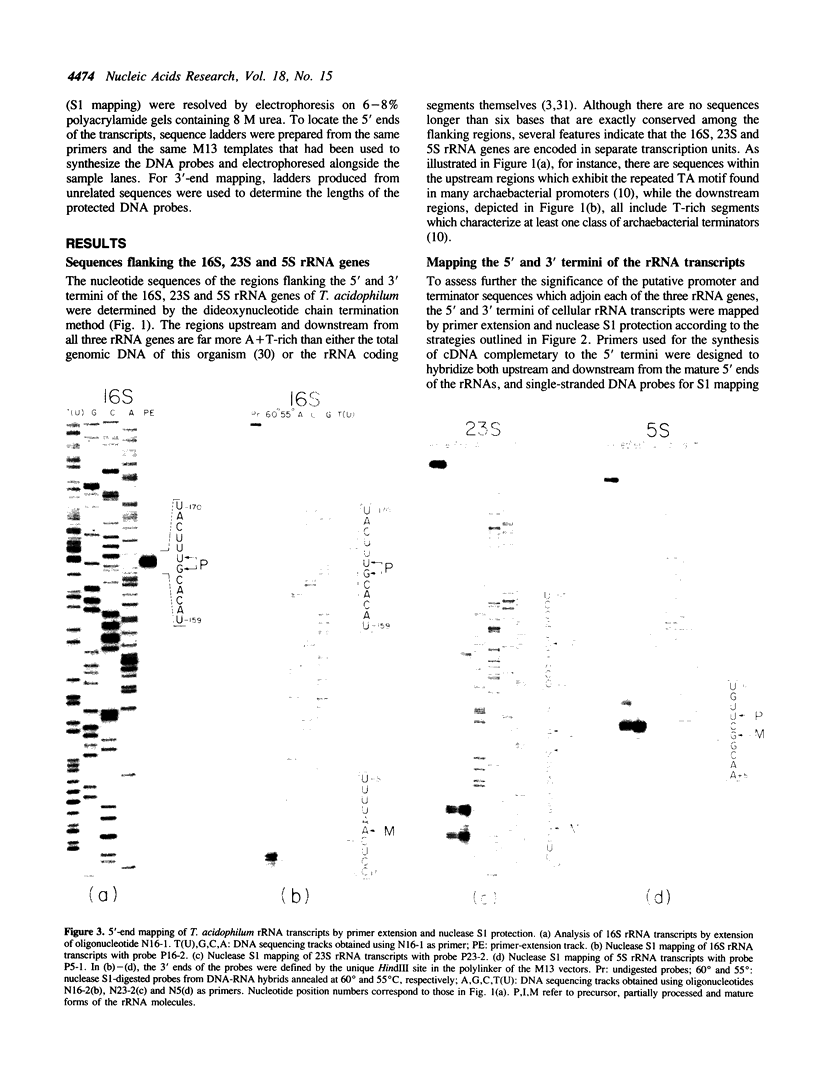
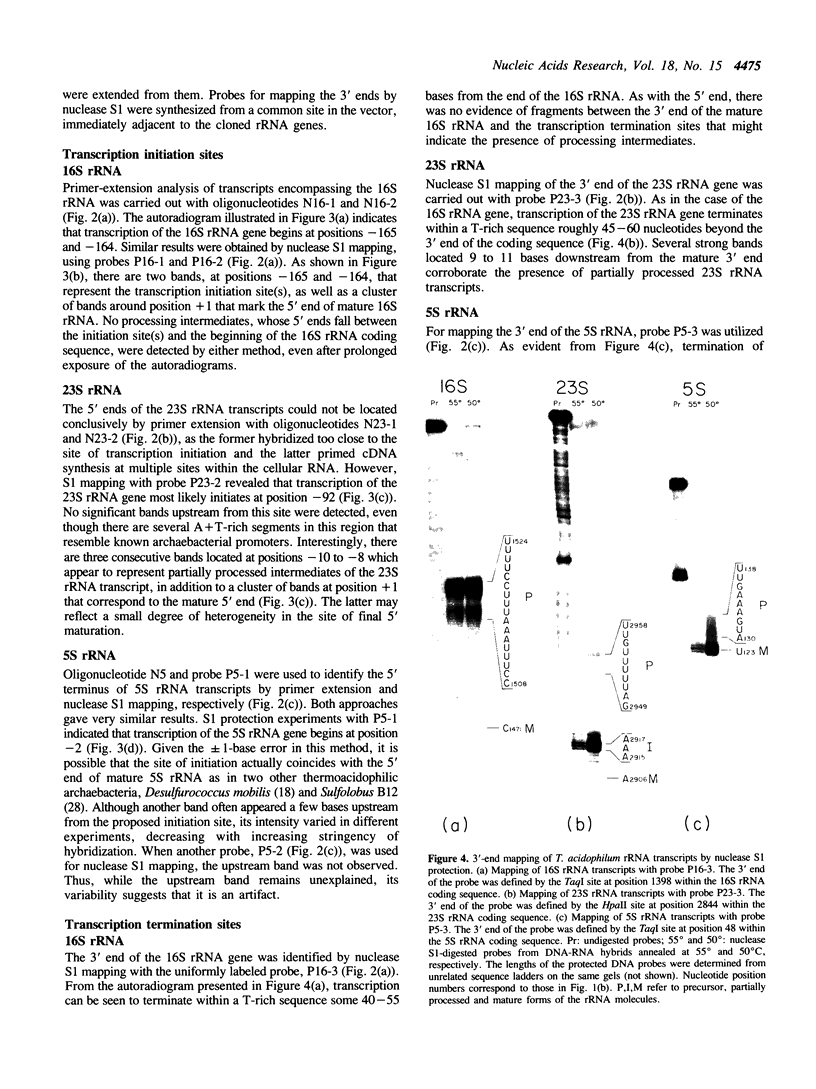
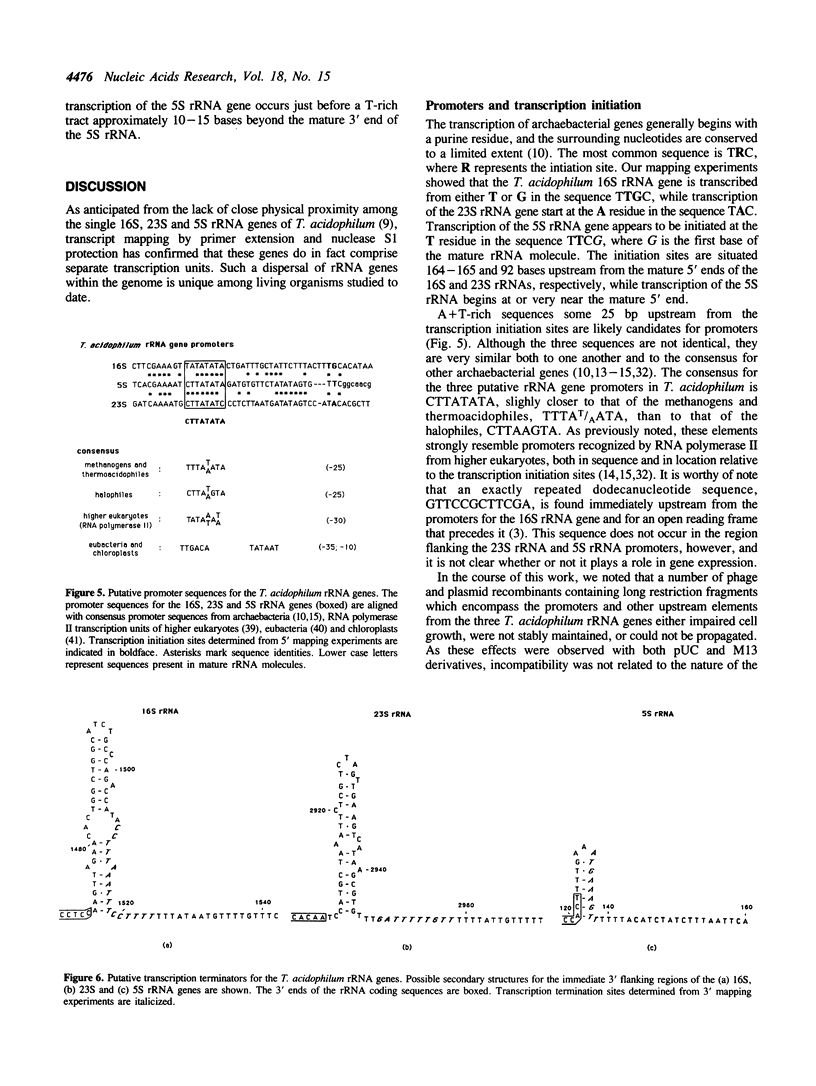
To elucidate the organization of the transcription units encoding the 16S, 23S and 5S rRNAs in the archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum, the nucleotide sequences flanking the three rRNA genes were determined, and the 5' and 3' termini of the rRNA transcripts were mapped by primer extension and nuclease S1 protection. The results show that each of the rRNAs is transcribed separately, consistent with the lack of physical proximity among them in the T. acidophilum genome. The transcription initiation sites are preceded at an interval of approximately 25 base pairs by conserved A + T-rich sequences of the form CTTATATA, which strongly resemble the archaebacterial promoter consensus, TTTAT/AATA. In all three cases, transcription termination occurs within T-rich tracts just downstream from inverted repeats which can be folded into relatively stable stem-loop structures. While no partially processed intermediates of the 16S or 5S rRNA transcripts were detected, the 23S rRNA transcript appears to be processed by a RNase III-like activity prior to final maturation. This is the only organism known in the prokaryotic world in which the 16S, 23S and 5S rRNAs are all expressed from separate transcription units.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Daniels C. J., Reeve J. N. Gene structure, organization, and expression in archaebacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;16(4):287–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Thomm M., Beckler G. S., Frey G., Stetter K. O., Reeve J. N. An archaebacterial RNA polymerase binding site and transcription initiation of the hisA gene in Methanococcus vannielii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):135–150. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chant J., Dennis P. Archaebacteria: transcription and processing of ribosomal RNA sequences in Halobacterium cutirubrum. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1091–1097. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darland G., Brock T. D., Samsonoff W., Conti S. F. A thermophilic, acidophilic mycoplasma isolated from a coal refuse pile. Science. 1970 Dec 25;170(3965):1416–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3965.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassarma S., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Bacterio-opsin mRNA in wild-type and bacterio-opsin-deficient Halobacterium halobium strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):125–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R. K., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. An unusual rRNA operon constellation: in Thermus thermophilus HB8 the 23S/5S rRNA operon is a separate entity from the 16S rRNA operon. Biochimie. 1987 Oct;69(10):1097–1104. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. C., Sirdeskmukh R., Schlessinger D. Nucleolytic processing of ribonucleic acid transcripts in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):428–451. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.428-451.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Garrett R. A. Novel expression of the ribosomal RNA genes in the extreme thermophile and archaebacterium Desulfurococcus mobilis. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3521–3530. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Leffers H., Garrett R. A., Wich G., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Gene organization, transcription signals and processing of the single ribosomal RNA operon of the archaebacterium Thermoproteus tenax. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4821–4835. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung S. D., Lin C. M. Chloroplast promoters from higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7543–7549. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A. Origin of the eukaryotic nucleus: eukaryotes and eocytes are genotypically related. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):109–118. doi: 10.1139/m89-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liesack W., Stackebrandt E. Evidence for unlinked rrn operons in the Planctomycete Pirellula marina. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5025–5030. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5025-5030.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ree H. K., Cao K. M., Thurlow D. L., Zimmermann R. A. The structure and organization of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene from the archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):124–133. doi: 10.1139/m89-019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Voos W., Kaniecki J., Grampp B., Schulz W., Zillig W. Putative promoter elements for the ribosomal RNA genes of the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus sp. strain B12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5581–5595. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Zillig W. Analysis of transcription in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus indicates that archaebacterial promoters are homologous to eukaryotic pol II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):1–19. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Zillig W. Transcription termination in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus: signal structures and linkage to transcription initiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2445–2459. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel R., Thomm M., Gerardy-Schahn R., Zillig W., Stetter K. O., Huet J. Structural homology between different archaebacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerases analyzed by immunological comparison of their components. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):751–755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A. K., Schlessinger D. Processing pathway of Escherichia coli 16S precursor rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1649–1663. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomm M., Wich G. An archaebacterial promoter element for stable RNA genes with homology to the TATA box of higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):151–163. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu J., Zillig W. Organization of rRNA structural genes in the archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7231–7245. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wich G., Hummel H., Jarsch M., Bär U., Böck A. Transcription signals for stable RNA genes in Methanococcus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2459–2479. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. G., Redborg A. H., Cue D. R., Whitman W. B., Konisky J. Complementation of argG and hisA mutations of Escherichia coli by DNA cloned from the archaebacterium Methanococcus voltae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):19–29. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.19-29.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Klenk H. P., Palm P., Pühler G., Gropp F., Garrett R. A., Leffers H. The phylogenetic relations of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases of archaebacteria, eukaryotes, and eubacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):73–80. doi: 10.1139/m89-011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Palm P., Reiter W. D., Gropp F., Pühler G., Klenk H. P. Comparative evaluation of gene expression in archaebacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 2;173(3):473–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]