Abstract
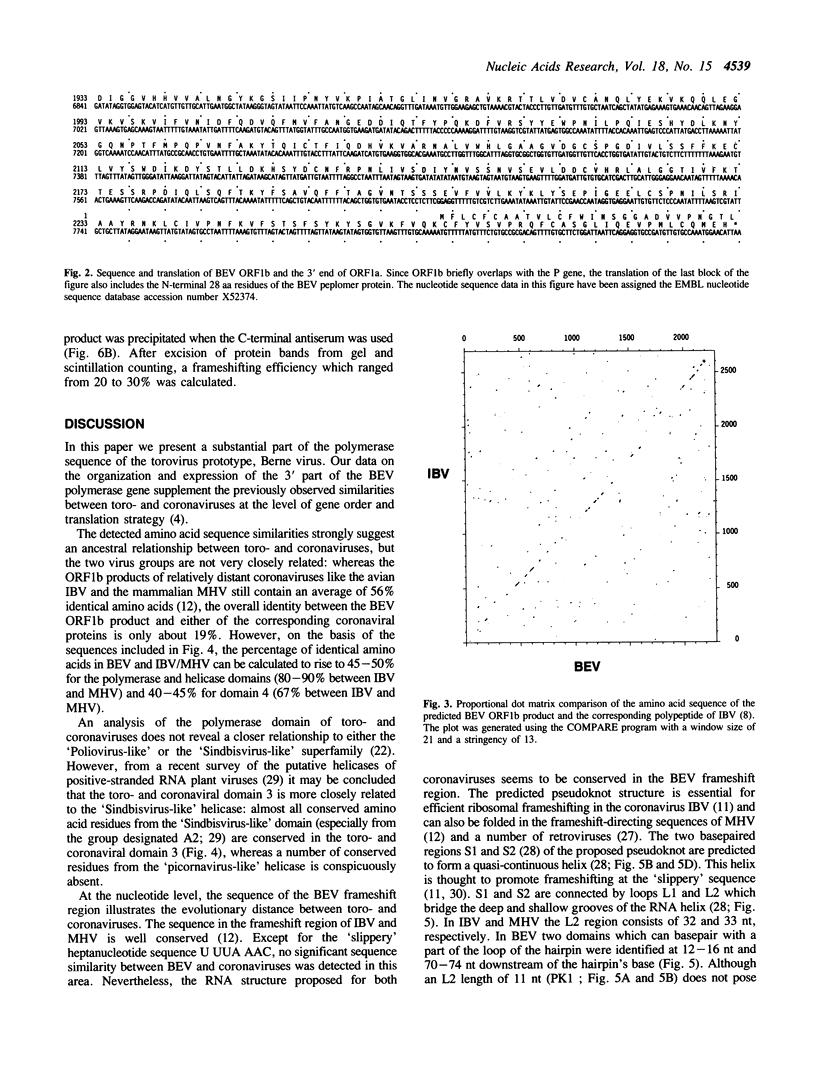
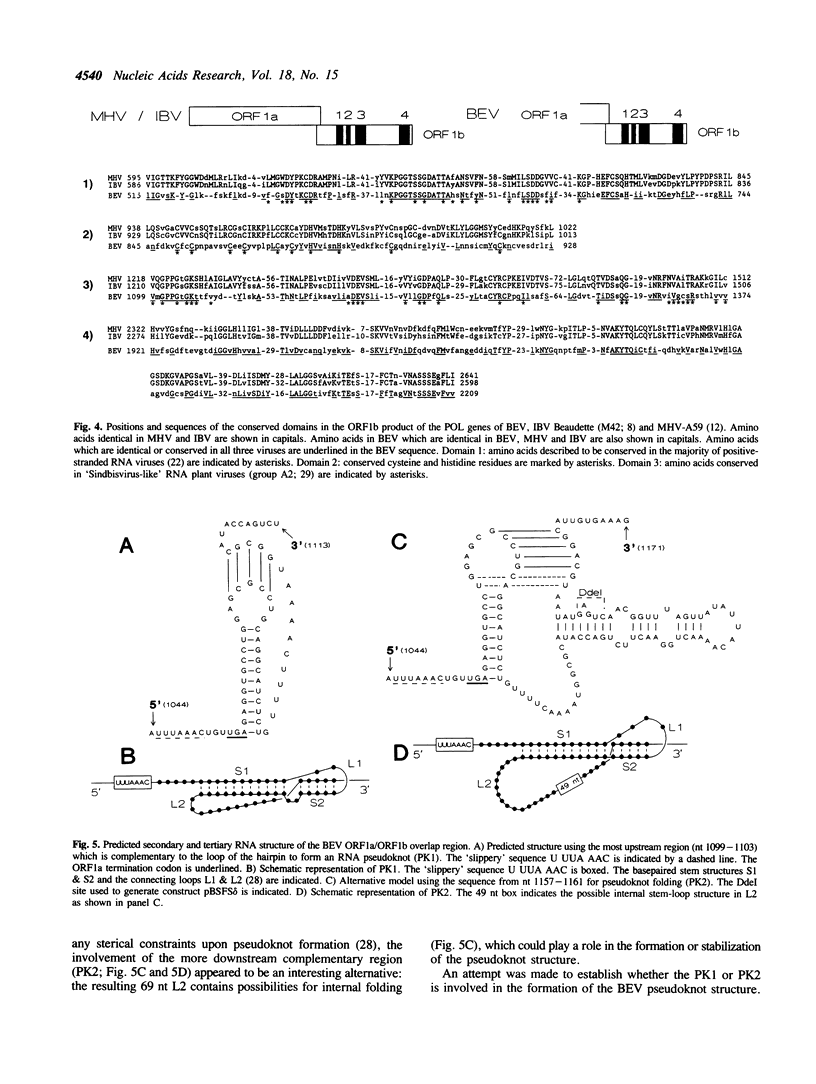
Sequence analysis of the 3' part (8 kb) of the polymerase gene of the torovirus prototype Berne virus (BEV) revealed that this area contains at least two open reading frames (provisionally designated ORF1a and ORF1b) which overlap by 12 nucleotides. The complete sequence of ORF1b (6873 nucleotides) was determined. Like the coronaviruses, BEV was shown to express its ORF1b by ribosomal frameshifting during translation of the genomic RNA. The predicted tertiary RNA structure (a pseudoknot) in the toro- and coronaviral frameshift-directing region is similar. Analysis of the amino acid sequence of the predicted BEV ORF1b translation product revealed homology with the ORF1b product of coronaviruses. Four conserved domains were identified: the putative polymerase domain, an area containing conserved cysteine and histidine residues, a putative helicase motif, and a domain which seems to be unique for toro- and coronaviruses. The data on the 3' part of the polymerase gene of BEV supplement previously observed similarities between toro- and coronaviruses at the level of genome organization and expression. The two virus families are more closely related to each other than to other families of positive-stranded RNA viruses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J., Niemann H., Smeekens S., Rottier P., Warren G. Sequence and topology of a model intracellular membrane protein, E1 glycoprotein, from a coronavirus. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):751–752. doi: 10.1038/308751a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boursnell M. E., Brown T. D., Foulds I. J., Green P. F., Tomley F. M., Binns M. M. Completion of the sequence of the genome of the coronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):57–77. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredenbeek P. J., Pachuk C. J., Noten A. F., Charité J., Luytjes W., Weiss S. R., Spaan W. J. The primary structure and expression of the second open reading frame of the polymerase gene of the coronavirus MHV-A59; a highly conserved polymerase is expressed by an efficient ribosomal frameshifting mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1825–1832. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Boursnell M. E., Binns M. M., Bilimoria B., Blok V. C., Brown T. D., Inglis S. C. An efficient ribosomal frame-shifting signal in the polymerase-encoding region of the coronavirus IBV. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3779–3785. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Stohlman S. A., Harmon R. C., Lai M. M., Frelinger J. A., Weiner L. P. Antigenic relationships of murine coronaviruses: analysis using monoclonal antibodies to JHM (MHV-4) virus. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):296–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90498-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbach R., Wellink J. Evolution of plus-strand RNA viruses. Intervirology. 1988;29(5):260–267. doi: 10.1159/000150054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Coronavirus genome: prediction of putative functional domains in the non-structural polyprotein by comparative amino acid sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4847–4861. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V. Viral proteins containing the purine NTP-binding sequence pattern. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8413–8440. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habili N., Symons R. H. Evolutionary relationship between luteoviruses and other RNA plant viruses based on sequence motifs in their putative RNA polymerases and nucleic acid helicases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9543–9555. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C. A new superfamily of replicative proteins. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–23. doi: 10.1038/333022b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horzinek M. C., Flewett T. H., Saif L. J., Spaan W. J., Weiss M., Woode G. N. A new family of vertebrate viruses: Toroviridae. Intervirology. 1987;27(1):17–24. doi: 10.1159/000149710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Madhani H. D., Masiarz F. R., Varmus H. E. Signals for ribosomal frameshifting in the Rous sarcoma virus gag-pol region. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90031-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamer G., Argos P. Primary structural comparison of RNA-dependent polymerases from plant, animal and bacterial viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7269–7282. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachuk C. J., Bredenbeek P. J., Zoltick P. W., Spaan W. J., Weiss S. R. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the putative polymerase of mouse hepatitis coronavirus, strain A59. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90520-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleij C. W., Rietveld K., Bosch L. A new principle of RNA folding based on pseudoknotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1717–1731. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Sauvaget I., Delarue M., Tordo N. Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P. RNA pseudoknots that interact with components of the translation apparatus. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90395-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E. J., Ederveen J., Spaan W. J., Weiss M., Horzinek M. C. Characterization of Berne virus genomic and messenger RNAs. J Gen Virol. 1988 Sep;69(Pt 9):2135–2144. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-9-2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E. J., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. A 3'-coterminal nested set of independently transcribed mRNAs is generated during Berne virus replication. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):331–338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.331-338.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E. J., den Boon J. A., Spaan W. J., Verjans G. M., Horzinek M. C. Identification and primary structure of the gene encoding the Berne virus nucleocapsid protein. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3363–3370. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Cavanagh D., Horzinek M. C. Coronaviruses: structure and genome expression. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):2939–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. H., Strauss E. G. Evolution of RNA viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:657–683. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M., Horzinek M. C. The proposed family Toroviridae: agents of enteric infections. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1987;92(1-2):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01310058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



