Abstract
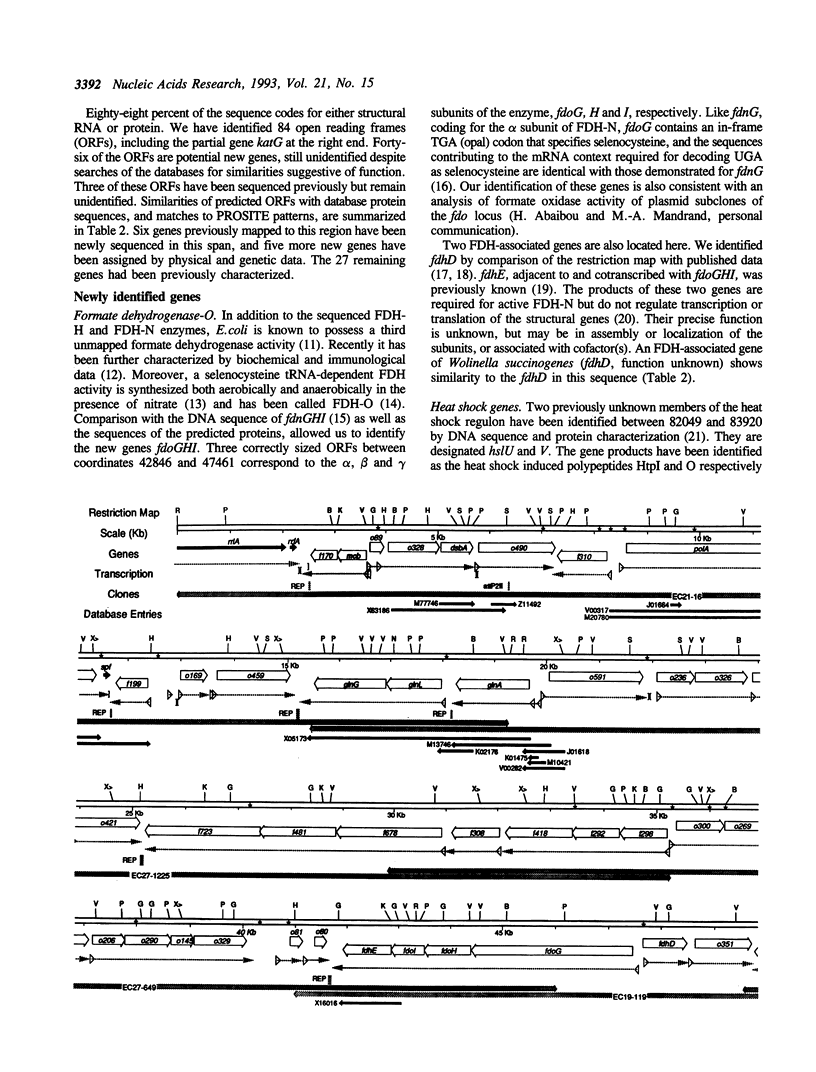
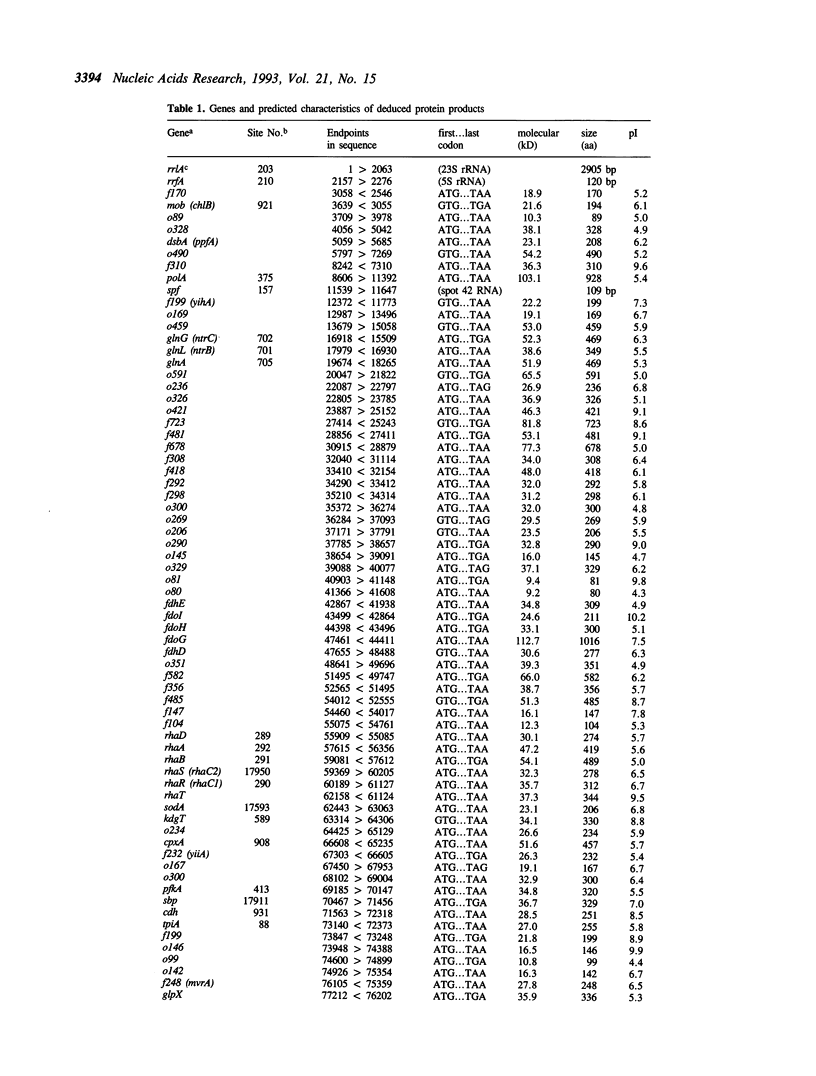
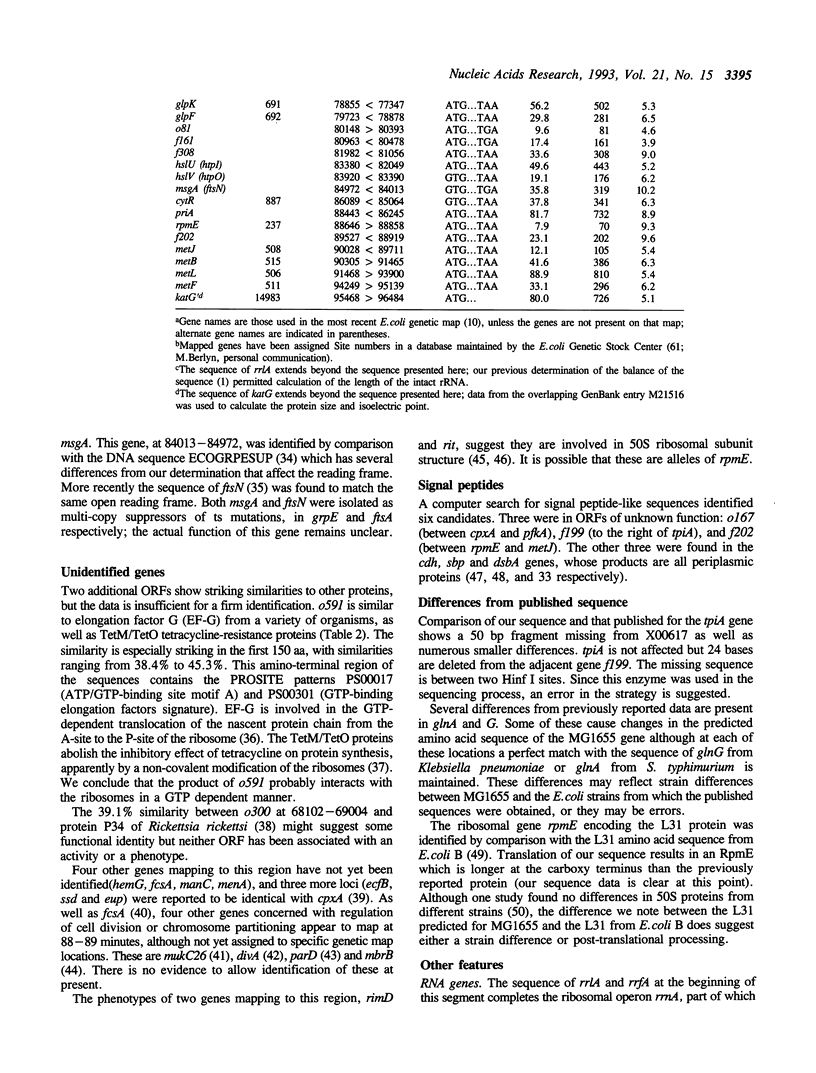
The DNA sequence of 96.5 kilobases of the Escherichia coli K-12 genome has been determined, spanning the region between rrnA at 87.2 minutes and katG at 89.2 minutes on the genetic map. The sequence includes 84 open reading frames, of which 46 code for unidentified proteins. Six previously mapped but unsequenced genes have been identified in this span: mob, fdhD, rhaD, rhaA, rhaB, and kdgT. In addition, five new genes have been assigned: the heat shock genes hsIU and hsIV, and the genes fdoG, fdoH, and fdoI, which encode the three subunits of formate dehydrogenase-O. The arrangement of the genes relative to possible promoters and terminators suggests 57 potential transcription units. Other features include the precise location of the bacteriophage P2 attachment site attP2II, and eleven REP elements, including one containing 9 REP sequences--one of the largest such elements known. This segment brings the total length of contiguous finished sequence to 325 kilobases.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldea M., Maples V. F., Kushner S. R. Generation of a detailed physical and genetic map of the ilv-metE-udp region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90533-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen C., Reverchon S., Robert-Baudouy J. Nucleotide sequence of the Erwinia chrysanthemi gene encoding 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate permease. Gene. 1989 Nov 30;83(2):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Baumstark B. R., Bellini W. J. Nucleotide sequence of the P34 gene from Rickettsia rickettsii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7168–7168. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badía J., Baldomà L., Aguilar J., Boronat A. Identification of the rhaA, rhaB and rhaD gene products from Escherichia coli K-12. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Dec;53(3):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A. PROSITE: a dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2013–2018. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldomá L., Badía J., Sweet G., Aguilar J. Cloning, mapping and gene product identification of rhaT from Escherichia coli K12. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Oct;60(1-2):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90353-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., McGovern K., Beckwith J. Identification of a protein required for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):581–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg B. L., Baron C., Stewart V. Nitrate-inducible formate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli K-12. II. Evidence that a mRNA stem-loop structure is essential for decoding opal (UGA) as selenocysteine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22386–22391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg B. L., Li J., Heider J., Stewart V. Nitrate-inducible formate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli K-12. I. Nucleotide sequence of the fdnGHI operon and evidence that opal (UGA) encodes selenocysteine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22380–22385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlyn M. B., Letovsky S. Genome-related datasets within the E. coli Genetic Stock Center database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6143–6151. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Primary structure of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L31. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):501–508. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant R. E., Sypherd P. S. Genetic analysis of cold-sensitive ribosome maturation mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1082–1092. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1082-1092.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burland V., Daniels D. L., Plunkett G., 3rd, Blattner F. R. Genome sequencing on both strands: the Janus strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3385–3390. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burland V., Plunkett G., 3rd, Daniels D. L., Blattner F. R. DNA sequence and analysis of 136 kilobases of the Escherichia coli genome: organizational symmetry around the origin of replication. Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):551–561. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A., Forchhammer K., Heider J., Baron C. Selenoprotein synthesis: an expansion of the genetic code. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieśla Z., Bagdasarian M., Szczurkiewicz W., Przygońska M., Klopotowski T. Defective cell division in thermosensitive mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(2):107–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00582221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D. L., Plunkett G., 3rd, Burland V., Blattner F. R. Analysis of the Escherichia coli genome: DNA sequence of the region from 84.5 to 86.5 minutes. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):771–778. doi: 10.1126/science.1379743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimri G. P., Rudd K. E., Morgan M. K., Bayat H., Ames G. F. Physical mapping of repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences in Escherichia coli and phylogenetic distribution among Escherichia coli strains and other enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4583–4593. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4583-4593.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. MacPattern: protein pattern searching on the Apple Macintosh. Comput Appl Biosci. 1991 Jan;7(1):105–106. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/7.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Saurin W., Perrin D., Bachellier S., Hofnung M. Palindromic units are part of a new bacterial interspersed mosaic element (BIME). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1375–1383. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González J. C., Banerjee R. V., Huang S., Sumner J. S., Matthews R. G. Comparison of cobalamin-independent and cobalamin-dependent methionine synthases from Escherichia coli: two solutions to the same chemical problem. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 7;31(26):6045–6056. doi: 10.1021/bi00141a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga S., Niki H., Imamura R., Ogura T., Yamanaka K., Feng J., Ezaki B., Jaffé A. Mutants defective in chromosome partitioning in E. coli. Res Microbiol. 1991 Feb-Apr;142(2-3):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90029-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain K., Begg K. J., Salmond G. P., Donachie W. D. ParD: a new gene coding for a protein required for chromosome partitioning and septum localization in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):73–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isihara H., Hogg R. W. Amino acid sequence of the sulfate-binding protein from Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4614–4618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Indermaur L. W., Rajagopalan K. V. Molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Requirement of the chlB gene product for the formation of molybdopterin guanine dinucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12140–12145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Crothers D. M. A computer graphics study of sequence-directed bending in DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(2):429–435. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Couchoux-Luthaud G., Santini C. L., Giordano G. Mutants of Escherichia coli specifically deficient in respiratory formate dehydrogenase activity. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Dec;134(12):3129–3139. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-12-3129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Ritzenthaler P., Mata-Gilsinger M. Construction and expression of hybrid plasmids containing the structural gene of the Escherichia coli K-12 3-deoxy-2-oxo-D-gluconate transport system. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):600–606. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.600-606.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldave K. Eukaryotic protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1109–1149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishitani J., Wilcox G. Cloning and characterization of the L-rhamnose regulon in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Gene. 1991 Aug 30;105(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Kuwano M. Mutation affecting the thermolability of the 50S ribosomal subunit in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):677–679. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.677-679.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Takata R., Dekio S. Genetic studies of the ribosomal proteins in Escherichia coli. 3. Compositions of ribosomal proteins in various strains of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;107(1):32–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00433221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINSENT J. The need for selenite and molybdate in the formation of formic dehydrogenase by members of the coli-aerogenes group of bacteria. Biochem J. 1954 May;57(1):10–16. doi: 10.1042/bj0570010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier J., Mandrand M. A., Holt S. E., Boxer D. H., Giordano G. A second phenazine methosulphate-linked formate dehydrogenase isoenzyme in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 30;1107(2):305–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90417-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power J. The L-rhamnose genetic system in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1967 Mar;55(3):557–568. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R., Hirschberg C. B., Dowhan W., Wickner W. T., Kennedy E. P. A membrane-bound pyrophosphatase in Escherichia coli catalyzing the hydrolysis of cytidine diphosphate-diglyceride. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2245–2247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainwater S., Silverman P. M. The Cpx proteins of Escherichia coli K-12: evidence that cpxA, ecfB, ssd, and eup mutations all identify the same gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2456–2461. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2456-2461.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss J., Kleinhofs A., Klingmüller W. Cloning of seven differently complementing DNA fragments with chl functions from Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Feb;206(2):352–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00333594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Speer B. S., Shoemaker N. B. New perspectives in tetracycline resistance. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):151–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santini C. L., Karibian D., Vasishta A., Boxer D., Giordano G. Escherichia coli molybdoenzymes can be activated by protein FA from several gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Dec;135(12):3467–3475. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers G., Heider J., Zehelein E., Böck A. Expression and operon structure of the sel genes of Escherichia coli and identification of a third selenium-containing formate dehydrogenase isoenzyme. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):4983–4993. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.4983-4993.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlindwein C., Giordano G., Santini C. L., Mandrand M. A. Identification and expression of the Escherichia coli fdhD and fdhE genes, which are involved in the formation of respiratory formate dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):6112–6121. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.6112-6121.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlindwein C., Mandrand M. A. Nucleotide sequence of the fdhE gene involved in respiratory formate dehydrogenase formation in Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1991 Jan 2;97(1):147–148. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. L., Blattner F. R. Formal description of a DNA oriented computer language. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):69–84. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharples G. J., Lloyd R. G. A novel repeated DNA sequence located in the intergenic regions of bacterial chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6503–6508. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V., Lin J. T., Berg B. L. Genetic evidence that genes fdhD and fdhE do not control synthesis of formate dehydrogenase-N in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4417–4423. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4417-4423.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin J. F., Schleif R. F. Positive regulation of the Escherichia coli L-rhamnose operon is mediated by the products of tandemly repeated regulatory genes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):789–799. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90405-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trun N. J., Gottesman S. On the bacterial cell cycle: Escherichia coli mutants with altered ploidy. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2036–2047. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu A., Bertani L. E., Haggård-Ljungquist E. Control of prophage integration and excision in bacteriophage P2: nucleotide sequences of the int gene and att sites. Gene. 1989 Aug 1;80(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


