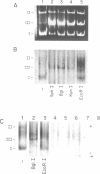
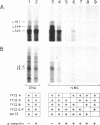
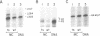Abstract
Using SV40 minichromosomes assembled in vivo, we have studied the relationship between a nucleosome-free promoter-region and initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II on chromatin templates in vitro. Our data suggest that accessibility of DNA to transcription factors, programmed into the structure of the chromatin, is crucial for initiation of transcription. First, minichromosomes competent to be transcribed in vitro contained nucleosome-free promoter regions. Second, tsC219 minichromosomes, most of which contain the nucleosome-free promoter region, supported transcription more efficiently both in vivo and in vitro than wild-type minichromosomes, in which only a subset contain the nucleosome-free region. We have also identified basal transcription factors associated with the in vivo-assembled chromatin templates. A striking correlation was observed between minichromosomes associated with in vivo initiated RNA polymerases and those associated with the basal transcription factors TFIID and TFIIE/F, and to a lesser extent, TFIIB. Of these associated factors, only TFIID was poised for ready assembly into preinitiation complexes and therefore for subsequent initiation of transcription. However, an active chromatin template could also be maintained in the absence of the binding of TFIID. Finally, our data are consistent with the presence of TFIIF in elongating ternary complexes on the chromatin templates.
Full text
PDF

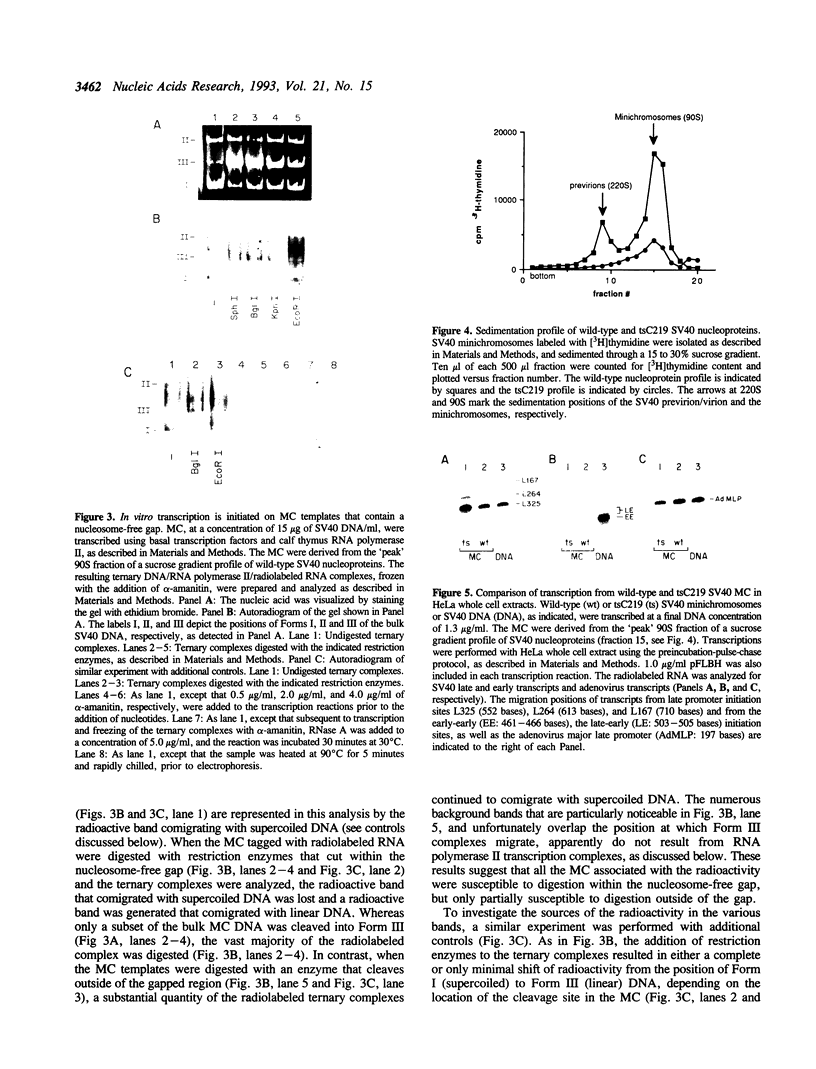

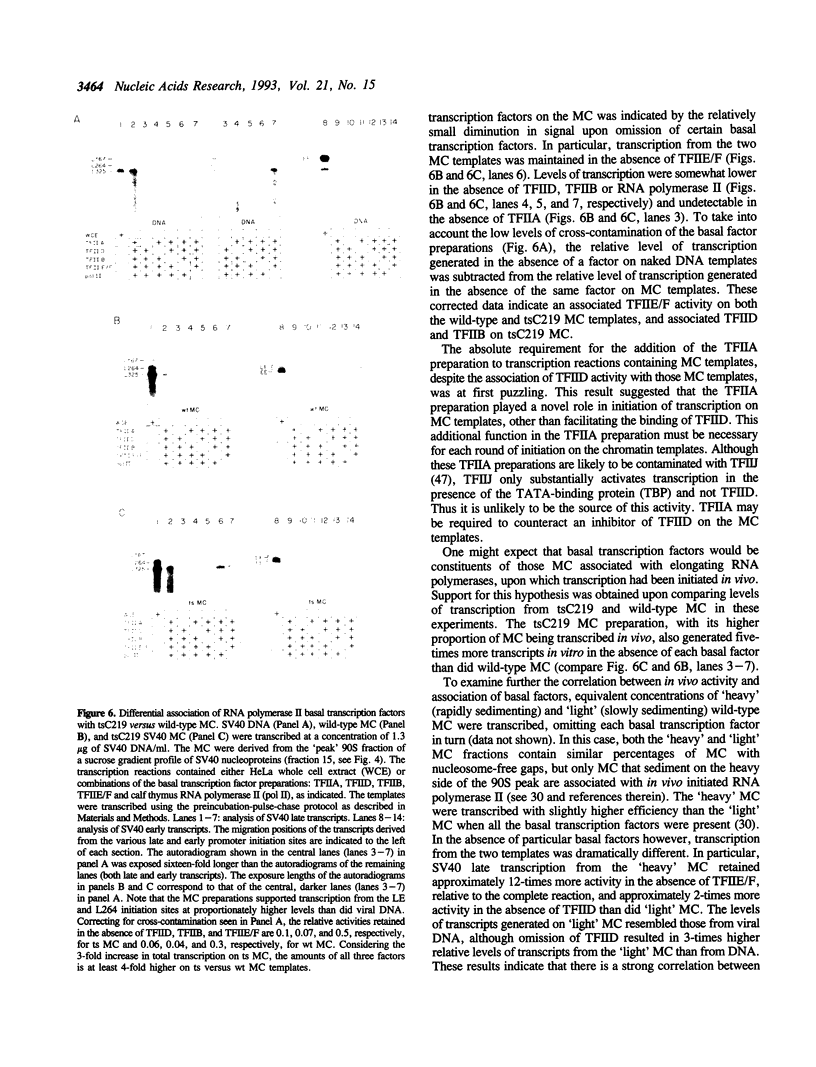




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almer A., Rudolph H., Hinnen A., Hörz W. Removal of positioned nucleosomes from the yeast PHO5 promoter upon PHO5 induction releases additional upstream activating DNA elements. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2689–2696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almouzni G., Méchali M., Wolffe A. P. Competition between transcription complex assembly and chromatin assembly on replicating DNA. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):573–582. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08145.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose C., Blasquez V., Bina M. A block in initiation of simian virus 40 assembly results in the accumulation of minichromosomes containing an exposed regulatory region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3287–3291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose C., Lowman H., Rajadhyaksha A., Blasquez V., Bina M. Location of nucleosomes in simian virus 40 chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 20;214(4):875–884. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90342-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose C., Rajadhyaksha A., Lowman H., Bina M. Locations of nucleosomes on the regulatory region of simian virus 40 chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 20;210(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Cordingley M. G., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor access is mediated by accurately positioned nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):688–698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batson S. C., Sundseth R., Heath C. V., Samuels M., Hansen U. In vitro initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II on in vivo-assembled chromatin templates. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1639–1651. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner I., Kuhn C., Fanning E. Identification and characterization of fast-sedimenting SV40 nucleoprotein complexes. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):54–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Nyfeler K. Transcription of Simian Virus 40 chromosomes in an extract of HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):9–14. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01116.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Flores O., Krauskopf A., Reinberg D., Aloni Y. Role of the mammalian transcription factors IIF, IIS, and IIX during elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1195–1206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., Kramer R. A. Modulation of chromatin structure associated with derepression of the acid phosphatase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7223–7227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bina M., Blasquez V., Ng S. C., Beecher S. SV40 morphogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):565–569. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasquez V., Stein A., Ambrose C., Bina M. Simian virus 40 protein VP1 is involved in spacing nucleosomes in minichromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan R. L., Gralla J. D. Factor interactions at simian virus 40 GC-box promoter elements in intact nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1554–1558. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kornberg R. D. A yeast ARS-binding protein activates transcription synergistically in combination with other weak activating factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):887–897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Killeen M., Sopta M., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. RAP30/74: a general initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1602–1613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. Proteins that bind to RNA polymerase II are required for accurate initiation of transcription at the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2923–2930. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai H., Luse D. S. Transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Properties of preinitiation, initiation, and elongation complexes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):298–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Lobos S., Merino A., Buckbinder L., Weinmann R., Natarajan V., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Role of factors IID and MLTF in transcription from the adenovirus major late and IVa2 promoters. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7704–7714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. Formation of transcription preinitiation complexes with an amanitin-resistant RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17128–17135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasman D. I., Lue N. F., Buchman A. R., LaPointe J. W., Lorch Y., Kornberg R. D. A yeast protein that influences the chromatin structure of UASG and functions as a powerful auxiliary gene activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):503–514. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choder M., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A direct analysis of transcribed minichromosomes: all transcribed SV40 minichromosomes have a nuclease-hypersensitive region within a nucleosome-free domain. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2929–2936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02234.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. F., FitzGerald P. C., Brubaker J. M., Simpson R. T. Sequence-specific interaction of histones with the simian virus 40 enhancer region in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12394–12397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Flores O., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification and analysis of transcription factor IIA and identification of transcription factor IIJ. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):413–421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrin L. K., Mann R. K., Kayne P. S., Grunstein M. Yeast histone H4 N-terminal sequence is required for promoter activation in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1023–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90554-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Statistical positioning of nucleosomes by specific protein-binding to an upstream activating sequence in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90603-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felts S. J., Weil P. A., Chalkley R. Transcription factor requirements for in vitro formation of transcriptionally competent 5S rRNA gene chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2390–2401. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
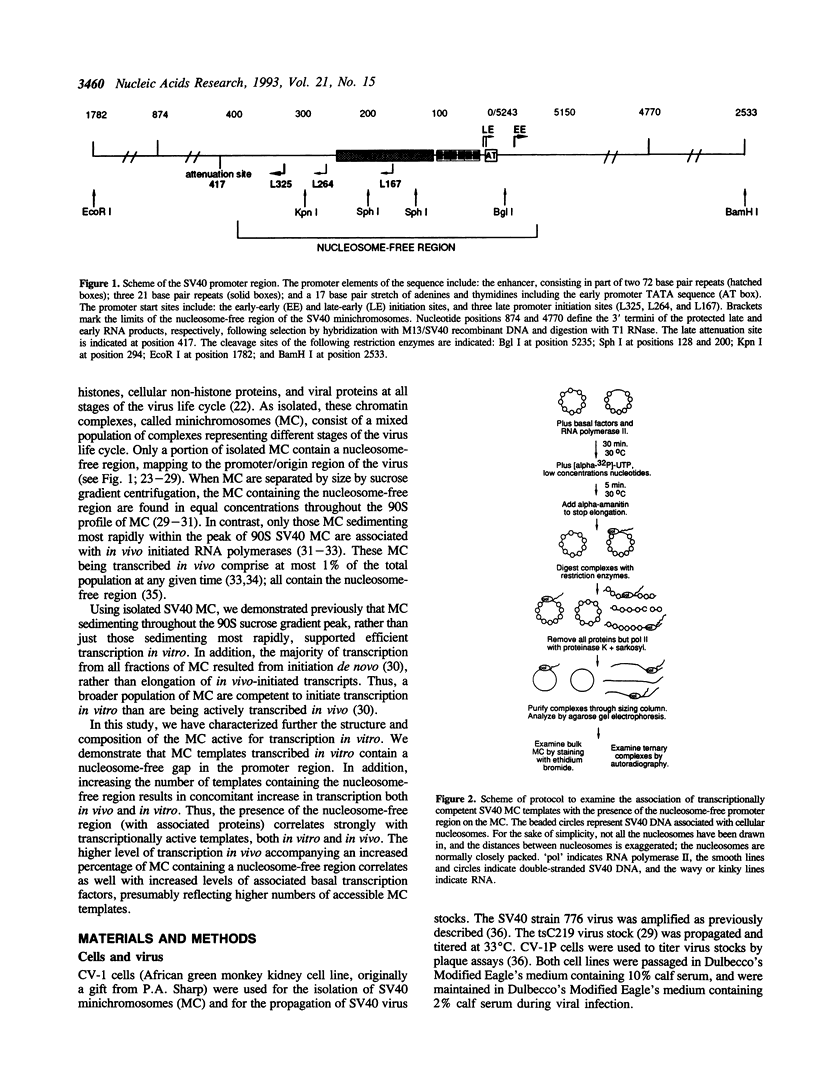
- Flores O., Ha I., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and subunit composition of transcription factor IIF. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5629–5634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Burton Z., Greenblatt J., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. RNA polymerase II-associating protein 30 is an essential component of transcription factor IIF. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10812–10816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Factors IIE and IIF independently interact with RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8913–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariglio P., Llopis R., Oudet P., Chambon P. The template of the isolated native simian virus 40 transcriptional complexes is a minichromosome. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 15;131(1):75–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90302-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R. D., Montelone B. A., Walter C. F., Innis J. W., Scott W. A. Role of specific simian virus 40 sequences in the nuclease-sensitive structure in viral chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R. D., Woodworth-Gutai M., Scott W. A. Deletion mutants which affect the nuclease-sensitive site in simian virus 40 chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):782–788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. RNA polymerase-associated transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90165-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Chromatin structure: deduced from a minichromosome. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1202–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Dieckmann M., Berg P. Electron microscope localization of a protein bound near the origin of simian virus 40 DNA replication. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.167-172.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Kim U. J., Kayne P., Grunstein M. Depletion of histone H4 and nucleosomes activates the PHO5 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2221–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann J. P., Scott W. A. Nuclease-sensitive sites in the two major intracellular simian virus 40 nucleoproteins. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1034–1038. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1034-1038.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J., Shales M., Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J., Greenblatt J. Reduced binding of TFIID to transcriptionally compromised mutants of VP16. Nature. 1991 Jun 13;351(6327):588–590. doi: 10.1038/351588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis J. W., Scott W. A. DNA replication and chromatin structure of simian virus 40 insertion mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1499–1507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):263–265. doi: 10.1038/285263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. Formation of a nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes is dependent upon a restricted segment of DNA. Virology. 1982 Jul 30;120(2):340–348. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Krasnow M. A. Differential regulation of transcription preinitiation complex assembly by activator and repressor homeo domain proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2177–2189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongstra J., Reudelhuber T. L., Oudet P., Benoist C., Chae C. B., Jeltsch J. M., Mathis D. J., Chambon P. Induction of altered chromatin structures by simian virus 40 enhancer and promoter elements. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):708–714. doi: 10.1038/307708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knezetic J. A., Luse D. S. The presence of nucleosomes on a DNA template prevents initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90541-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. The location of nucleosomes in chromatin: specific or statistical. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):579–580. doi: 10.1038/292579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llopis R., Perrin F., Bellard F., Gariglio P. Quantitation of transcribing native simian virus 40 minichromosomes extracted from CV1 cells late in infection. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):82–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.82-90.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. Nucleosomes inhibit the initiation of transcription but allow chain elongation with the displacement of histones. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90561-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T. Transcription of adenovirus 2 major late and peptide IX genes under conditions of in vitro nucleosome assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1401–1408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse R. H. Nucleosomes inhibit both transcriptional initiation and elongation by RNA polymerase III in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2343–2351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir U., Fodor E., Rutter W. J. Capturing nuclear sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins by using simian virus 40-derived minichromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):982–987. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Wrange O. Inhibition of chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes correlates with derepression of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5259–5265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Brüggemeier U., Beato M. Nucleosome positioning modulates accessibility of regulatory proteins to the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90087-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Dynamic interaction between a Drosophila transcription factor and RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. Y., Shimizu M., Johnson L., Grunstein M., Simpson R. T. Stable nucleosome positioning and complete repression by the yeast alpha 2 repressor are disrupted by amino-terminal mutations in histone H4. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):411–425. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Moyne G., Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Walter C. F., Cryer B. L. Barriers to nuclease Bal31 digestion across specific sites in simian virus 40 chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):604–610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straka C., Hörz W. A functional role for nucleosomes in the repression of a yeast promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):361–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundseth R., Hansen U. Activation of RNA polymerase II transcription by the specific DNA-binding protein LSF. Increased rate of binding of the basal promoter factor TFIIB. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7845–7855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Protein/DNA architecture of the DNase I hypersensitive region of the Drosophila hsp26 promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2191–2201. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Stability of transcription complexes on class II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):342–344. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O., Bohn M. A stretch of "late" SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Gralla J. D., Carey M. The acidic activator GAL4-AH can stimulate polymerase II transcription by promoting assembly of a closed complex requiring TFIID and TFIIA. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1716–1727. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Regnier E., Oudet P. Restriction enzyme accessibility and RNA polymerase localization on transcriptionally active SV40 minichromosomes isolated late in infection. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):84–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90350-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Ruhlmann C., Oudet P. Transcriptionally active SV40 minichromosomes are restriction enzyme sensitive and contain a nucleosome-free origin region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2045–2058. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. Binding of transcription factor TFIID to the major late promoter during in vitro nucleosome assembly potentiates subsequent initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G., Kingston R. E. An upstream transcription factor, USF (MLTF), facilitates the formation of preinitiation complexes during in vitro chromatin assembly. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1299–1308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Activation domains of stably bound GAL4 derivatives alleviate repression of promoters by nucleosomes. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Advances in RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):488–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]