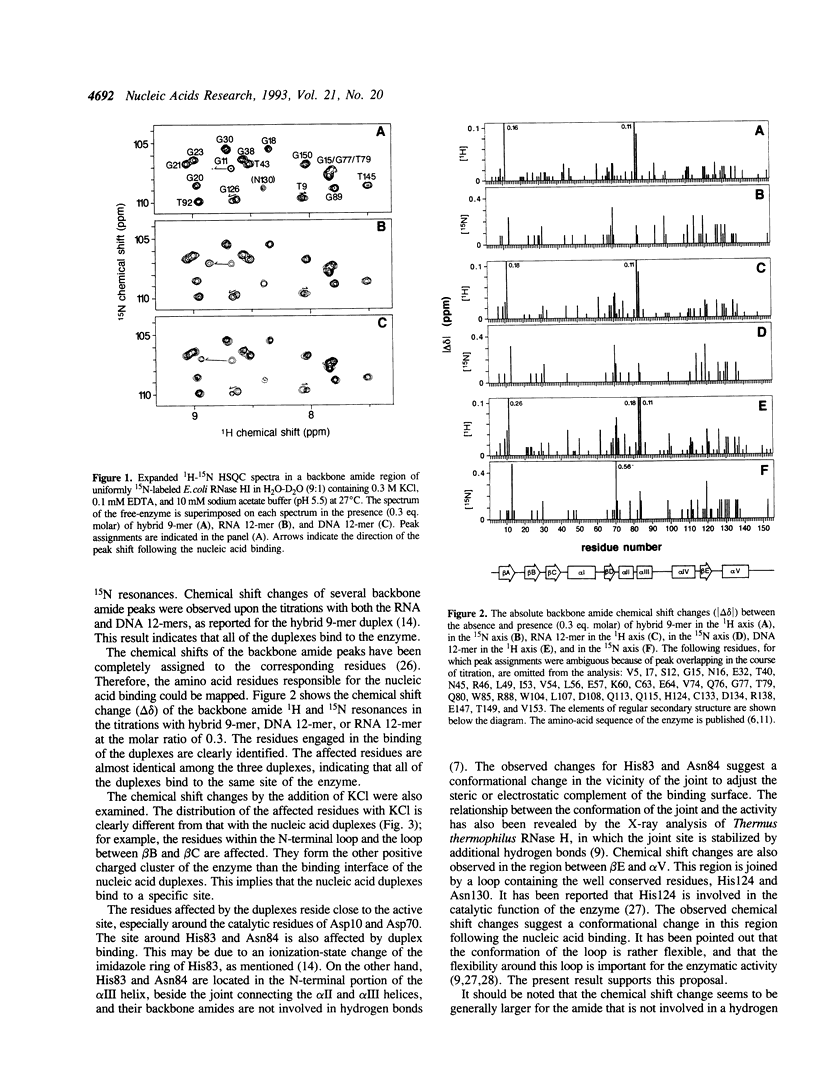
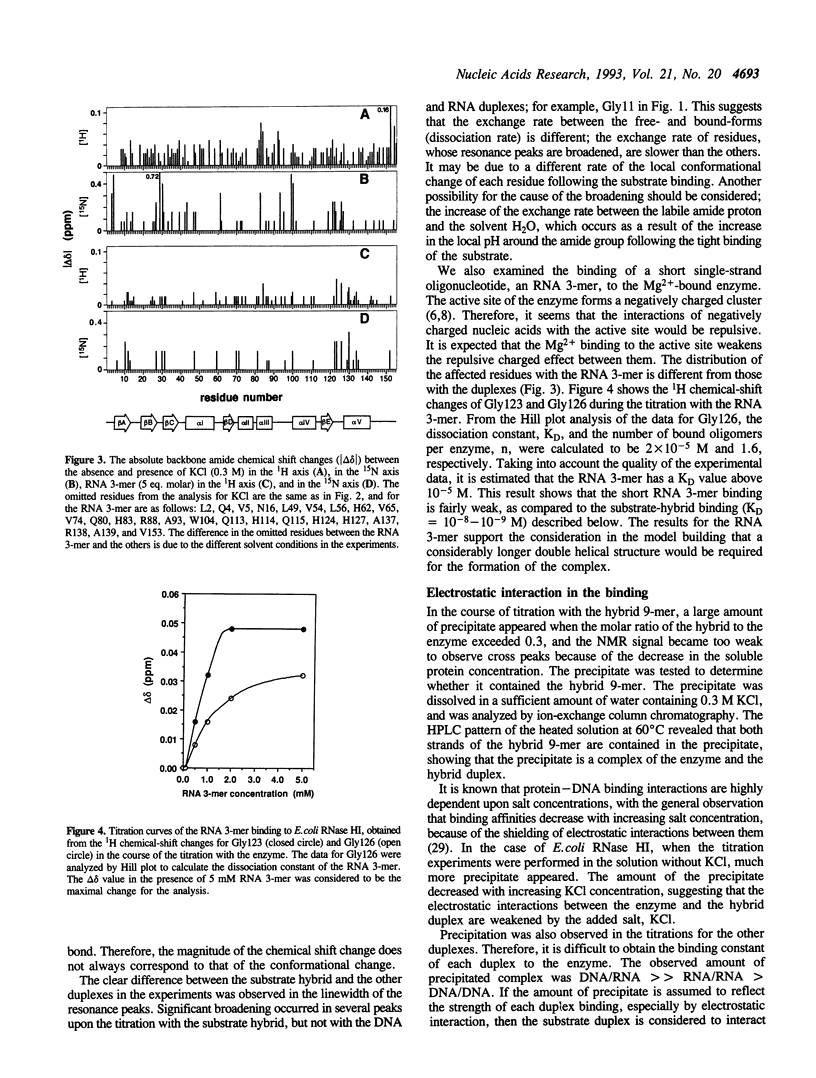
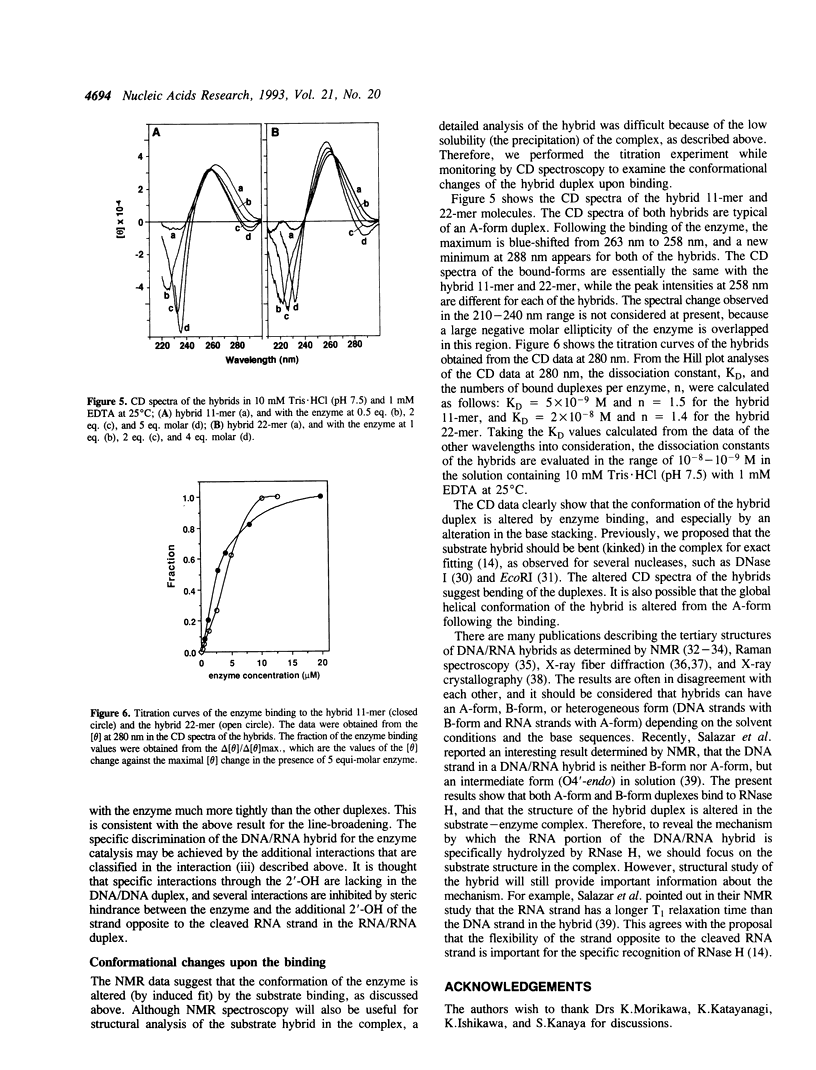
Abstract
To clarify the mechanism by which the RNA portion of a DNA/RNA hybrid is specifically hydrolyzed by ribonuclease H (RNase H), the binding of a DNA/RNA hybrid, a DNA/DNA duplex, or an RNA/RNA duplex to RNase HI from Escherichia coli was investigated by 1H-15N heteronuclear NMR. Chemical shift changes of backbone amide resonances were monitored while the substrate, a hybrid 9-mer duplex, a DNA/DNA 12-mer duplex, or an RNA/RNA 12-mer duplex was titrated. The amino acid residues affected by the addition of each 12-mer duplex were almost identical to those affected by the substrate hybrid binding, and resided close to the active site of the enzyme. The results reveal that all the duplexes, hybrid-, DNA-, and RNA-duplex, bind to the enzyme. From the linewidth analysis of the resonance peaks, it was found that the exchange rates for the binding were different between the hybrid and the other duplexes. The NMR and CD data suggest that conformational changes occur in the enzyme and the hybrid duplex upon binding.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold E., Jacobo-Molina A., Nanni R. G., Williams R. L., Lu X., Ding J., Clark A. D., Jr, Zhang A., Ferris A. L., Clark P. Structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase/DNA complex at 7 A resolution showing active site locations. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):85–89. doi: 10.1038/357085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Millane R. P., Park H. S. DNA-RNA hybrid secondary structures. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):631–640. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benevides J. M., Thomas G. J., Jr A solution structure for poly(rA).poly(dT) with different furanose pucker and backbone geometry in rA and dT strands and intrastrand hydrogen bonding of adenine 8CH. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3868–3873. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. H., Flynn P., Reid B. High-resolution NMR study of a synthetic DNA-RNA hybrid dodecamer containing the consensus pribnow promoter sequence: d(CGTTATAATGCG).r(CGCAUUAUAACG). Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2435–2443. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. H., Flynn P., Reid B. Solid-phase synthesis and high-resolution NMR studies of two synthetic double-helical RNA dodecamers: r(CGCGAAUUCGCG) and r(CGCGUAUACGCG). Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2422–2435. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch R. J. Ribonuclease H: from discovery to 3D structure. New Biol. 1990 Sep;2(9):771–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. F., 2nd, Hostomska Z., Hostomsky Z., Jordan S. R., Matthews D. A. Crystal structure of the ribonuclease H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):88–95. doi: 10.1126/science.1707186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Site specific enzymatic cleavage of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):179–192. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., McClure M. A. Origins and evolutionary relationships of retroviruses. Q Rev Biol. 1989 Mar;64(1):1–30. doi: 10.1086/416128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta G., Sarma M. H., Sarma R. H. Secondary structure of the hybrid poly(rA).poly(dT) in solution. Studies involving NOE at 500 MHz and stereochemical modelling within the constraints of NOE data. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare D. R., Wemmer D. E., Chou S. H., Drobny G., Reid B. R. Assignment of the non-exchangeable proton resonances of d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G) using two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance methods. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 15;171(3):319–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Hayase Y., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E. Sequence-dependent hydrolysis of RNA using modified oligonucleotide splints and RNase H. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 11;215(2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa K., Okumura M., Katayanagi K., Kimura S., Kanaya S., Nakamura H., Morikawa K. Crystal structure of ribonuclease H from Thermus thermophilus HB8 refined at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):529–542. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai S., Ohtsuka E. 5'-Levulinyl and 2'-tetrahydrofuranyl protection for the synthesis of oligoribonucleotides by the phosphoramidite approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9443–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaya S., Kohara A., Miura Y., Sekiguchi A., Iwai S., Inoue H., Ohtsuka E., Ikehara M. Identification of the amino acid residues involved in an active site of Escherichia coli ribonuclease H by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4615–4621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaya S., Oobatake M., Nakamura H., Ikehara M. pH-dependent thermostabilization of Escherichia coli ribonuclease HI by histidine to alanine substitutions. J Biotechnol. 1993 Mar;28(1):117–136. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(93)90129-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayanagi K., Miyagawa M., Matsushima M., Ishikawa M., Kanaya S., Ikehara M., Matsuzaki T., Morikawa K. Three-dimensional structure of ribonuclease H from E. coli. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):306–309. doi: 10.1038/347306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayanagi K., Miyagawa M., Matsushima M., Ishikawa M., Kanaya S., Nakamura H., Ikehara M., Matsuzaki T., Morikawa K. Structural details of ribonuclease H from Escherichia coli as refined to an atomic resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):1029–1052. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90260-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Wang J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1377403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClarin J. A., Frederick C. A., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Grable J., Rosenberg J. M. Structure of the DNA-Eco RI endonuclease recognition complex at 3 A resolution. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1526–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.3024321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H., Oda Y., Iwai S., Inoue H., Ohtsuka E., Kanaya S., Kimura S., Katsuda C., Katayanagi K., Morikawa K. How does RNase H recognize a DNA.RNA hybrid? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11535–11539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda Y., Nakamura H., Kanaya S., Ikehara M. Binding of metal ions to E. coli RNase HI observed by 1H-15N heteronuclear 2D NMR. J Biomol NMR. 1991 Sep;1(3):247–255. doi: 10.1007/BF01875518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda Y., Yoshida M., Kanaya S. Role of histidine 124 in the catalytic function of ribonuclease HI from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):88–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Marky L. A., Broka C., Rice J. A., Itakura K., Breslauer K. J. Premelting and melting transitions in the d(CGCGAATTCGCG) self-complementary duplex in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):428–436. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Lohman M. L., De Haseth P. Ion effects on ligand-nucleic acid interactions. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 25;107(2):145–158. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar M., Fedoroff O. Y., Miller J. M., Ribeiro N. S., Reid B. R. The DNA strand in DNA.RNA hybrid duplexes is neither B-form nor A-form in solution. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 27;32(16):4207–4215. doi: 10.1021/bi00067a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H., Matsumoto U. Direct evidence for a bimorphic structure of a DNA-RNA hybrid, poly(rA).poly(dT), at high relative humidity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8682–8684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Lahm A., Oefner C. Structure refined to 2A of a nicked DNA octanucleotide complex with DNase I. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):464–468. doi: 10.1038/332464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Fujii S., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G. A., van Boeckel S. A., Rich A. Molecular structure of r(GCG)d(TATACGC): a DNA--RNA hybrid helix joined to double helical DNA. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):601–604. doi: 10.1038/299601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger U. Ribonucleases H of retroviral and cellular origin. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;48(2):259–280. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90083-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki T., Yoshida M., Kanaya S., Nakamura H., Nagayama K. Assignments of backbone 1H, 13C, and 15N resonances and secondary structure of ribonuclease H from Escherichia coli by heteronuclear three-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 18;30(24):6036–6047. doi: 10.1021/bi00238a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W., Hendrickson W. A., Crouch R. J., Satow Y. Structure of ribonuclease H phased at 2 A resolution by MAD analysis of the selenomethionyl protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1398–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.2169648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Pheiffer B. H. A RNA.DNA hybrid that can adopt two conformations: an x-ray diffraction study of poly(rA).poly(dT) in concentrated solution or in fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):78–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


