Abstract
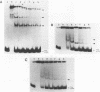
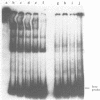
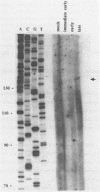
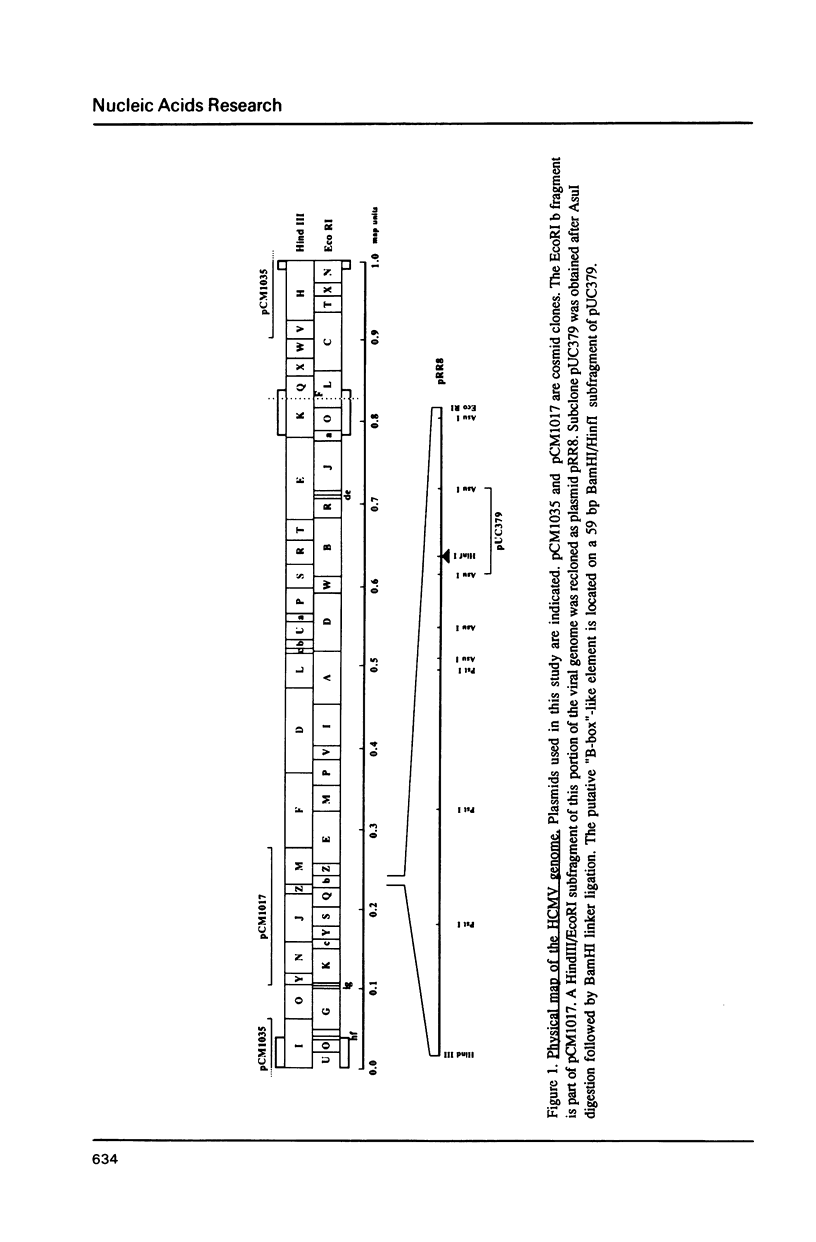
Through computer analysis of a human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) genomic region, previously identified to be homologous to human genomic DNA, an element showing significant similarity to the 3'-internal control region (3'-ICR or B-block) of a eukaryotic RNA polymerase III promoter could be detected. This region-located on the EcoRI b fragment within the UL segment of the viral genome of HCMV strain AD 169-cannot be transcribed in vitro in an RNA polymerase III specific transcription system. However, this part of the viral genome is able to compete for components of the RNA polymerase III transcription complex as shown in template exclusion experiments and by gel retardation assays. Two different synthetic oligonucleotides complementary to the 3'-ICR and to nucleotides located immediately downstream of this promoter element can anneal specifically to a HCMV-encoded ribonucleic acid (termed CMER) synthesized in human foreskin fibroblasts (HFF) late in virus replication. As a consequence of identifying the transcription initiation point by primer extension analyses the position of the 5'-internal control region (5'-ICR or A-block) of the CMER gene could be uncovered. Both identified control regions (the A-block as well as the B-block) of the transcription unit exhibit significant similarities to corresponding regulatory elements of other class III genes, including virus encoded class III genes. Initiation of in vivo transcription occurs 15 nucleotides upstream of the 5'-border of the 5'-ICR and the two non-contiguous gene internal promoter elements are separated by 79 nucleotides.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M., Blankenship M. L., Brown G. D., Kaplan A. S. Size and complexity of human cytomegalovirus DNA. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Amon-Böhm E., Bertling W., Marschalek R., Nerke K. A family of non-allelic tRNA(ValGUU) genes from the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90502-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Bertling W., Pistel F., Amon E. Characterisation of a Dictyostelium discoideum DNA fragment coding for a putative tRNAValGUU gene. Evidence for a single transcription unit consisting of two overlapping class III genes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):449–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Nerke K., Marschalek R. Influence of different 5'-flanking sequences of tRNA genes on their in vivo transcription efficiencies in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling A., Keil G., Nowak B., Fleckenstein B., Berthelot N., Sheldrick P. Genome structure and virion polypeptides of the primate herpesviruses Herpesvirus aotus types 1 and 3: comparison with human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):715–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.715-726.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleckenstein B., Müller I., Collins J. Cloning of the complete human cytomegalovirus genome in cosmids. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions of the adenovirus VAI RNA gene. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen J. L., Walig C., Wertheim P., van der Noordaa J. Human cytomegalovirus DNA. I. Molecular weight and infectivity. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):813–816. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.813-816.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenaway P. J., Oram J. D., Downing R. G., Patel K. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: BamHI, EcoRI and PstI restriction endonuclease cleavage maps. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P., Arrand J. R. In vitro transcription of two Epstein-Barr virus specified small RNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3407–3425. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B. Genes for VA-RNA in adenovirus 2. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):223–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy S., Kamine J., Desrosiers R. C. Viral-encoded small RNAs in herpes virus saimiri induced tumors. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1625–1632. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Mariano T. M., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. A mechanism for the control of protein synthesis by adenovirus VA RNAI. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Philipson L. Location of sequences on the adenovirus genome coding for the 5.5S RNA. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen R. D., Staprans S. I., Shaw S. B., Spector D. H. Sequences in human cytomegalovirus which hybridize with the avian retrovirus oncogene v-myc are G + C rich and do not hybridize with the human c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1525–1530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa M. D., Gottlieb E., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Striking similarities are exhibited by two small Epstein-Barr virus-encoded ribonucleic acids and the adenovirus-associated ribonucleic acids VAI and VAII. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):785–796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymo L. Identification of transcribed regions of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in Burkitt lymphoma-derived cells. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):8–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.8-18.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüger R., Bornkamm G. W., Fleckenstein B. Human cytomegalovirus DNA sequences with homologies to the cellular genome. J Gen Virol. 1984 Aug;65(Pt 8):1351–1364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-8-1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Sharp S., Dingermann T., Söll D. Transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes in vitro. II. Formation of stable complexes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2447–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA prevents phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit subsequent to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S. J., Schaack J., Cooley L., Burke D. J., Söll D. Structure and transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;19(2):107–144. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S., DeFranco D., Dingermann T., Farrell P., Söll D. Internal control regions for transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6657–6661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S. B., Rasmussen R. D., McDonough S. H., Staprans S. I., Vacquier J. P., Spector D. H. Cell-related sequences in the DNA genome of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):843–848. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.843-848.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman S., Schmidt O., Söll D., Hovemann B. The nucleotide sequence of a cloned Drosophila arginine tRNA gene and its in vitro transcription in Xenopus germinal vesicle extracts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10290–10294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund H., Pettersson U., Vennström B., Philipson L., Mathews M. B. A new species of virus-coded low molecular weight RNA from cells infected with adenovirus type 2. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamashiro J. C., Hock L. J., Spector D. H. Construction of a cloned library of the EcoRI fragments from the human cytomegalovirus genome (strain AD169). J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):547–557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.547-557.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Cloning of the human cytomegalovirus genome as endonuclease XbaI fragments. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Raskas H. J., Roeder R. G. Role of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases II and III in transcription of the adenovirus genome late in productive infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3426–3439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]