Abstract
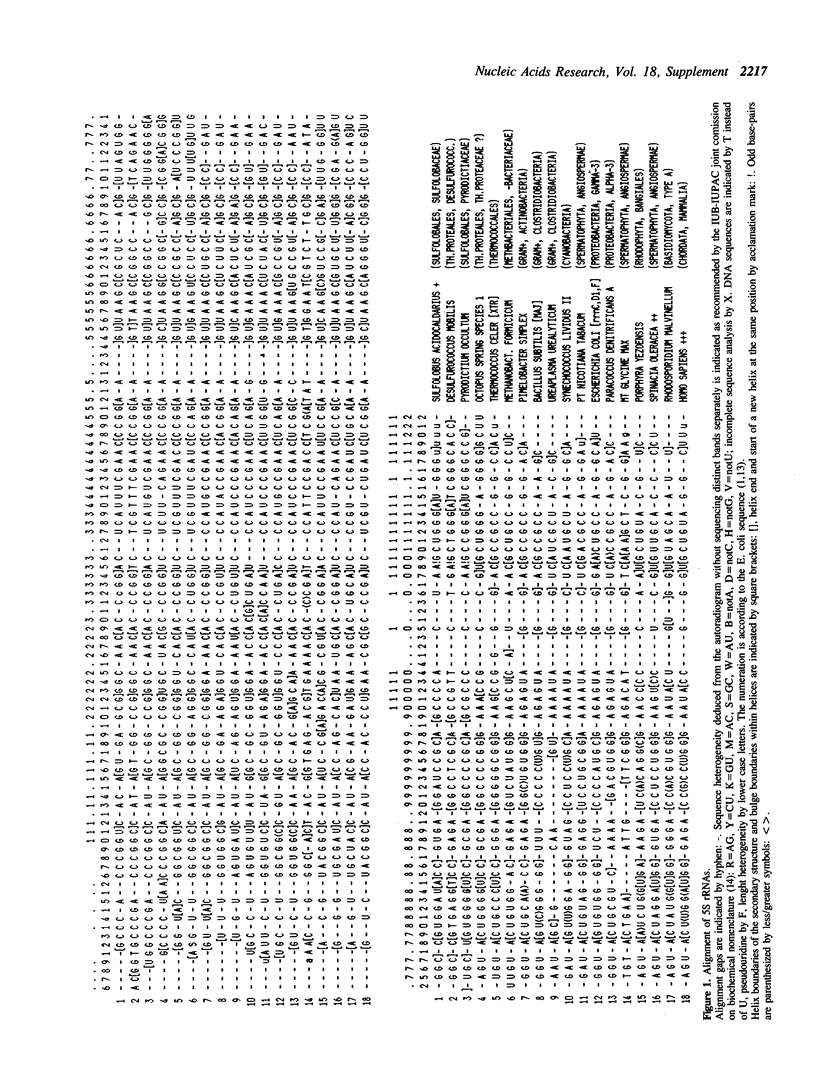
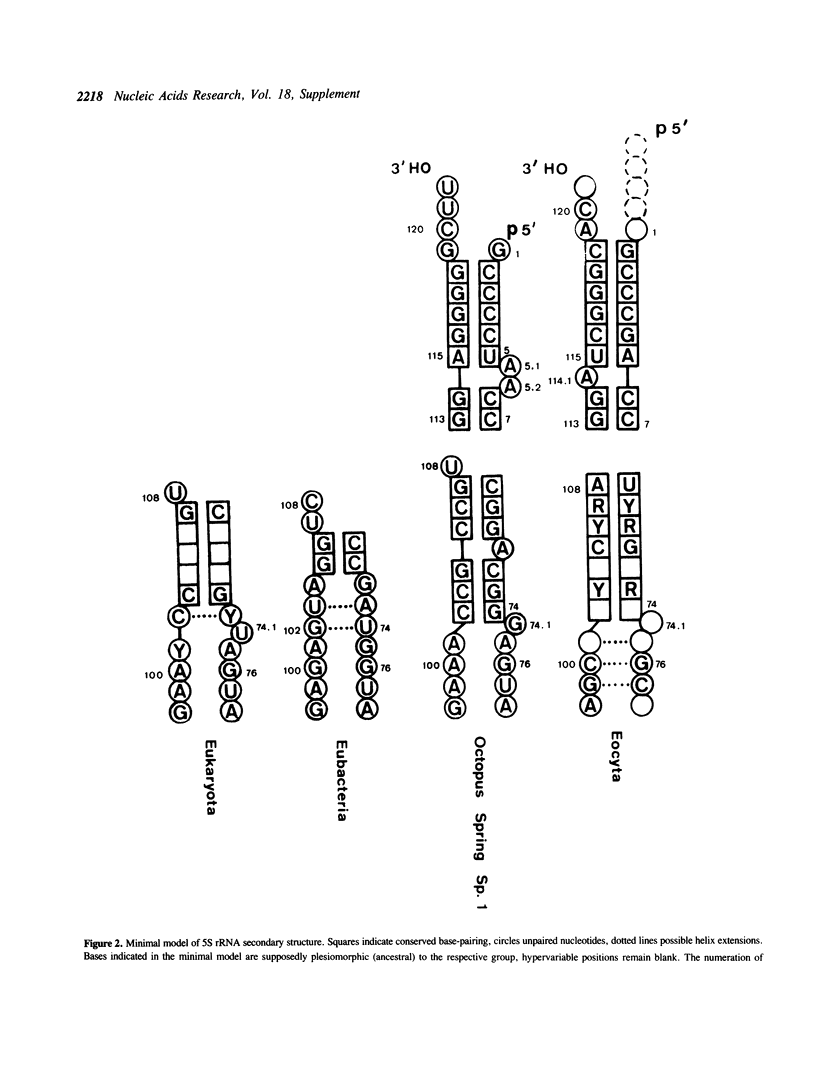
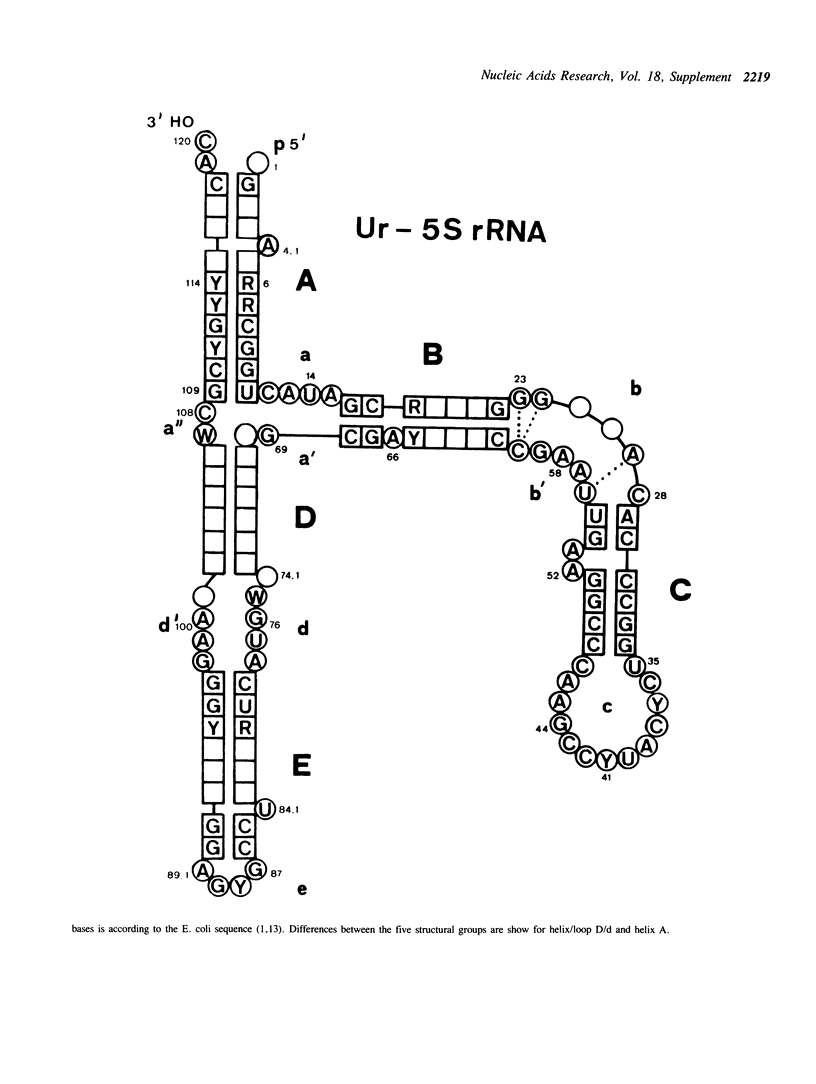
The BERLIN RNA DATABANK as of Dezember 31, 1989, contains a total of 667 sequences of 5S rRNAs or their genes, which is an increase of 114 new sequence entries over the last compilation (1). It covers sequences from 44 archaebacteria, 267 eubacteria, 20 plastids, 6 mitochondria, 319 eukaryotes and 11 eukaryotic pseudogenes. The hardcopy shows only the list (Table 1) of those organisms whose sequences have been determined. The BERLIN RNA DATABANK uses the format of the EMBL Nucleotide Sequence Data Library complemented by a Sequence Alignment (SA) field including secondary structure information.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J. A model for the interaction of nucleic acids with transcription factor IIIA. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 15;217(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80663-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J., Delihas N., Hanas J. S., Wu C. W. 5S RNA structure and interaction with transcription factor A. 1. Ribonuclease probe of the structure of 5S RNA from Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5752–5759. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J., Delihas N., Hanas J. S., Wu C. W. 5S RNA structure and interaction with transcription factor A. 2. Ribonuclease probe of the 7S particle from Xenopus laevis immature oocytes and RNA exchange properties of the 7S particle. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5759–5766. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. Nomenclature for incompletely specified bases in nucleic acid sequences: recommendations 1984. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3021–3030. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andersen J. Generalized structures of the 5S ribosomal RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7323–7344. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Woese C. R. 5S RNA secondary structure. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):505–507. doi: 10.1038/256505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonell M. T., Colwell R. R. Nuclease S1 analysis of eubacterial 5S rRNA secondary structure. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(3):237–242. doi: 10.1007/BF02099753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Nucleotide sequence of 5 S RNA from Torulopsis utilis. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):106–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80904-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters J., Erdmann V. A. Compilation of 5S rRNA and 5S rRNA gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16 (Suppl):r1–70. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


