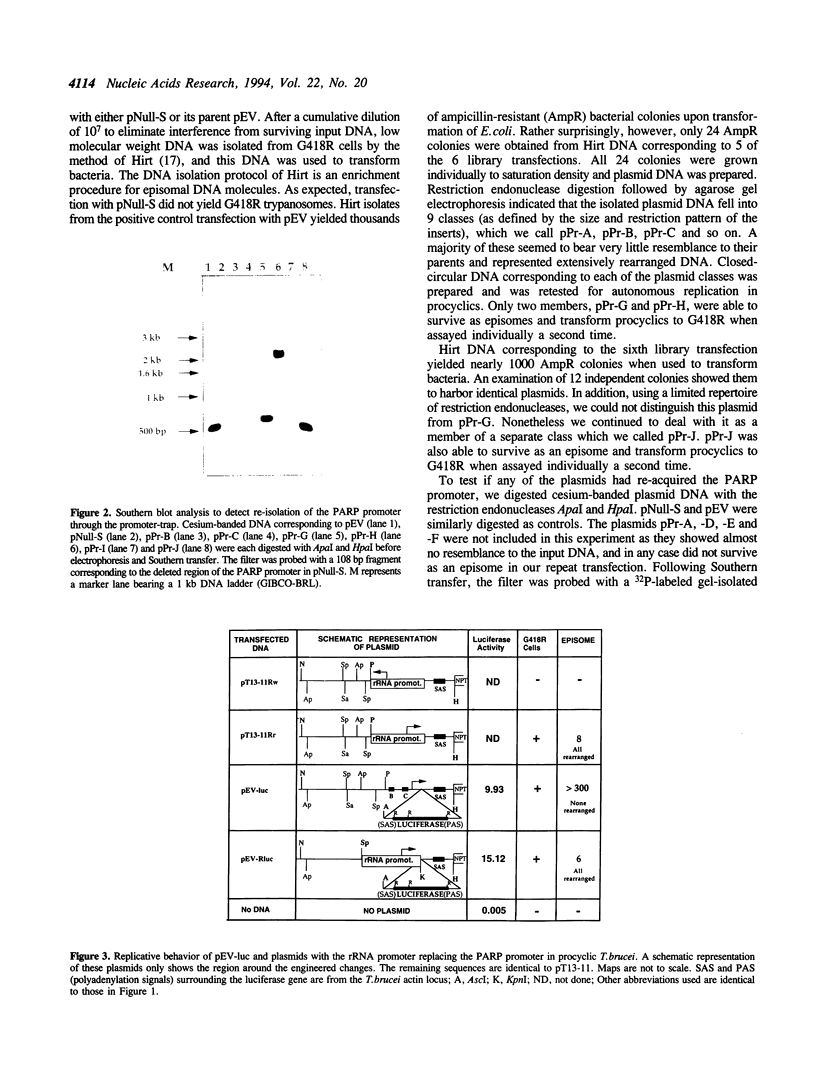
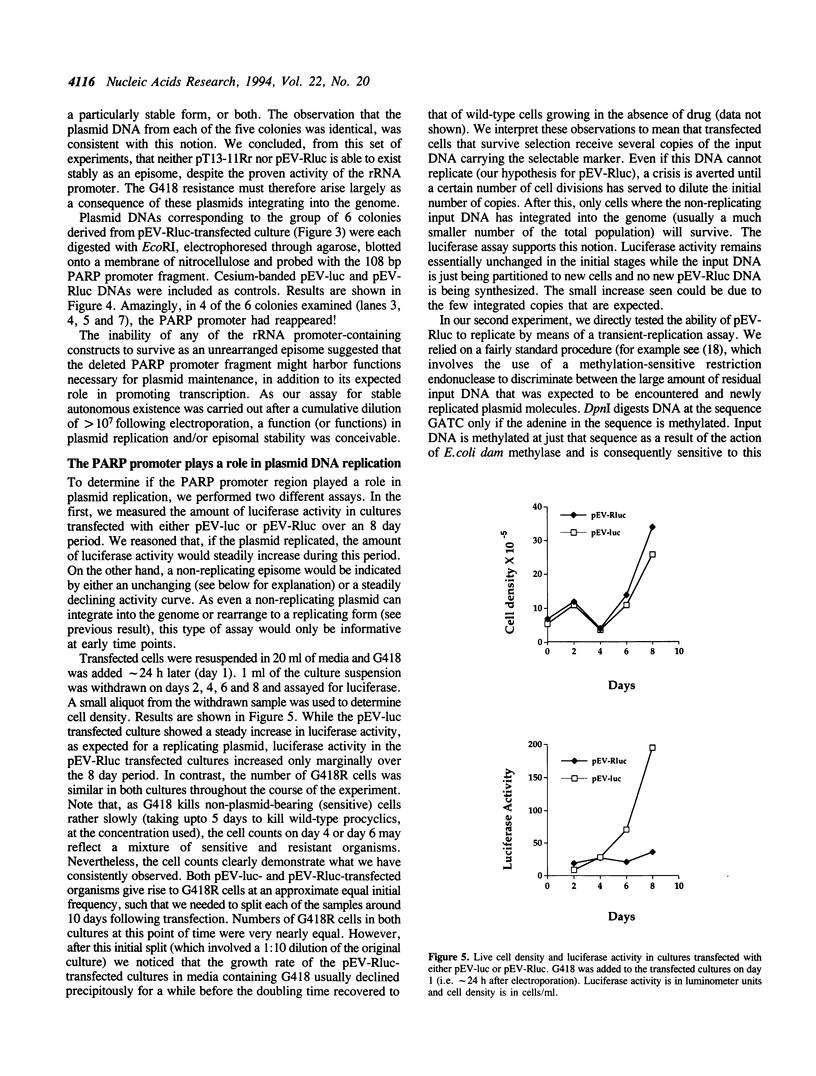
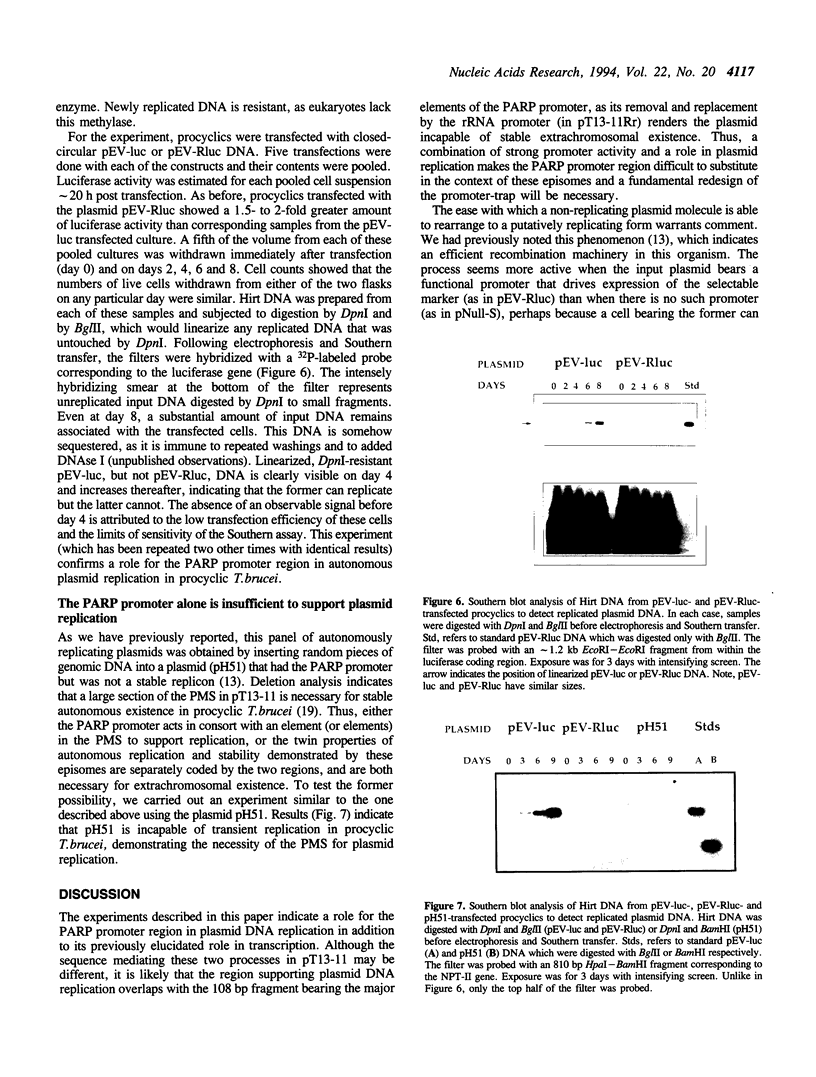
Abstract
We have previously reported the construction and characterization of an autonomously replicating plasmid in Trypanosoma brucei. In this plasmid the procyclic acidic repetitive protein (PARP) gene promoter drives the transcription of a selectable marker. Deletion of this promoter incapacitates the plasmid, suggesting its utilization as a promoter-trap. Three independent libraries were created by inserting variously digested T.brucei genomic DNA into this promoterless construct. Transfection of these libraries into procyclic T.brucei and the subsequent isolation of episomes led only to the reisolation of the PARP promoter. Additionally, a ribosomal RNA promoter failed to keep the construct as an episome, although it can sustain mRNA transcription in T.brucei and was shown to be an efficient promoter in this construct. Finally, by using a transient replication assay involving the methylation-sensitive restriction endonuclease DpnI to distinguish between input and replicated DNA, we showed that the PARP promoter-bearing construct could replicate autonomously in procyclic T.brucei, but the corresponding construct with the rRNA promoter could not. The close association between elements that sustain transcription and DNA replication in T.brucei mirrors results observed in several higher eukaryotes and their viruses and suggests an ancient origin of this feature.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S. P., Kobayashi R., Stillman B. Yeast origin recognition complex functions in transcription silencing and DNA replication. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1844–1849. doi: 10.1126/science.8266072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Stillman B. ATP-dependent recognition of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication by a multiprotein complex. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):128–134. doi: 10.1038/357128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellofatto V., Torres-Muñoz J. E., Cross G. A. Stable transformation of Leptomonas seymouri by circular extrachromosomal elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6711–6715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards A., Van der Ploeg L. H., Frasch A. C., Borst P., Boothroyd J. C., Coleman S., Cross G. A. Activation of trypanosome surface glycoprotein genes involves a duplication-transposition leading to an altered 3' end. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Huang J., Van der Ploeg L. H. The promoter for the procyclic acidic repetitive protein (PARP) genes of Trypanosoma brucei shares features with RNA polymerase I promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2644–2652. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bénard M., Pierron G. Mapping of a Physarum chromosomal origin of replication tightly linked to a developmentally-regulated profilin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3309–3315. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers V. B., van der Ploeg L. H., Cross G. A. DNA-mediated transformation of bloodstream-form Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2537–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Fueri J. P., Itzhaki J. E., Bellofatto V., Sherman D. R., Wisdom G. S., Vijayasarathy S., Mowatt M. R. Transcription of the procyclic acidic repetitive protein genes of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3036–3047. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curotto de Lafaille M. A., Laban A., Wirth D. F. Gene expression in Leishmania: analysis of essential 5' DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2703–2707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphili M. L. How transcription factors regulate origins of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 May;3(5):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90137-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker R. S., Yamaguchi M., Possenti R., Bradley M. K., DePamphilis M. L. In vitro initiation of DNA replication in simian virus 40 chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10863–10872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Cocker J. H. Protein-DNA interactions at a yeast replication origin. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):169–172. doi: 10.1038/357169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foss M., McNally F. J., Laurenson P., Rine J. Origin recognition complex (ORC) in transcriptional silencing and DNA replication in S. cerevisiae. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1838–1844. doi: 10.1126/science.8266071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z. S., DePamphilis M. L. Specific transcription factors stimulate simian virus 40 and polyomavirus origins of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2514–2524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H. Transcription factors and the control of DNA replication. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held P. G., Heintz N. H. Eukaryotic replication origins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 6;1130(3):235–246. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90435-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoang A. T., Wang W., Gralla J. D. The replication activation potential of selected RNA polymerase II promoter elements at the simian virus 40 origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3087–3093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozák P., Hassan A. B., Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Visualization of replication factories attached to nucleoskeleton. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):361–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90235-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J., Van der Ploeg L. H. Requirement of a polypyrimidine tract for trans-splicing in trypanosomes: discriminating the PARP promoter from the immediately adjacent 3' splice acceptor site. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3877–3885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug M., Carruthers V. B., Hartmann C., Sherman D. S., Cross G. A., Clayton C. A possible role for the 3'-untranslated region in developmental regulation in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Sep;61(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90161-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan P. J., Haase S. B., Calos M. P. Isolation of human sequences that replicate autonomously in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1026–1033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leipe D. D., Gunderson J. H., Nerad T. A., Sogin M. L. Small subunit ribosomal RNA+ of Hexamita inflata and the quest for the first branch in the eukaryotic tree. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 May;59(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90005-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Botchan M. R. The acidic transcriptional activation domains of VP16 and p53 bind the cellular replication protein A and stimulate in vitro BPV-1 DNA replication. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1207–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90649-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marahrens Y., Stillman B. A yeast chromosomal origin of DNA replication defined by multiple functional elements. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):817–823. doi: 10.1126/science.1536007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micklem G., Rowley A., Harwood J., Nasmyth K., Diffley J. F. Yeast origin recognition complex is involved in DNA replication and transcriptional silencing. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):87–89. doi: 10.1038/366087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., Nasmyth K. A. Role of DNA replication in the repression of silent mating type loci in yeast. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):247–251. doi: 10.1038/312247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills A. D., Blow J. J., White J. G., Amos W. B., Wilcock D., Laskey R. A. Replication occurs at discrete foci spaced throughout nuclei replicating in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1989 Nov;94(Pt 3):471–477. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayasu H., Berezney R. Mapping replicational sites in the eucaryotic cell nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):1–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
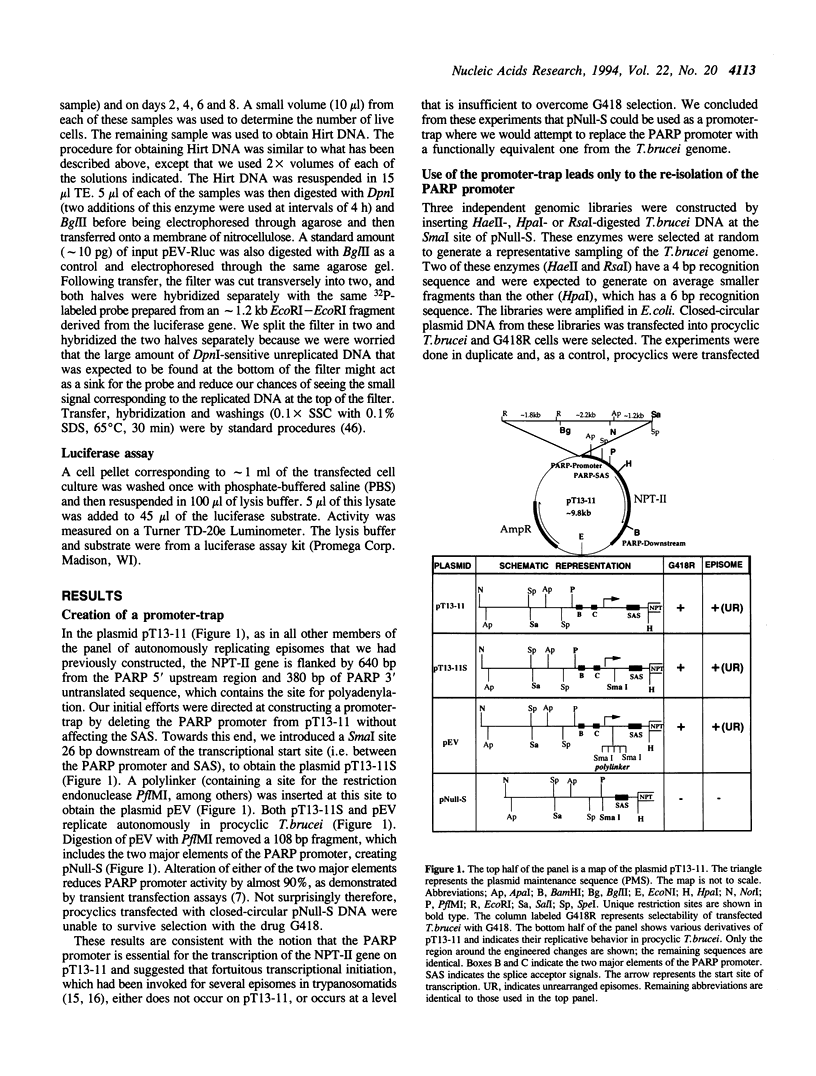
- Patnaik P. K., Bellofatto V., Hartree D., Cross G. A. An episome of Trypanosoma brucei can exist as an extrachromosomal element in a broad range of trypanosomatids but shows different requirements for stable replication. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 Jul;66(1):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patnaik P. K., Kulkarni S. K., Cross G. A. Autonomously replicating single-copy episomes in Trypanosoma brucei show unusual stability. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2529–2538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Yates J., Sugden B. A putative origin of replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus is composed of two cis-acting components. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1822–1832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier D. H., Rine J. An origin of DNA replication and a transcription silencer require a common element. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):659–663. doi: 10.1126/science.1585179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko G., Chung H. M., Pham V. P., Van der Ploeg L. H. RNA polymerase I can mediate expression of CAT and neo protein-coding genes in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3387–3397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko G., Le Blancq S., Smith J., Lee M. G., Rattray A., Van der Ploeg L. H. Procyclic acidic repetitive protein (PARP) genes located in an unusually small alpha-amanitin-resistant transcription unit: PARP promoter activity assayed by transient DNA transfection of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3492–3504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko G., Lee M. G., Van der Ploeg L. H. The PARP and VSG genes of Trypanosoma brucei do not resemble RNA polymerase II transcription units in sensitivity to Sarkosyl in nuclear run-on assays. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):303–306. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. R., Janz L., Hug M., Clayton C. Anatomy of the parp gene promoter of Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3379–3386. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Elwood H. J., Gunderson J. H. Evolutionary diversity of eukaryotic small-subunit rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1383–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Alonso R. A., Peattie D. A. Phylogenetic meaning of the kingdom concept: an unusual ribosomal RNA from Giardia lamblia. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2911720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav M., Stenlund A. Transient replication of BPV-1 requires two viral polypeptides encoded by the E1 and E2 open reading frames. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):449–457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P. Relationship of eukaryotic DNA replication to committed gene expression: general theory for gene control. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):512–542. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.512-542.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomerdijk J. C., Kieft R., Borst P. Efficient production of functional mRNA mediated by RNA polymerase I in Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):772–775. doi: 10.1038/353772a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomerdijk J. C., Kieft R., Shiels P. G., Borst P. Alpha-amanitin-resistant transcription units in trypanosomes: a comparison of promoter sequences for a VSG gene expression site and for the ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5153–5158. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomerdijk J. C., Ouellette M., ten Asbroek A. L., Kieft R., Bommer A. M., Clayton C. E., Borst P. The promoter for a variant surface glycoprotein gene expression site in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2791–2801. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]