Abstract
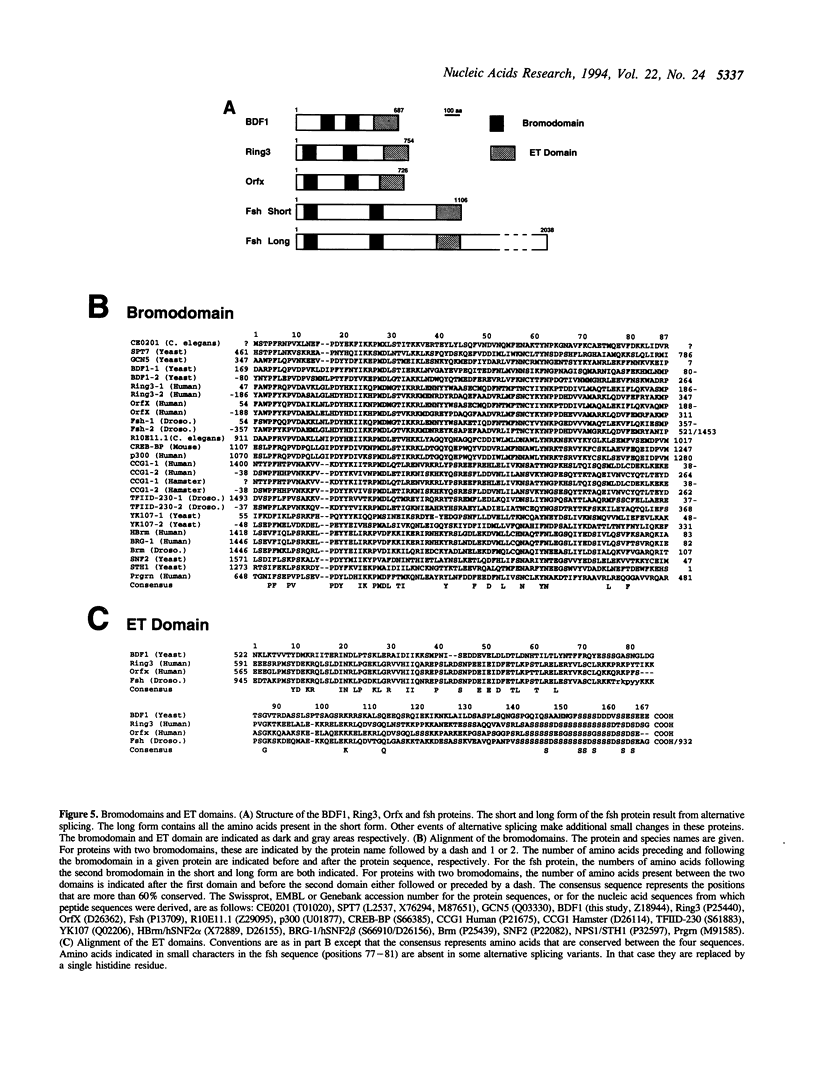
While screening for genes that affect the synthesis of yeast snRNPs, we identified a thermosensitive mutant that abolishes the production of a reporter snRNA at the non-permissive temperature. This mutant defines a new gene, named BDF1. In a bdf1-1 strain, the reporter snRNA synthesized before the temperature shift remains stable at the non-permissive temperature. This demonstrates that the BDF1 gene affects the synthesis rather than the stability of the reporter snRNA and suggests that the BDF1 gene encodes a transcription factor. BDF1 is present in single copy on yeast chromosome XII, and is important for normal vegetative growth but not essential for cell viability. bdf1 null mutants share common phenotypes with several mutants affecting general transcription and are defective in snRNA production. BDF1 encodes a protein of 687 amino-acids containing two copies of the bromodomain, a motif also present in other transcription factors as well as a new conserved domain, the ET domain, also present in Drosophila and human proteins.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams E., Neigeborn L., Carlson M. Molecular analysis of SNF2 and SNF5, genes required for expression of glucose-repressible genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3643–3651. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arany Z., Sellers W. R., Livingston D. M., Eckner R. E1A-associated p300 and CREB-associated CBP belong to a conserved family of coactivators. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck S., Hanson I., Kelly A., Pappin D. J., Trowsdale J. A homologue of the Drosophila female sterile homeotic (fsh) gene in the class II region of the human MHC. DNA Seq. 1992;2(4):203–210. doi: 10.3109/10425179209020804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernués J., Simmen K. A., Lewis J. D., Gunderson S. I., Polycarpou-Schwarz M., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Mattaj I. W. Common and unique transcription factor requirements of human U1 and U6 snRNA genes. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3573–3585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg H., Silver P. A split zinc-finger protein is required for normal yeast growth. Gene. 1991 Oct 30;107(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90302-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Transcription of a yeast U6 snRNA gene requires a polymerase III promoter element in a novel position. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1345–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnol A. F., Margottin F., Huet J., Almouzni G., Prioleau M. N., Méchali M., Sentenac A. TFIIIC relieves repression of U6 snRNA transcription by chromatin. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):475–477. doi: 10.1038/362475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnol A. F., Margottin F., Schultz P., Marsolier M. C., Oudet P., Sentenac A. Basal promoter and enhancer element of yeast U6 snRNA gene. J Mol Biol. 1993 Oct 20;233(4):644–658. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns N., Grimwade B., Ross-Macdonald P. B., Choi E. Y., Finberg K., Roeder G. S., Snyder M. Large-scale analysis of gene expression, protein localization, and gene disruption in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1994 May 1;8(9):1087–1105. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.9.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns B. R., Kim Y. J., Sayre M. H., Laurent B. C., Kornberg R. D. A multisubunit complex containing the SWI1/ADR6, SWI2/SNF2, SWI3, SNF5, and SNF6 gene products isolated from yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., West R. W., Jr, Johnson S. L., Gans H., Kruger B., Ma J. TSF3, a global regulatory protein that silences transcription of yeast GAL genes, also mediates repression by alpha 2 repressor and is identical to SIN4. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):831–840. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba H., Muramatsu M., Nomoto A., Kato H. Two human homologues of Saccharomyces cerevisiae SWI2/SNF2 and Drosophila brahma are transcriptional coactivators cooperating with the estrogen receptor and the retinoic acid receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 May 25;22(10):1815–1820. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.10.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrivia J. C., Kwok R. P., Lamb N., Hagiwara M., Montminy M. R., Goodman R. H. Phosphorylated CREB binds specifically to the nuclear protein CBP. Nature. 1993 Oct 28;365(6449):855–859. doi: 10.1038/365855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düsterhöft A., Philippsen P. DNA sequencing and analysis of a 24.7 kb segment encompassing centromere CEN11 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals nine previously unknown open reading frames. Yeast. 1992 Sep;8(9):749–759. doi: 10.1002/yea.320080908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R., Ewen M. E., Newsome D., Gerdes M., DeCaprio J. A., Lawrence J. B., Livingston D. M. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of the adenovirus E1A-associated 300-kD protein (p300) reveals a protein with properties of a transcriptional adaptor. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 15;8(8):869–884. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.8.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantoni A., Dare A. O., Tschudi C. RNA polymerase III-mediated transcription of the trypanosome U2 small nuclear RNA gene is controlled by both intragenic and extragenic regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2021–2028. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Marzouki N., Ruet A., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Two polypeptide chains in yeast transcription factor tau interact with DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7505–7511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgakopoulos T., Thireos G. Two distinct yeast transcriptional activators require the function of the GCN5 protein to promote normal levels of transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4145–4152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Lampen J. O. Beta-D-fructofuranoside fructohydrolase from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:504–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C. Messenger RNA splicing in yeast: clues to why the spliceosome is a ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):157–163. doi: 10.1126/science.1853200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Happel A. M., Swanson M. S., Winston F. The SNF2, SNF5 and SNF6 genes are required for Ty transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1991 May;128(1):69–77. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Happel A. M., Winston F. A mutant tRNA affects delta-mediated transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):361–374. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Dollard C., Winston F., Beck S., Trowsdale J., Dawid I. B. The bromodomain: a conserved sequence found in human, Drosophila and yeast proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2603–2603. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Mozer B. A., Bhatia-Dey N., Dawid I. B. The Drosophila fsh locus, a maternal effect homeotic gene, encodes apparent membrane proteins. Dev Biol. 1989 Jul;134(1):246–257. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn J. N., Brown S. A., Clark C. D., Winston F. Evidence that SNF2/SWI2 and SNF5 activate transcription in yeast by altering chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2288–2298. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatake K., Hasegawa S., Takada R., Nakatani Y., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. The p250 subunit of native TATA box-binding factor TFIID is the cell-cycle regulatory protein CCG1. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):179–181. doi: 10.1038/362179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. H., Dawid I. B. The maternal-effect gene fsh is essential for the specification of the central region of the Drosophila embryo. New Biol. 1990 Feb;2(2):163–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khavari P. A., Peterson C. L., Tamkun J. W., Mendel D. B., Crabtree G. R. BRG1 contains a conserved domain of the SWI2/SNF2 family necessary for normal mitotic growth and transcription. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):170–174. doi: 10.1038/366170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokubo T., Gong D. W., Yamashita S., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Nakatani Y. Drosophila 230-kD TFIID subunit, a functional homolog of the human cell cycle gene product, negatively regulates DNA binding of the TATA box-binding subunit of TFIID. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):1033–1046. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Treitel M. A., Carlson M. Functional interdependence of the yeast SNF2, SNF5, and SNF6 proteins in transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2687–2691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescure A., Lutz Y., Eberhard D., Jacq X., Krol A., Grummt I., Davidson I., Chambon P., Tora L. The N-terminal domain of the human TATA-binding protein plays a role in transcription from TATA-containing RNA polymerase II and III promoters. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1166–1175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescure A., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W., Krol A., Carbon P. A factor with Sp1 DNA-binding specificity stimulates Xenopus U6 snRNA in vivo transcription by RNA polymerase III. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 20;228(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90828-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Tanaka M., Sullivan M. L., Hernandez N. A TBP complex essential for transcription from TATA-less but not TATA-containing RNA polymerase III promoters is part of the TFIIIB fraction. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1029–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90397-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lührmann R., Kastner B., Bach M. Structure of spliceosomal snRNPs and their role in pre-mRNA splicing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 30;1087(3):265–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90001-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margottin F., Dujardin G., Gérard M., Egly J. M., Huet J., Sentenac A. Participation of the TATA factor in transcription of the yeast U6 gene by RNA polymerase C. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):424–426. doi: 10.1126/science.1989075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Boelens W., Izaurralde E., Jarmolowski A., Kambach C. Nucleocytoplasmic transport and snRNP assembly. Mol Biol Rep. 1993 Aug;18(2):79–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00986760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Tollervey D., Séraphin B. Small nuclear RNAs in messenger RNA and ribosomal RNA processing. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):47–53. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moenne A., Camier S., Anderson G., Margottin F., Beggs J., Sentenac A. The U6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is transcribed by RNA polymerase C (III) in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):271–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchardt C., Yaniv M. A human homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae SNF2/SWI2 and Drosophila brm genes potentiates transcriptional activation by the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4279–4290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06112.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Yoon J. B., Gerster T., Roeder R. G. Oct-1 and Oct-2 potentiate functional interactions of a transcription factor with the proximal sequence element of small nuclear RNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3247–3261. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Carlson M. Genes affecting the regulation of SUC2 gene expression by glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1984 Dec;108(4):845–858. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.4.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Baeuerle P. A., Lührmann R. Nuclear import-export: in search of signals and mechanisms. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90135-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Simmons T., Shuster E. O., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Genetic analysis of small nuclear RNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: viable sextuple mutant. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3150–3159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson B., Guthrie C. An essential yeast snRNA with a U5-like domain is required for splicing in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):613–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90537-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Dingwall A., Scott M. P. Five SWI/SNF gene products are components of a large multisubunit complex required for transcriptional enhancement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):2905–2908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.2905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I. Characterization of the yeast SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 genes, which encode a global activator of transcription. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90192-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert S., Wang E. H., Tjian R. Cloning and expression of human TAFII250: a TBP-associated factor implicated in cell-cycle regulation. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):175–179. doi: 10.1038/362175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski C. L., Henry R. W., Lobo S. M., Hernandez N. Targeting TBP to a non-TATA box cis-regulatory element: a TBP-containing complex activates transcription from snRNA promoters through the PSE. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1535–1548. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seraphin B., Rosbash M. Identification of functional U1 snRNA-pre-mRNA complexes committed to spliceosome assembly and splicing. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen K. A., Bernués J., Parry H. D., Stunnenberg H. G., Berkenstam A., Cavallini B., Egly J. M., Mattaj I. W. TFIID is required for in vitro transcription of the human U6 gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1853–1862. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen K. A., Waldschmidt R., Bernués J., Parry H. D., Seifart K. H., Mattaj I. W. Proximal sequence element factor binding and species specificity in vertebrate U6 snRNA promoters. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):873–884. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90249-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz F., Liao X. C., Rosbash M. U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle-protein interactions are revealed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by in vivo competition assays. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2126–2133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. N., Conesa C., Lefebvre O., Carles C., Ruet A., Quemeneur E., Gagnon J., Sentenac A. Isolation of TFC1, a gene encoding one of two DNA-binding subunits of yeast transcription factor tau (TFIIIC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Abovich N., Rosbash M. Genetic depletion indicates a late role for U5 snRNP during in vitro spliceosome assembly. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3857–3860. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Kretzner L., Rosbash M. A U1 snRNA:pre-mRNA base pairing interaction is required early in yeast spliceosome assembly but does not uniquely define the 5' cleavage site. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2533–2538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03101.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Deuring R., Scott M. P., Kissinger M., Pattatucci A. M., Kaufman T. C., Kennison J. A. brahma: a regulator of Drosophila homeotic genes structurally related to the yeast transcriptional activator SNF2/SWI2. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90191-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. H., Tjian R. Promoter-selective transcriptional defect in cell cycle mutant ts13 rescued by hTAFII250. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):811–814. doi: 10.1126/science.8303298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widner W. R., Wickner R. B. Evidence that the SKI antiviral system of Saccharomyces cerevisiae acts by blocking expression of viral mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4331–4341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto H., Yamashita I. The GAM1/SNF2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a highly charged nuclear protein required for transcription of the STA1 gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):270–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00282476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga S. K., Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I., Yamamoto K. R. Roles of SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 proteins for transcriptional enhancement by steroid receptors. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1598–1604. doi: 10.1126/science.1360703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]