Abstract
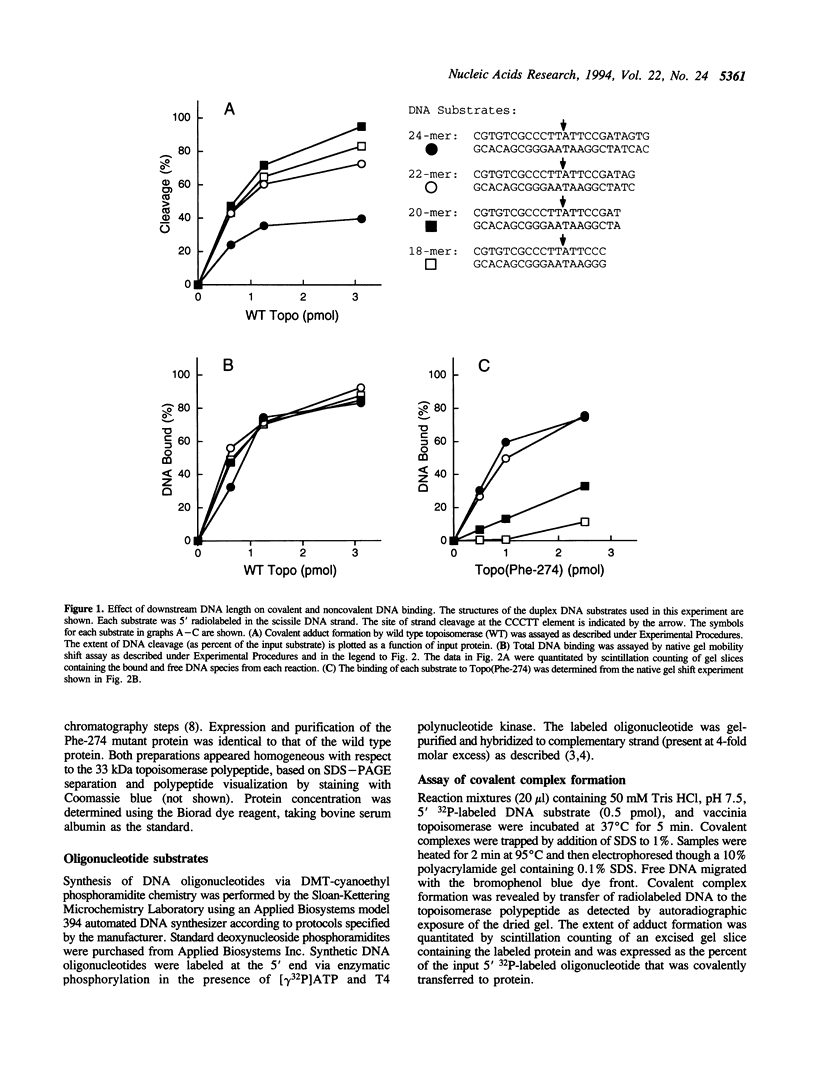
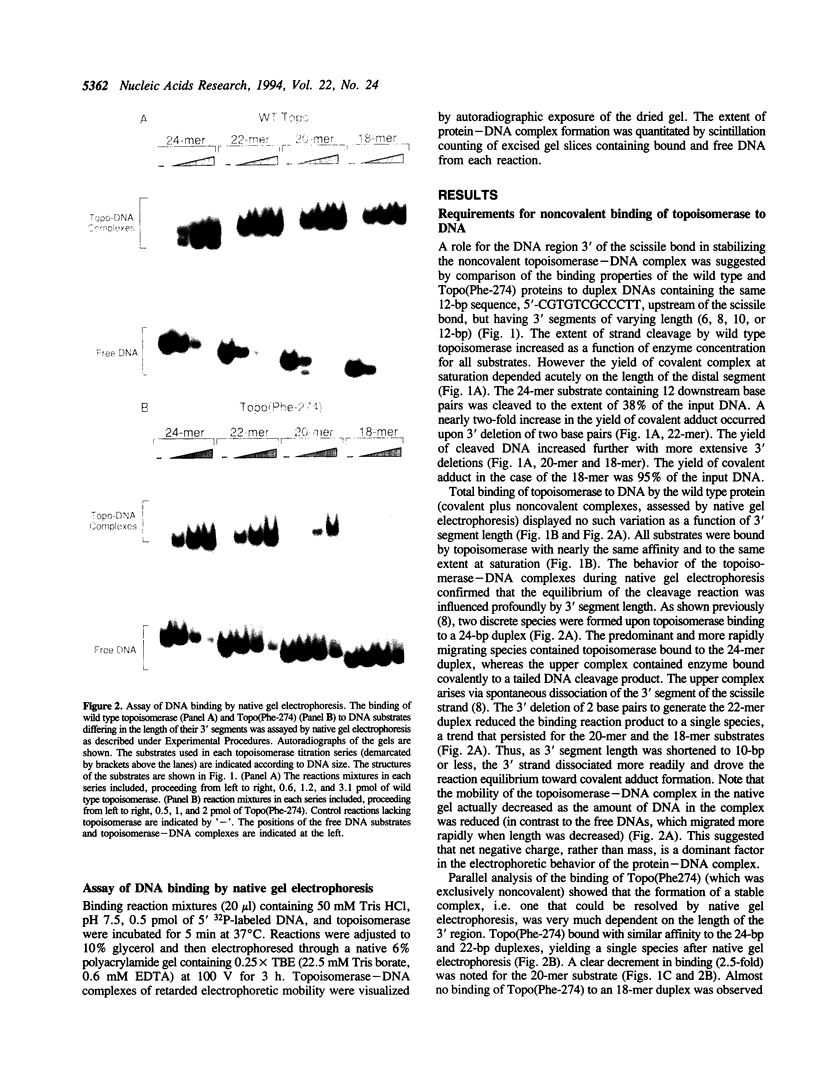
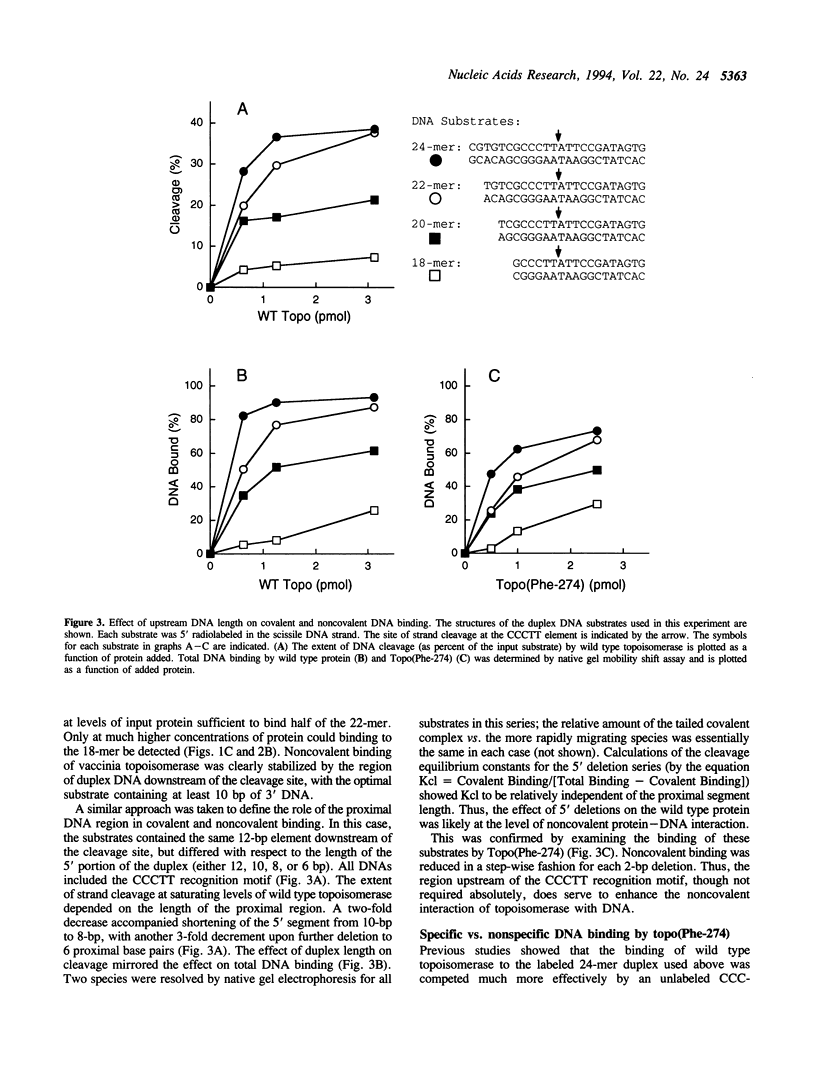
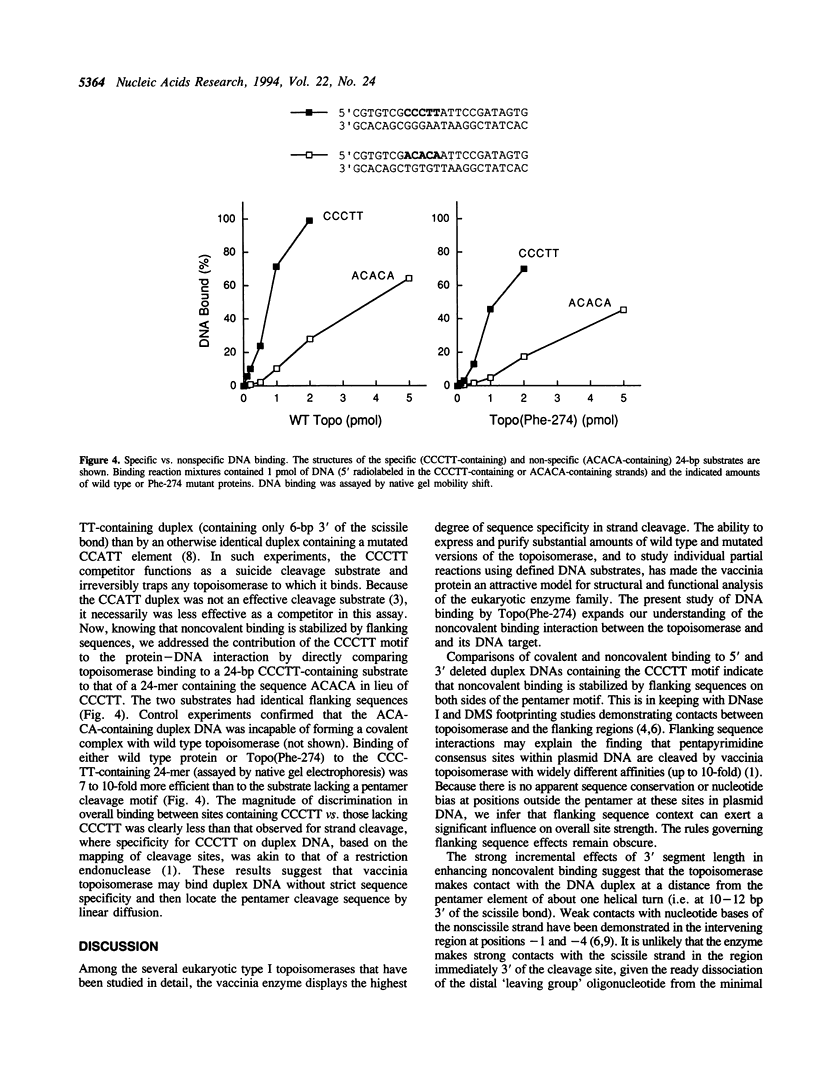
Vaccinia DNA topoisomerase binds duplex DNA and forms a covalent adduct at sites containing a conserved sequence element 5'(C/T)CCTT decreases in the scissile strand. Distinctive aspects of noncovalent versus covalent interaction emerge from analysis of the binding properties of Topo(Phe-274), a mutated protein which is unable to cleave DNA, but which binds DNA noncovalently. Whereas DNA cleavage by wild type enzyme is most efficient with 'suicide' substrates containing fewer than 10 base pairs distal to the scissile bond, optimal noncovalent binding by Topo(Phe-274) requires at least 10-bp of DNA 3' of the cleavage site. Thus, the region of DNA flanking the pentamer motif serves to stabilize the noncovalent topoisomerase-DNA complex. This result is consistent with the downstream dimensions of the DNA binding site deduced from nuclease footprinting. Topo(Phe-274) binds to duplex DNA lacking the consensus pentamer with 7-10-fold lower affinity than to CCCTT-containing DNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Champoux J. J., McCoubrey W. K., Jr, Been M. D. DNA structural features that lead to strand breakage by eukaryotic type-I topoisomerase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:435–442. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen K., Svejstrup A. B., Andersen A. H., Westergaard O. Eukaryotic topoisomerase I-mediated cleavage requires bipartite DNA interaction. Cleavage of DNA substrates containing strand interruptions implicates a role for topoisomerase I in illegitimate recombination. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9690–9701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen K., Westergaard O. Characterization of intra- and intermolecular DNA ligation mediated by eukaryotic topoisomerase I. Role of bipartite DNA interaction in the ligation process. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):721–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack W. E., Terry B. J., Modrich P. Involvement of outside DNA sequences in the major kinetic path by which EcoRI endonuclease locates and leaves its recognition sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4010–4014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConaughy B. L., Young L. S., Champoux J. J. The effect of salt on the binding of the eucaryotic DNA nicking-closing enzyme to DNA and chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 27;655(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morham S. G., Shuman S. Covalent and noncovalent DNA binding by mutants of vaccinia DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15984–15992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S. DNA strand transfer reactions catalyzed by vaccinia topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8620–8627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Golder M., Moss B. Characterization of vaccinia virus DNA topoisomerase I expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16401–16407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Kane E. M., Morham S. G. Mapping the active-site tyrosine of vaccinia virus DNA topoisomerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9793–9797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Prescott J. Specific DNA cleavage and binding by vaccinia virus DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17826–17836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S. Site-specific DNA cleavage by vaccinia virus DNA topoisomerase I. Role of nucleotide sequence and DNA secondary structure. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1796–1803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S. Site-specific interaction of vaccinia virus topoisomerase I with duplex DNA. Minimal DNA substrate for strand cleavage in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11372–11379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Turner J. Site-specific interaction of vaccinia virus topoisomerase I with base and sugar moieties in duplex DNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18943–18950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stivers J. T., Shuman S., Mildvan A. S. Vaccinia DNA topoisomerase I: single-turnover and steady-state kinetic analysis of the DNA strand cleavage and ligation reactions. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 11;33(1):327–339. doi: 10.1021/bi00167a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejstrup J. Q., Christiansen K., Andersen A. H., Lund K., Westergaard O. Minimal DNA duplex requirements for topoisomerase I-mediated cleavage in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12529–12535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry B. J., Jack W. E., Modrich P. Facilitated diffusion during catalysis by EcoRI endonuclease. Nonspecific interactions in EcoRI catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13130–13137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry B. J., Jack W. E., Rubin R. A., Modrich P. Thermodynamic parameters governing interaction of EcoRI endonuclease with specific and nonspecific DNA sequences. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9820–9825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



