Abstract
A simple and rapid method for the analysis of genetic polymorphisms has been developed using allele-specific oligonucleotide arrays bound to glass supports. Allele-specific oligonucleotides are covalently immobilized on glass slides in arrays of 3 mm spots. Genomic DNA is amplified by PCR using one fluorescently tagged primer oligonucleotide and one biotinylated primer oligonucleotide. The two complementary DNA strands are separated, the fluorescently tagged strand is hybridized to the support-bound oligonucleotide array, and the hybridization pattern is detected by fluorescence scanning. Multiple polymorphisms present in the PCR product may be detected in parallel. The effect of spacer length, surface density and hybridization conditions were evaluated, as was the relative efficacy of hybridization with single or double-stranded PCR products. The utility of the method was demonstrated in the parallel analysis of 5 point mutations from exon 4 of the human tyrosinase gene.
Full text
PDF




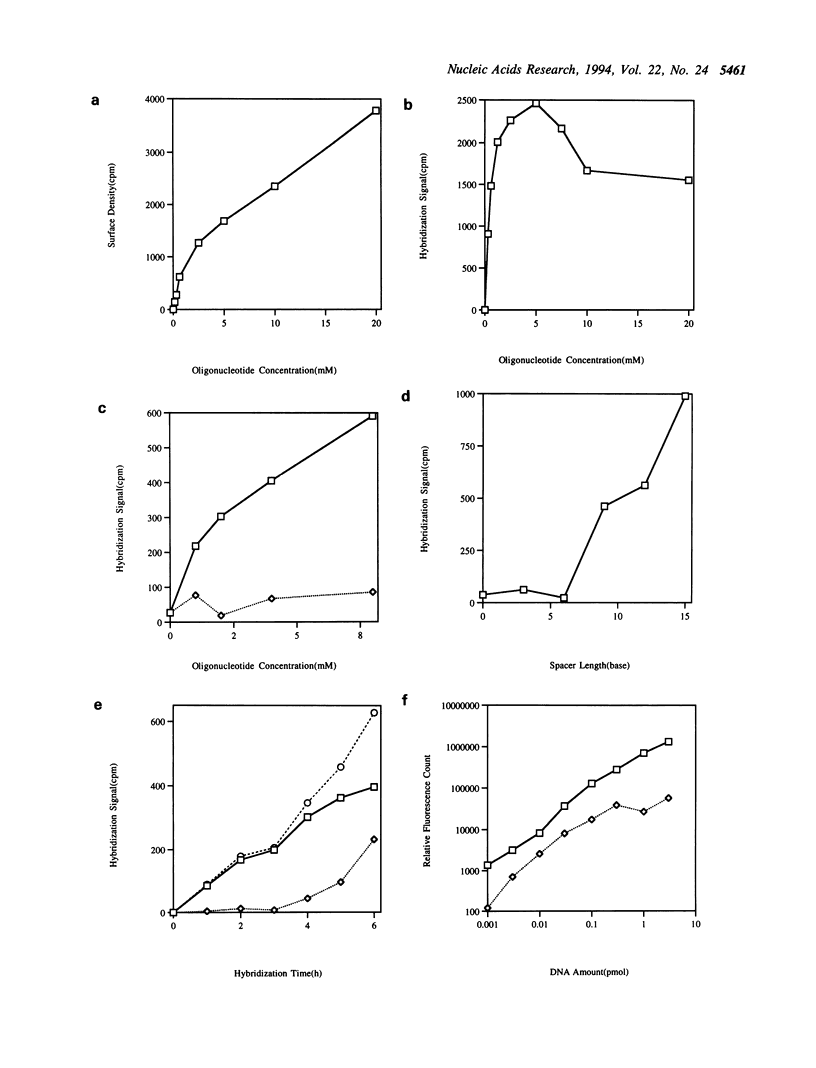

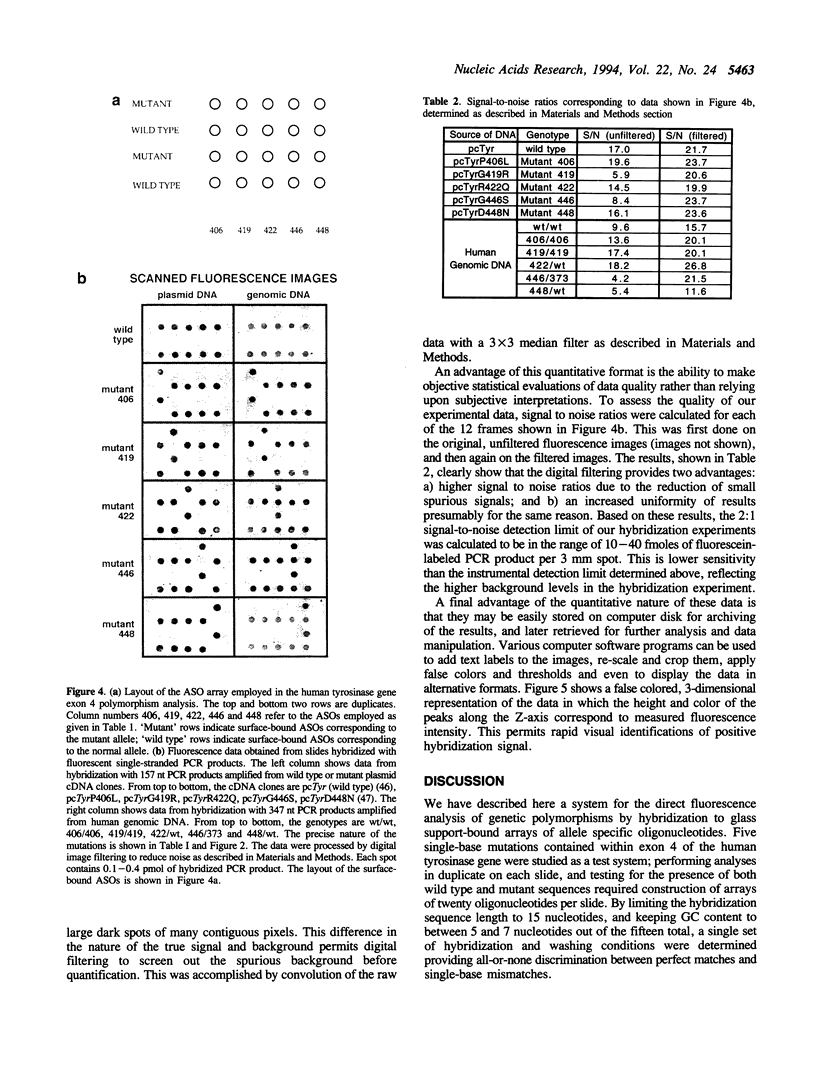


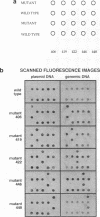
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bains W., Smith G. C. A novel method for nucleic acid sequence determination. J Theor Biol. 1988 Dec 7;135(3):303–307. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard B., Fuller B. B., Vijayasaradhi S., Houghton A. N. Induction of pigmentation in mouse fibroblasts by expression of human tyrosinase cDNA. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2029–2042. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Frank R., Blöcker H., Marky L. A. Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3746–3750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broude N. E., Sano T., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Enhanced DNA sequencing by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3072–3076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardullo R. A., Agrawal S., Flores C., Zamecnik P. C., Wolf D. E. Detection of nucleic acid hybridization by nonradiative fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8790–8794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caskey C. T. Disease diagnosis by recombinant DNA methods. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1223–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.3296189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. G., Malcolm A. D. Mutation detection. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):582–583. doi: 10.1038/353582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drmanac R., Drmanac S., Strezoska Z., Paunesku T., Labat I., Zeremski M., Snoddy J., Funkhouser W. K., Koop B., Hood L. DNA sequence determination by hybridization: a strategy for efficient large-scale sequencing. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1649–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.8503011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drmanac R., Labat I., Brukner I., Crkvenjakov R. Sequencing of megabase plus DNA by hybridization: theory of the method. Genomics. 1989 Feb;4(2):114–128. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahy E., Davis G. R., DiMichele L. J., Ghosh S. S. Design and synthesis of polyacrylamide-based oligonucleotide supports for use in nucleic acid diagnostics. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1819–1826. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor S. P., Read J. L., Pirrung M. C., Stryer L., Lu A. T., Solas D. Light-directed, spatially addressable parallel chemical synthesis. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):767–773. doi: 10.1126/science.1990438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. S., Musso G. F. Covalent attachment of oligonucleotides to solid supports. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5353–5372. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebel L. B., Strunk K. M., Spritz R. A. Organization and nucleotide sequences of the human tyrosinase gene and a truncated tyrosinase-related segment. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingeras T. R., Kwoh D. Y., Davis G. R. Hybridization properties of immobilized nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5373–5390. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. W., Fodor S. P. Combinatorial chemistry--applications of light-directed chemical synthesis. Trends Biotechnol. 1994 Jan;12(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(94)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khrapko K. R., Lysov YuP, Khorlin A. A., Ivanov I. B., Yershov G. M., Vasilenko S. K., Florentiev V. L., Mirzabekov A. D. A method for DNA sequencing by hybridization with oligonucleotide matrix. DNA Seq. 1991;1(6):375–388. doi: 10.3109/10425179109020793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khrapko K. R., Lysov YuP, Khorlyn A. A., Shick V. V., Florentiev V. L., Mirzabekov A. D. An oligonucleotide hybridization approach to DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 9;256(1-2):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81730-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegren U., Kaiser R., Caskey C. T., Hood L. DNA diagnostics--molecular techniques and automation. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):229–237. doi: 10.1126/science.3051381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Gall I., Millasseau P., Dausset J., Cohen D. Two DR beta allelic series defined by exon II-specific synthetic oligonucleotide genomic hybridization: a method of HLA typing? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7836–7840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. G., Connell C. R., Bloch W. Allelic discrimination by nick-translation PCR with fluorogenic probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 11;21(16):3761–3766. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.16.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund V., Schmid R., Rickwood D., Hornes E. Assessment of methods for covalent binding of nucleic acids to magnetic beads, Dynabeads, and the characteristics of the bound nucleic acids in hybridization reactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10861–10880. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyonnet S., Caillaud C., Rey F., Berthelon M., Frezal J., Rey J., Munnich A. Guthrie cards for detection of point mutations in phenylketonuria. Lancet. 1988 Aug 27;2(8609):507–507. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskos U., Southern E. M. Oligonucleotide hybridizations on glass supports: a novel linker for oligonucleotide synthesis and hybridization properties of oligonucleotides synthesised in situ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1679–1684. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D. DNA sequencing by hybridization--a megasequencing method and a diagnostic tool? Trends Biotechnol. 1994 Jan;12(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(94)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Maniatis T. Recent advances in the development of methods for detecting single-base substitutions associated with human genetic diseases. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):275–284. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease A. C., Solas D., Sullivan E. J., Cronin M. T., Holmes C. P., Fodor S. P. Light-generated oligonucleotide arrays for rapid DNA sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5022–5026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen S. R., Larsen M. R., Rasmussen S. E. Covalent immobilization of DNA onto polystyrene microwells: the molecules are only bound at the 5' end. Anal Biochem. 1991 Oct;198(1):138–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90518-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Walsh P. S., Levenson C. H., Erlich H. A. Genetic analysis of amplified DNA with immobilized sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6230–6234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Kaiser R. J., Sanders J. Z., Hood L. E. The synthesis and use of fluorescent oligonucleotides in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:260–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Case-Green S. C., Elder J. K., Johnson M., Mir K. U., Wang L., Williams J. C. Arrays of complementary oligonucleotides for analysing the hybridisation behaviour of nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 25;22(8):1368–1373. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.8.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Maskos U., Elder J. K. Analyzing and comparing nucleic acid sequences by hybridization to arrays of oligonucleotides: evaluation using experimental models. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1008–1017. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90014-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A., Strunk K. M., Giebel L. B., King R. A. Detection of mutations in the tyrosinase gene in a patient with type IA oculocutaneous albinism. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 14;322(24):1724–1728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006143222407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi R. K., Hearing V. J., Urabe K., Aroca P., Spritz R. A. Mutational mapping of the catalytic activities of human tyrosinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23707–23712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi R. K., Strunk K. M., Giebel L. B., Weleber R. G., Spritz R. A. Tyrosinase gene mutations in type I (tyrosinase-deficient) oculocutaneous albinism define two clusters of missense substitutions. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jul 15;43(5):865–871. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness J., Chen L. The use of oligodeoxynucleotide probes in chaotrope-based hybridization solutions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5143–5151. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetmur J. G. DNA probes: applications of the principles of nucleic acid hybridization. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(3-4):227–259. doi: 10.3109/10409239109114069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Coyne M. Y., Will S. G., Levenson C. H., Kawasaki E. S. Single-base mutational analysis of cancer and genetic diseases using membrane bound modified oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3929–3933. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bockxmeer F. M., Mamotte C. D. Apolipoprotein epsilon 4 homozygosity in young men with coronary heart disease. Lancet. 1992 Oct 10;340(8824):879–880. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]