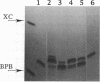
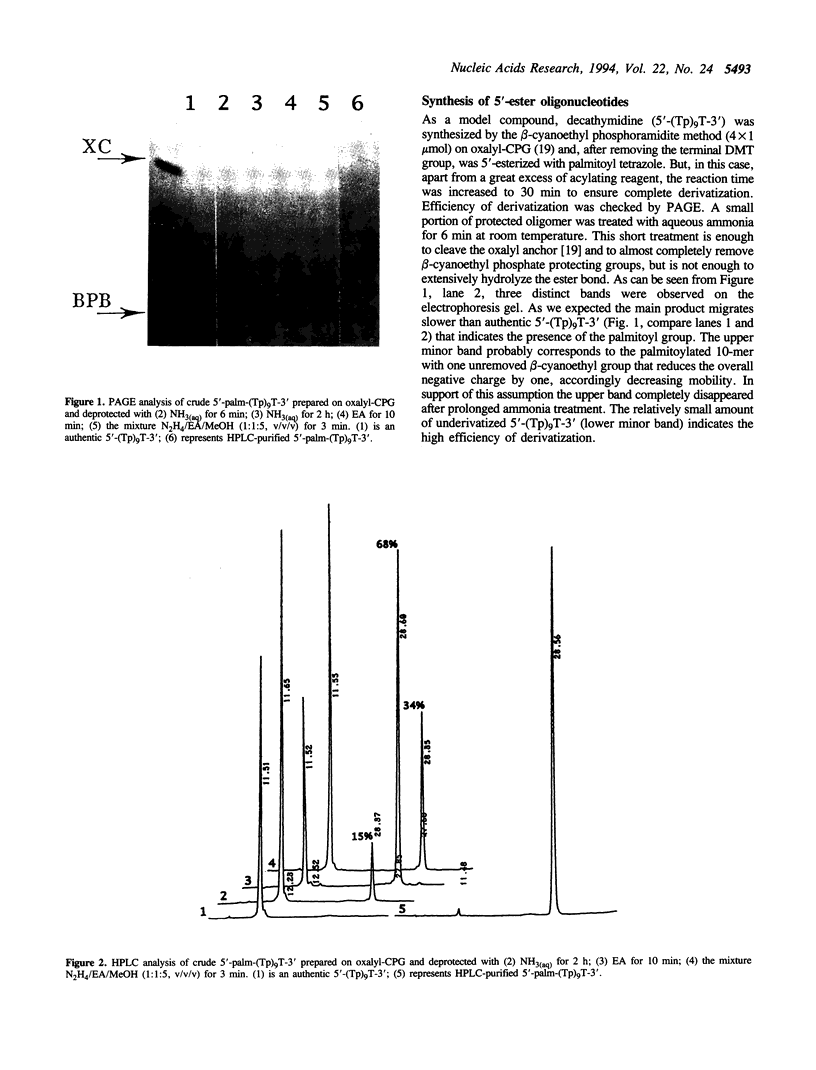
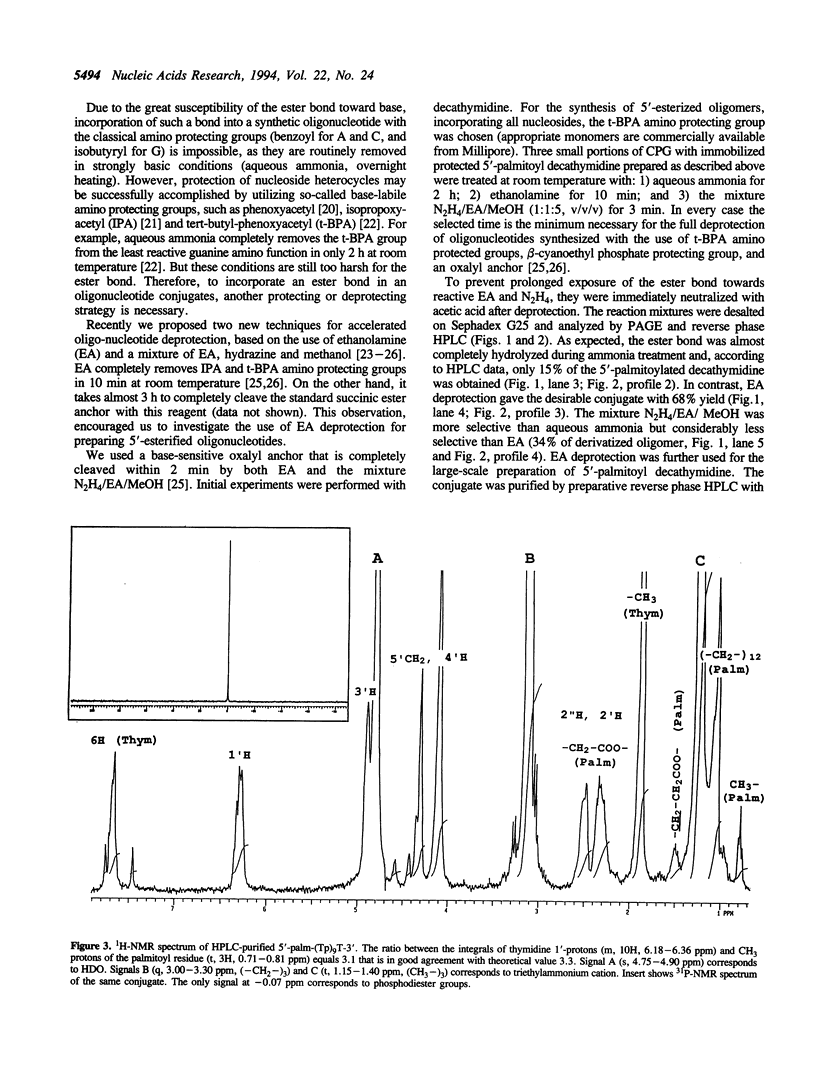
Abstract
Oligonucleotides bearing a terminal lipophilic group attached through a biodegradable ester bond should be useful as antisense pro-drugs with improved cellular uptake. The synthesis of 5'-ester oligonucleotides is, however, problematic due to lability of the ester bond during aqueous ammonia treatment that is commonly used for the deprotection of synthetic oligonucleotides. The synthesis of 5'-palmitoyl oligodeoxynucleotides was accomplished in good yield by the use of a combination of base-labile tert-butylphenoxyacetyl amino protecting groups (t-BPA), the oxalyl-CPG anchor group, and ethanolamine (EA) as a deprotecting reagent.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal S., Tang J. Y. GEM 91--an antisense oligonucleotide phosphorothioate as a therapeutic agent for AIDS. Antisense Res Dev. 1992 Winter;2(4):261–266. doi: 10.1089/ard.1992.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alul R. H., Singman C. N., Zhang G. R., Letsinger R. L. Oxalyl-CPG: a labile support for synthesis of sensitive oligonucleotide derivatives. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1527–1532. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayever E., Iversen P., Smith L., Spinolo J., Zon G. Systemic human antisense therapy begins. Antisense Res Dev. 1992 Summer;2(2):109–110. doi: 10.1089/ard.1992.2.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutorin A. S., Gus'kova L. V., Ivanova E. M., Kobetz N. D., Zarytova V. F., Ryte A. S., Yurchenko L. V., Vlassov V. V. Synthesis of alkylating oligonucleotide derivatives containing cholesterol or phenazinium residues at their 3'-terminus and their interaction with DNA within mammalian cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 28;254(1-2):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta B., Sims R. B., Valtieri M., Caracciolo D., Szczylik C., Venturelli D., Ratajczak M., Beran M., Gewirtz A. M. Normal and leukemic hematopoietic cells manifest differential sensitivity to inhibitory effects of c-myb antisense oligodeoxynucleotides: an in vitro study relevant to bone marrow purging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2351–2355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh M. K., Ghosh K., Cohen J. S. Phosphorothioate-phosphodiester oligonucleotide co-polymers: assessment for antisense application. Anticancer Drug Des. 1993 Feb;8(1):15–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh M. K., Mitra A. K. Effects of 5'-ester modification on the physicochemical properties and plasma protein binding of 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine. Pharm Res. 1991 Jun;8(6):771–775. doi: 10.1023/a:1015862319927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letsinger R. L., Zhang G. R., Sun D. K., Ikeuchi T., Sarin P. S. Cholesteryl-conjugated oligonucleotides: synthesis, properties, and activity as inhibitors of replication of human immunodeficiency virus in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6553–6556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKellar C., Graham D., Will D. W., Burgess S., Brown T. Synthesis and physical properties of anti-HIV antisense oligonucleotides bearing terminal lipophilic groups. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3411–3417. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhauser B., Wagner E. Effective incorporation of 2'-O-methyl-oligoribonucleotides into liposomes and enhanced cell association through modification with thiocholesterol. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):533–538. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polushin N. N., Morocho A. M., Chen B. C., Cohen J. S. On the rapid deprotection of synthetic oligonucleotides and analogs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 25;22(4):639–645. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polushin N. N., Pashkova I. N., Chakhmakhcheva O. G., Efimov V. A. Primenenie gidrazina dlia bystrogo deblokirovaniia sintetitcheskikh oligonukleotidov. Bioorg Khim. 1993 Mar;19(3):318–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polushin N. N., Pashkova I. N., Efimov V. A. Bystryi metod polnogo deblokirovaniia sinteticheskikh oligonukleotidov. Bioorg Khim. 1991 Aug;17(8):1145–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polushin N. N., Pashkova I. N., Efimov V. A. Rapid deprotection procedures for synthetic oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1991;(24):49–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczak M. Z., Kant J. A., Luger S. M., Hijiya N., Zhang J., Zon G., Gewirtz A. M. In vivo treatment of human leukemia in a scid mouse model with c-myb antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11823–11827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M. W., Adams A. D., Nelson J. S., Meyer R. B., Jr Acridine- and cholesterol-derivatized solid supports for improved synthesis of 3'-modified oligonucleotides. Bioconjug Chem. 1991 Jul-Aug;2(4):217–225. doi: 10.1021/bc00010a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulhof J. C., Molko D., Teoule R. The final deprotection step in oligonucleotide synthesis is reduced to a mild and rapid ammonia treatment by using labile base-protecting groups. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):397–416. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea R. G., Marsters J. C., Bischofberger N. Synthesis, hybridization properties and antiviral activity of lipid-oligodeoxynucleotide conjugates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3777–3783. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Davis P., Usman N., Pérez J., Hodge R., Kremsky J., Casale R. Labile exocyclic amine protection of nucleosides in DNA, RNA and oligonucleotide analog synthesis facilitating N-deacylation, minimizing depurination and chain degradation. Biochimie. 1993;75(1-2):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90019-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Pal R., DeVico A. L., Hoke G., Mumbauer S., Kinstler O., Sarngadharan M. G., Letsinger R. L. Mode of action of 5'-linked cholesteryl phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides in inhibiting syncytia formation and infection by HIV-1 and HIV-2 in vitro. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 5;30(9):2439–2444. doi: 10.1021/bi00223a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uznanski B., Grajkowski A., Wilk A. The isopropoxyacetic group for convenient base protection during solid-support synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides and their triester analogs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4863–4871. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]