Abstract
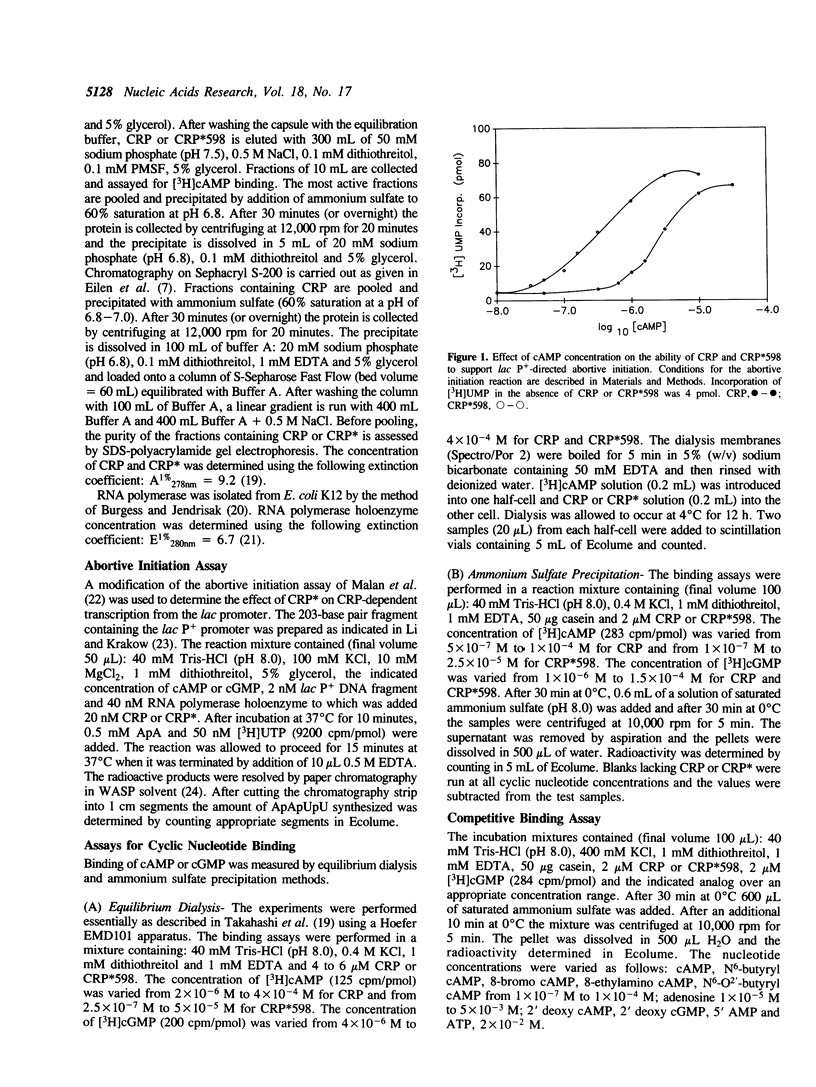
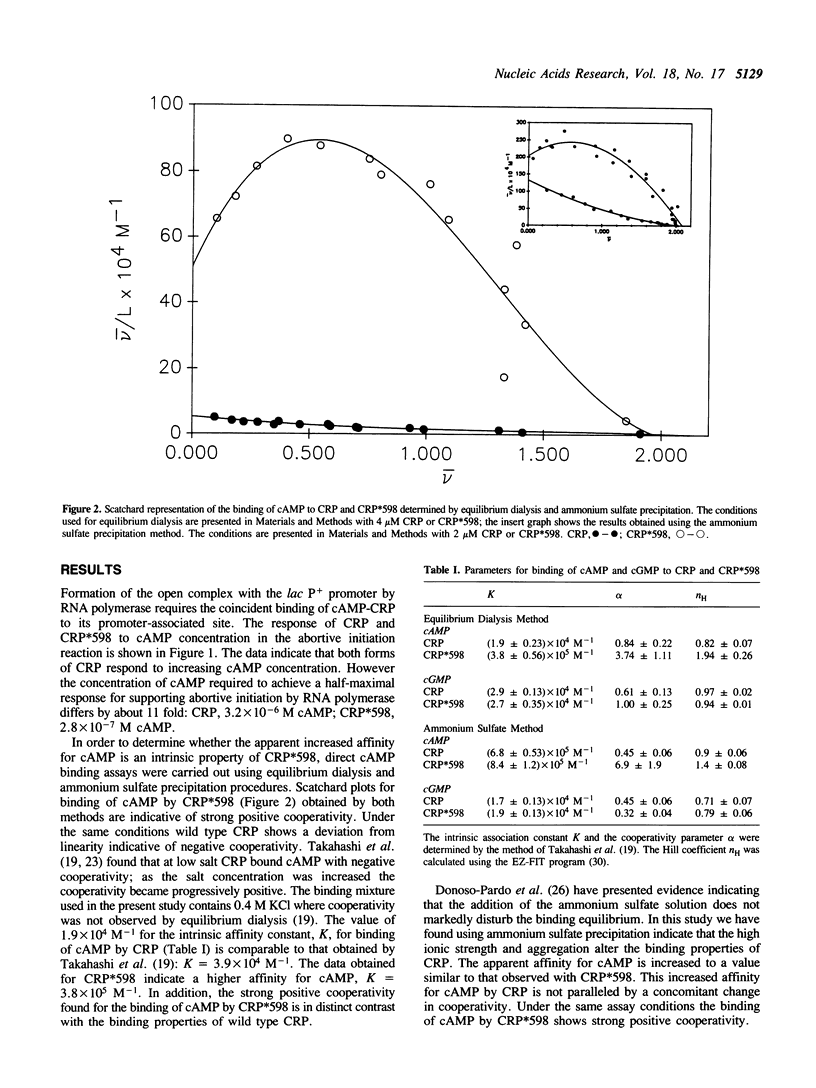
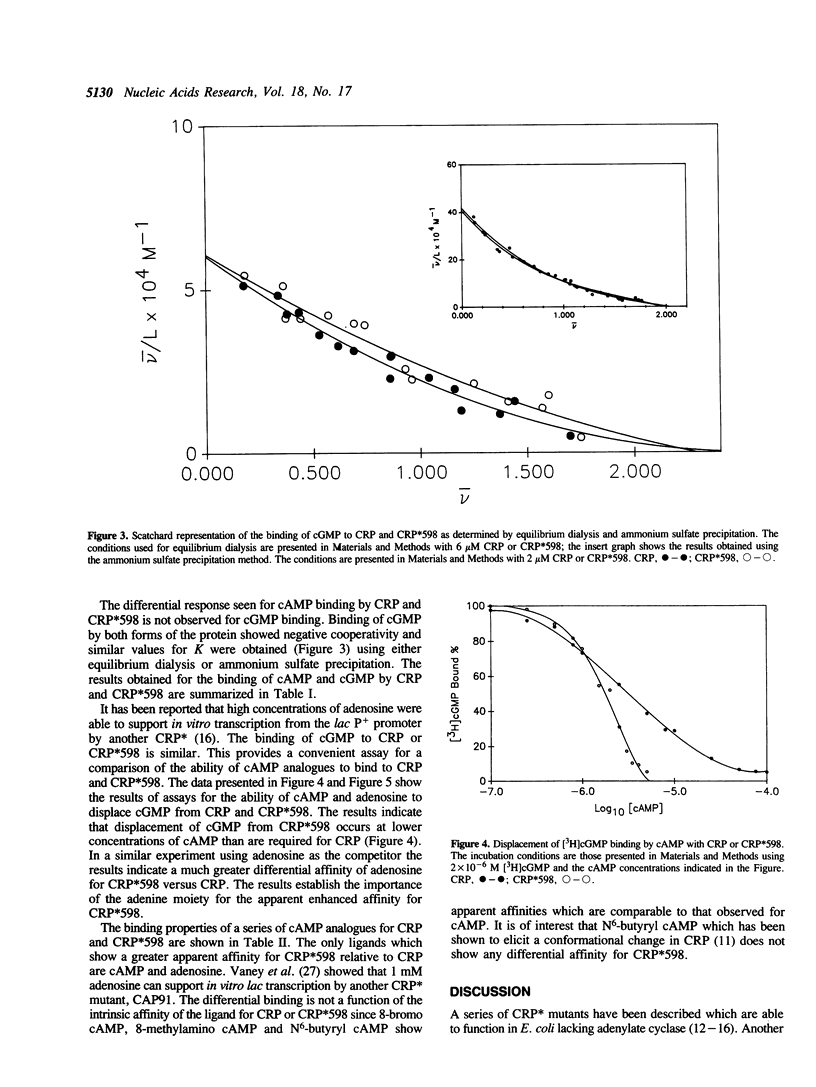
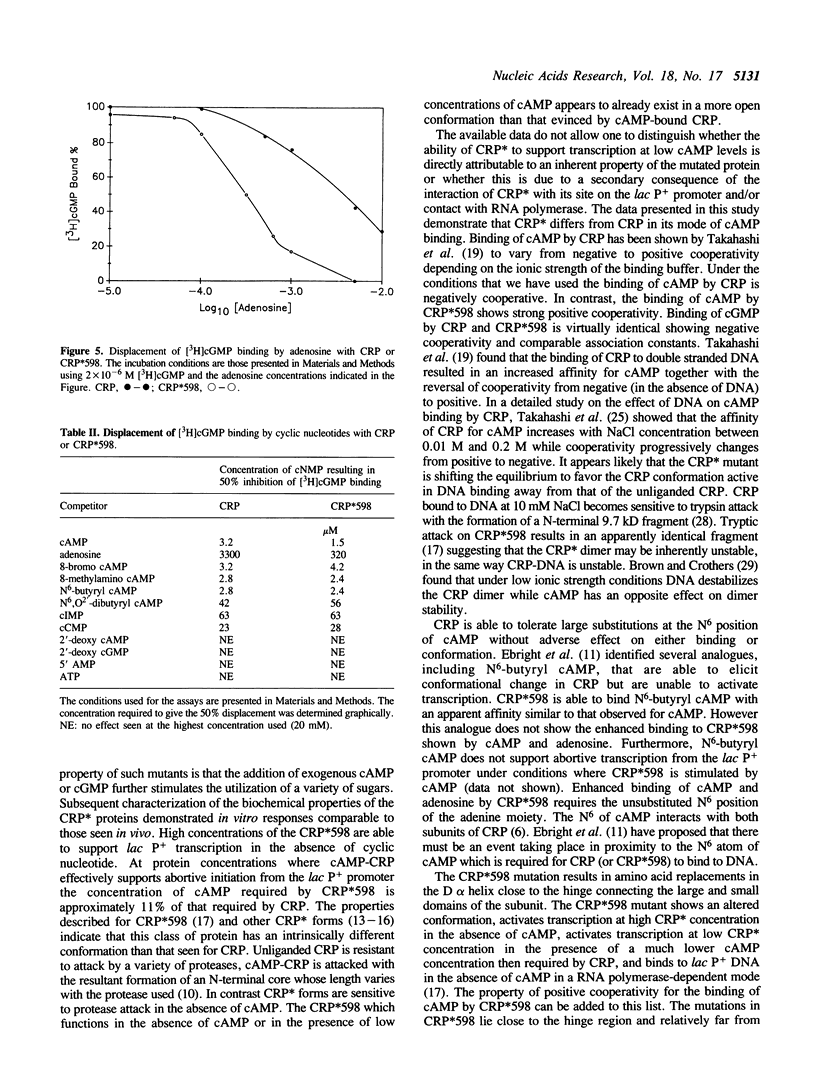
Wild type cAMP receptor protein (CRP) activates in vitro lac transcription only in the presence of cAMP. In contrast the mutant CRP*598 (Arg-142 to His, Ala-144 to Thr) can activate lac transcription in the absence of cyclic nucleotide or at concentrations of cAMP below that required by CRP. To further characterize the properties of CRP*598, the binding of cAMP and cGMP to CRP and CRP*598 has been determined. The intrinsic binding constant (K) values obtained for cAMP binding are: CRP, 1.9 x 10(4) M-1; CRP*598, 3.8 x 10(5) M-1. The K values obtained for cGMP binding are: CRP, 2.9 x 10(4) M-1; CRP*598, 2.7 x 10(4) M-1. The results indicate that the affinity of CRP and CRP*598 for cGMP is relatively unchanged while the affinity of CRP*598 for cAMP is approximately twenty times greater than that shown by CRP. Binding of cAMP by CRP and cGMP by CRP or CRP*598 exhibits slight negative cooperativity. The major difference seen is that CRP*598 binds cAMP with strong positive cooperativity. The importance of the unsubstituted N6 position of the adenine moiety is also shown by the similar affinity of both forms of CRP for N6-butyryl cAMP. The cAMP binding properties evinced by CRP*598 suggest that its intrinsically altered conformation may be related to that assumed by CRP in a CRP-DNA or a cAMP-CRP-DNA complex.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Fujimoto S., Ozaki N. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the gene for E. coli cAMP receptor protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1345–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Nakamura T., Mitani H., Mori H. Mutations that alter the allosteric nature of cAMP receptor protein of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3329–3332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04084.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angulo J., Krakow J. S. Sensitization of the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein to trypsin cleavage by polydeoxyribonucleotides and polyribonucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11315–11319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazy B., Ullmann A. Properties of cyclic AMP-independent catabolite gene activator proteins of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11645–11649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Crothers D. M. Modulation of the stability of a gene-regulatory protein dimer by DNA and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7387–7391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Gicquel-Sanzey B. Cloning and sequence of the crp gene of Escherichia coli K 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1363–1378. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoso-Pardo J. L., Turner P. C., King R. W. Cyclic nucleotide binding to cAMP receptor protein from Escherichia coli. Optical and ligand-binding studies. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Nov 2;168(3):687–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Le Grice S. F., Miller J. P., Krakow J. S. Analogs of cyclic AMP that elicit the biochemically defined conformational change in catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) but do not stimulate binding to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):91–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilen E., Krakow J. S. Cyclic AMP-mediated intersubunit disulfide crosslinking of the cyclic AMP receptor protein of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilen E., Pampeno C., Krakow J. S. Production and properties of the alpha core derived from the cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2469–2473. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garges S., Adhya S. Sites of allosteric shift in the structure of the cyclic AMP receptor protein. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):745–751. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harman J. G., Dobrogosz W. J. Mechanism of CRP-mediated cya suppression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):191–199. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.191-199.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harman J. G., McKenney K., Peterkofsky A. Structure-function analysis of three cAMP-independent forms of the cAMP receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16332–16339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow J. S., Pastan I. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor: loss of cAMP-dependent DNA binding activity after proteolysis in the presence of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2529–2533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S. A., Murthy N. S., Krakow J. S. Ligand-induced change in the radius of gyration of cAMP receptor protein from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 1;109(1):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. J., Orphanos P. D., Fischmann B. S., Beychok S. Physicochemical properties and interactions of Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase holoenzyme, core enzyme, subunits, and subassembly alpha 2 beta. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4808–4814. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. M., Krakow J. S. A monoclonal antibody that inhibits cyclic AMP binding by the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8383–8389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., Kolb A., Buc H., McClure W. R. Mechanism of CRP-cAMP activation of lac operon transcription initiation activation of the P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):881–909. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Cech C. L., Johnston D. E. A steady state assay for the RNA polymerase initiation reaction. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8941–8948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9-A resolution. Incorporation of amino acid sequence and interactions with cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9518–9524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrella F. W. EZ-FIT: a practical curve-fitting microcomputer program for the analysis of enzyme kinetic data on IBM-PC compatible computers. Anal Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;174(2):437–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren Y. L., Garges S., Adhya S., Krakow J. S. Cooperative DNA binding of heterologous proteins: evidence for contact between the cyclic AMP receptor protein and RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4138–4142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Straney S. B., Crothers D. M. Synergy between Escherichia coli CAP protein and RNA polymerase in the lac promoter open complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):41–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90522-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Blazy B., Baudras A. An equilibrium study of the cooperative binding of adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate to the adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate receptor protein from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 28;19(22):5124–5130. doi: 10.1021/bi00563a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Blazy B., Baudras A., Hillen W. Ligand-modulated binding of a gene regulatory protein to DNA. Quantitative analysis of cyclic-AMP induced binding of CRP from Escherichia coli to non-specific and specific DNA targets. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):783–796. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90244-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaney M. C., Gilliland G. L., Harman J. G., Peterkofsky A., Weber I. T. Crystal structure of a cAMP-independent form of catabolite gene activator protein with adenosine substituted in one of two cAMP-binding sites. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4568–4574. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of a complex of catabolite gene activator protein and cyclic AMP refined at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F. Y., Nath K., Wu C. W. Conformational transitions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein of Escherichia coli. A fluorescent probe study. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2567–2572. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


