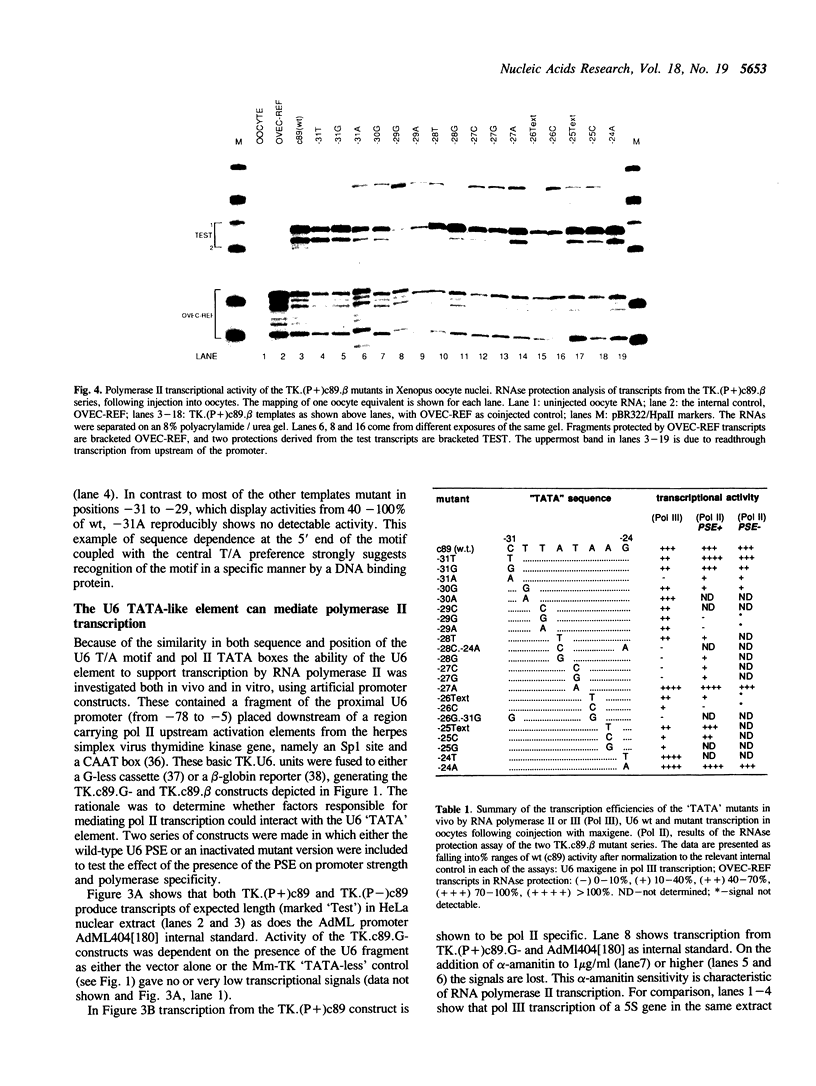
Abstract
The role of various sequences in determining the RNA polymerase III (pol III) specificity of the Xenopus U6 gene promoter has been investigated. A sequence closely resembling an RNA polymerase II (pol II) TATA box, which has previously been implicated in determining the pol III specificity of the U6 promoter, was analyzed in detail. The U6 TATA-like element, in a different promoter context, is shown to be capable of mediating RNA polymerase II transcription both in vitro and in oocyte microinjection experiments. Extensive mutagenesis of the TATA-like element in the context of the pol III and pol II promoters leads to the conclusion that the sequence requirements for function in the two contexts are dissimilar, suggesting that different factors may be involved in mediating pol II and pol III transcription. Further, as implied by the above results, it is shown that the polymerase III specificity of the U6 gene is not solely dependent upon the TATA-like element but rather reflects complex interaction between multiple components of the promoter.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Brown W. L., Groudine M. Accurate, TATA box-dependent polymerase III transcription from promoters of the c-myc gene in injected Xenopus oocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1179–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Function of a yeast TATA element-binding protein in a mammalian transcription system. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):37–42. doi: 10.1038/334037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallini B., Faus I., Matthes H., Chipoulet J. M., Winsor B., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Cloning of the gene encoding the yeast protein BTF1Y, which can substitute for the human TATA box-binding factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9803–9807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallini B., Huet J., Plassat J. L., Sentenac A., Egly J. M., Chambon P. A yeast activity can substitute for the HeLa cell TATA box factor. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):77–80. doi: 10.1038/334077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of a yeast his3 "TATA element": genetic evidence for a specific TATA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2691–2695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Sussman D. J., Zeller R., Leder P. The c-myc gene encodes superimposed RNA polymerase II and III promoters. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1001–1008. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90586-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concino M., Goldman R. A., Caruthers M. H., Weinmann R. Point mutations of the adenovirus major late promoter with different transcriptional efficiencies in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8493–8496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Henning D., Wright D., Reddy R. Upstream regulatory elements are necessary and sufficient for transcription of a U6 RNA gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):503–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenmann D. M., Dollard C., Winston F. SPT15, the gene encoding the yeast TATA binding factor TFIID, is required for normal transcription initiation in vivo. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1183–1191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giangrande A., Mettling C., Martin M., Ruiz C., Richards G. Drosophila Sgs3 TATA: effects of point mutations on expression in vivo and protein binding in vitro with staged nuclear extracts. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3459–3466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08510.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Isolation of the gene encoding the yeast TATA binding protein TFIID: a gene identical to the SPT15 suppressor of Ty element insertions. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1173–1181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Yeast TATA-binding protein TFIID binds to TATA elements with both consensus and nonconsensus DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5718–5722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Dathan N. A., Mattaj I. W. Functional analysis of mutant Xenopus U2 snRNAs. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):159–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90878-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbury P. A., Struhl K. Functional distinctions between yeast TATA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5298–5304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Wang C. K., Fujii H., Cromlish J. A., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Cloning and structure of a yeast gene encoding a general transcription initiation factor TFIID that binds to the TATA box. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):299–303. doi: 10.1038/341299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Manley J. L. DNA sequence required for initiation of transcription in vitro from the major late promoter of adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):820–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinert H., Benecke B. J. Transcription of human 7S K DNA in vitro and in vivo is exclusively controlled by an upstream promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1319–1331. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Appel B. Xenopus tropicalis U6 snRNA genes transcribed by Pol III contain the upstream promoter elements used by Pol II dependent U snRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2463–2478. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Transcription of a human U6 small nuclear RNA gene in vivo withstands deletion of intragenic sequences but not of an upstream TATATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7371–7379. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Upstream elements required for efficient transcription of a human U6 RNA gene resemble those of U1 and U2 genes even though a different polymerase is used. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):196–204. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Hernandez N. A 7 bp mutation converts a human RNA polymerase II snRNA promoter into an RNA polymerase III promoter. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Ifill S., Hernandez N. cis-acting elements required for RNA polymerase II and III transcription in the human U2 and U6 snRNA promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2891–2899. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Chambon P. The SV40 early region TATA box is required for accurate in vitro initiation of transcription. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):310–315. doi: 10.1038/290310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Dathan N. A., Parry H. D., Carbon P., Krol A. Changing the RNA polymerase specificity of U snRNA gene promoters. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Moorefield B., Pieler T. Common mechanisms of promoter recognition by RNA polymerases II and III. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry H. D., Mattaj I. W. Positive and negative functional interactions between promoter elements from different classes of RNA polymerase III-transcribed genes. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1097–1104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08215.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry H. D., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. The Xenopus U2 gene PSE is a single, compact, element required for transcription initiation and 3' end formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3633–3644. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Hamm J., Roeder R. G. The 5S gene internal control region is composed of three distinct sequence elements, organized as two functional domains with variable spacing. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Kao C. C., Pei R., Berk A. J. Yeast TATA-box transcription factor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7785–7789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Fisch T. M., Benecke B. J., Nevins J. R., Heintz N. Definition of multiple, functionally distinct TATA elements, one of which is a target in the hsp70 promoter for E1A regulation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):723–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Rooney R. J., Fisch T. M., Heintz N., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the c-fos promoter requires the TATAA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):513–517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vankan P., Filipowicz W. Structure of U2 snRNA genes of Arabidopsis thaliana and their expression in electroporated plant protoplasts. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):791–799. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02877.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Chambon P. A T to A base substitution and small deletions in the conalbumin TATA box drastically decrease specific in vitro transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1813–1824. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wefald F. C., Devlin B. H., Williams R. S. Functional heterogeneity of mammalian TATA-box sequences revealed by interaction with a cell-specific enhancer. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):260–262. doi: 10.1038/344260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Gerster T., Müller M. M., Schaffner G., Schaffner W. OVEC, a versatile system to study transcription in mammalian cells and cell-free extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6787–6798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Rosser D. S., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. A TATA box implicated in E1A transcriptional activation of a simple adenovirus 2 promoter. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):512–515. doi: 10.1038/326512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]