Abstract
Aims
The objective of this study was to evaluate the antistaphylococcal effect and elucidate the mechanism of action of orange essential oil against antibiotic resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains.
Methods and Results
Inhibitory effect of commercial orange essential oil (EO) against six S. aureus strains was tested by disc diffusion and agar dilution methods. The mechanism of EO action on MRSA was analyzed by transcriptional profiling. Morphological changes of EO treated S. aureus were examined by transmission electron microscopy. Results showed that 0.1% of cold pressed terpeneless Valencia orange oil (CPV) induced the cell wall stress stimulon consistent with inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Transmission electron microscopic observation revealed cell lysis and suggested a cell wall-lysis related mechanism of CPV.
Conclusions
CPV inhibits the growth of S. aureus, causes gene expression changes consistent with inhibition of cell wall synthesis and triggers cell lysis.
Significance and Impact of the Study
Multiple antibiotics resistance is becoming a serious problem in the management of S. aureus infections. In this study the altered expression of cell wall associated genes and subsequent cell lysis in MRSA caused by CPV suggests that it may be a potential antimicrobial agent to control antibiotic resistant S. aureus.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, Natural antimicrobial, Mechanism of Essential Oil
Introduction
In recent years methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) has appeared more in communities outside the hospital settings and has emerged as a major public health concern worldwide (Kennedy et al. 2008, DeLeo et al. 2010). Since infections caused by MRSA are increasing, as are rates of antibiotic therapy failures, new measures to treat and prevent this infectious pathogen are becoming inevitable (Pirri et al. 2009). One such approach to counter the antibiotic resistance emphasizes the search of biologically active pharmacophores possessing novel modes of action from natural resources (Saxena and Kumar 2002, Saleem et al. 2010). Natural products have been investigated and utilized to alleviate disease since early human history. Before the “synthetic era”, 80% of all medicines were obtained from roots, barks, leaves, flowers, seeds and fruits (McChesney et al. 2007).
Numerous studies have discovered promising novel antimicrobial candidates from plant derived essential oils (EOs). EOs are particularly interesting since some oils have been used by native groups for curative purposes in the past (Saravolatz et al. 1982, Burt 2004). Also, research data indicate that many EOs have antimicrobial activity. For instance, tea tree oil obtained from Melaleuca alternifolia has been shown to be active against a wide range of microorganisms (Gustafson et al. 1998, Hammer et al. 2006). In previous studies the antimicrobial activities of other EOs have also been investigated and their actions against various pathogens, including clinical MRSA isolates, have been demonstrated (Cox et al. 1998, Elsom and Hide 1999, Hammer et al. 1999, May et al. 2000, Takarada et al. 2002, Edwards-Jones et al. 2004, Brady et al. 2006, Prabuseenivasan et al. 2006, Chao et al. 2008, Doran et al. 2009, Tohidpour et al. 2010). There are also several clinical studies and case reports noting the successful use of EOs in treating MRSA nasal carriage and wound infections (Caelli et al. 2000, Sherry et al. 2001, Dryden et al. 2004, Sherry and Warnke 2004).
Fisher and Phillips (Fisher and Phillips 2006) studied the effectiveness of citrus EOs and their components citral, limonene, and linalool against a number of common foodborne pathogens Listeria monocytenes, S. aureus, Bacillus cereus, Escherichia coli O157, and Campylobacter jejuni both in vitro and on food models. Previous studies in our laboratory have demonstrated the inhibition of Salmonella (O’Bryan et al. 2008), Escherichia coli O157: H7 (Nannapaneni et al. 2008), Listeria (Shannon et al. 2011) and Campylobacter (Nannapaneni et al. 2009) by citrus derived cold pressed Valencia orange oil, terpeneless Valencia orange oil, cold pressed orange terpenes, high purity orange terpenes, d-limonene, and terpenes from orange essence. However, these oils were not tested specifically against antibiotic resistant S. aureus. Therefore, the objective of this study was to evaluate the inhibitory activity and mechanism of action of orange essential oil on S. aureus to determine their potential for use as antistaphylococcal agents against MRSA.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and growth conditions
The following S. aureus strains were used in this study: methicillin-susceptible strain SH1000 (Horsburgh et al. 2002), methicillin-resistant strains COL (Sabath et al. 1974), 13136 p−m+ (Brown and Reynolds 1980), and N315 (Kuroda et al. 2001), and methicillin- and vancomycin intermediate-resistant strains 13136 p−m+ V20 (Pfeltz et al. 2000), and Mu50 (Kuroda et al. 2001). Cultures were propagated in tryptic soya broth (TSB) (Difco Laboratories, Inc. Detroit, MI). A loop of bacteria from a tryptic soya agar (TSA) (Difco Laboratories, Inc.) was inoculated into a 10 mL tube of sterile TSB and subsequently incubated for 18 h at 37 °C, after which a 100 μL aliquot was transferred into a fresh sterile 10 mL of TSB, which was incubated an additional 18 h before use.
Orange essential oils
All essential oils were obtained as commercially available products of Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck from Firmenich Citrus Center, Safety Harbor, FL, USA and were stored per manufacturer’s recommendations at 4 °C prior to use. Oils tested included terpeneless cold pressed Valencia orange oil (CPV), Valencia orange oil, cold pressed orange terpenes, high purity orange terpenes, d-limonene, terpenes from orange essence, 5-fold concentrated Valencia orange oil, and cold pressed citronellal.
Disc diffusion assay for screening the inhibitory effect of EOs
Disc diffusion assay was carried out by the method described by O’Bryan et al. (O’Bryan et al. 2008). Overnight cultures of the S. aureus were streaked on sterile TSA (Difco Laboratories, Inc.) by dipping a sterile cotton swab into the culture. The swab was used to streak the agar plate to produce a lawn of growth by streaking the plate in 3 different directions. The orange EOs (10 μL) were aseptically pipetted onto sterile 6-mm paper discs (Becton Dickson, Franklin Lakes, NJ) and subsequently the paper discs were aseptically placed on the agar. Diameters of zones of inhibitions were measured in mm after 24 h of incubation at 37 °C. The assays were carried out on three independent experiments conducted in duplicate.
Minimum inhibitory concentration assay (MIC)
The MIC of CPV for S. aureus strains was performed by modified agar dilution method. A final concentration of 0.5% (v/v) Tween-80 (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) was incorporated into the agar medium to enhance oil solubility. Different concentrations of oil were added to the sterile TSA at 48 °C. Plates were dried at room temperature for 12 h prior to spot inoculation with 5 μL aliquots of culture containing approximately 5 Log CFU per spot of each organism in triplicate. Inoculated plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h and the MICs were determined as the lowest concentration of oil inhibiting visible growth of organisms on the agar plate. Experiments were carried out in three independent experiments in duplicate. Inhibition of bacterial growth in the plates containing test oil was judged by comparison with visible growth in control plates.
Growth inhibitory concentration (GIC) studies
Overnight grown cultures were used to inoculate (1% v/v) 20 ml TSB in 50 ml Erlenmeyer flasks and were grown at 37 °C with shaking at 200 rpm. Two different concentrations (½, and 1x of MIC) of EO were used in this study. After adding the EO to the log phase cultures (OD600 approximately 0.4) growth was measured at 600 nm at regular intervals in a Beckman DU65 spectrophotometer. A final concentration of 0.5% (v/v) Tween-80 (Sigma) was used as a dispersing agent for EO.
RNA extraction and transcriptional profiling
Based on the GIC study ½ x MIC concentration of EO was added to the log phase cells for 15 min of challenge. Control culture was not challenged with EO and was also incubated for 15 min. RNA extraction and microarray hybridization was carried out as described by Muthaiyan et al. (2008). Briefly, total bacterial RNA was extracted from 3 ml of culture which was mixed with 6 ml of bacterial RNA protect solution (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) and subsequently centrifuged to collect the cells. To extract the RNA, bacterial pellets were resuspended in 1 ml of Trizol (Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY) and the cells were broken using the FastPrep system (Qbiogene, Irvine, CA) at a speed setting of 6.0 for 40 seconds. Extracted RNA was purified using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen). cDNA was generated from DNase treated and purified RNA by using random hexamers (Invitrogen) as primers for reverse transcription. The primers were annealed (70 °C for 10 min, followed by 1 min incubation in ice) to total RNA (2.5 μg) and were extended with SuperScript III reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen) with 0.1 M dithiothreitol 12.5 m mol dNTP/aa-UTP (Ambion, Austin, TX) mix at 42 °C. Residual RNA was removed by alkaline treatment followed by neutralization, and cDNA was purified with a QIAquick PCR purification kit (Qiagen). Purified aminoallyl-modified cDNA was subsequently labeled with Cy3 or Cy5 mono-functional NHS ester cyanogen dyes (GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Labeled cDNA was purified using a QIAquick PCR purification kit (Qiagen) and the purified labeled cDNA was hybridized with S. aureus genome microarrays version 6.0 provided by the Pathogen Functional Genomics Resource Center (PFGRC).
Microarray data analysis
Hybridization signals were scanned using an Axon4000B scanner with Acuity 6.0 software (Molecular Devices, Inc. U.S.) and scans were saved as TIFF images. Data analysis was performed by TM4 microarray software suite (Saeed et al. 2003). Scans were analyzed using TM4-Spotfinder software and the local background was subsequently subtracted. The data set was normalized by applying the LOWESS algorithm using TM4-MIDAS software. The normalized log2 ratio of test/control signal for each spot was recorded. Significant changes of gene expression were identified with significance analysis of microarrays (SAM) software using one class mode (Tusher et al. 2001). The differentially regulated genes were further classified according to the functional categories described in the comprehensive microbial resource of TIGR (http://cmr.tigr.org/tigr-scripts/CMR/shared/Genomes.cgi). As per our standard transcriptional profiling protocol, to minimize the technical and biological variations and to ensure that the data obtained were of good quality three independent cultures were used to prepare RNA samples and each RNA preparation was used to make probes for at least two separate arrays for which the incorporated dye was reversed (Muthaiyan et al. 2008).
Microarray data accession number
The data discussed in this publication have been deposited in NCBI’s Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and are accessible through GEO Series accession number GSE33465 (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE33465) (Edgar et al. 2002).
Electron microscopy
TSB grown exponential phase S. aureus COL was treated with ½ x MIC of the CPV for 30 min. Following the treatment, 2 mL of the culture was collected by centrifugation at 10,000 RPM for 10 min. The cell pellets were subsequently fixed in Karnovsky’s fixative for 2 h under a weak vacuum. Samples were rinsed 3 times in 0.05 mol cacodylate buffer, pH 7.2, post fixed in 1% osmium tetroxide (aqueous), rinsed with distilled water and stained with 0.5% uranyl acetate overnight at 4°C. The sample was dehydrated in a graded ethanol series, followed by propylene oxide, and embedded in Spurr’s medium. Ultra-thin sections were cut with a diamond knife on a MT2B Ultratome (Dupont Company, Newtown, CT). Sections were placed on 300 mesh copper grid, and stained with 2% aqueous uranyl acetate, followed by lead citrate. Grids were viewed at 80 kv with a JEM 100 CX transmission electron microscope (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan).
RESULTS
Inhibitory effect of citrus oils against S. aureus
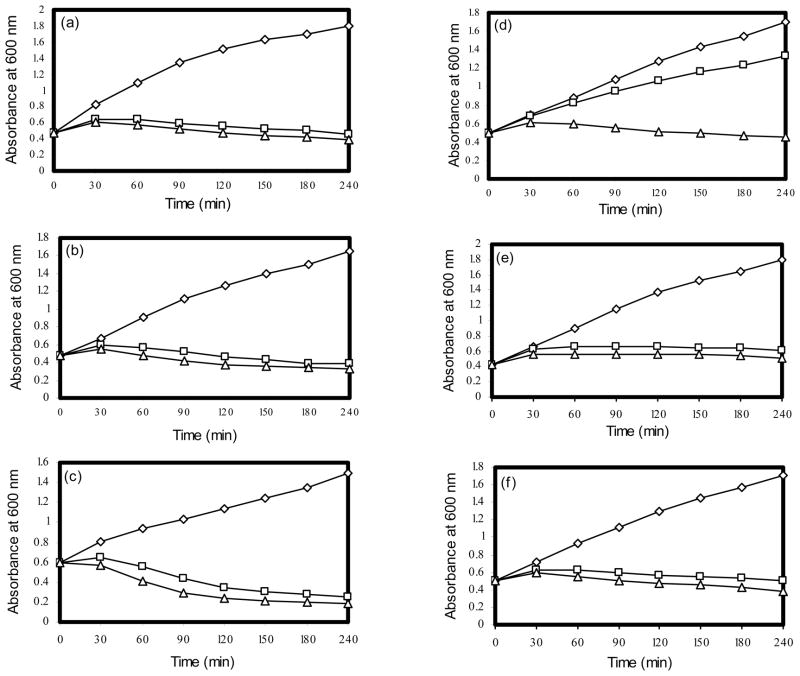
Of the eight EOs tested terpeneless cold pressed Valencia orange oil (CPV) and cold pressed citronellal exhibited a high level inhibition against all S. aureus strains in disc diffusion assays (Table 1). The MICs of CPV for six S. aureus strains were determined by agar dilution method. CPV concentration at 0.18% caused complete inhibition for the strains 13136 p−m+ and 13136 p−m+V20. However, for strains COL, Mu50, and N315 0.21% CPV was required to inhibit the growth. Based on the MICs, growth inhibitory concentration was determined for CPV to choose the concentration and duration of treatment for transcriptional profiling studies. Two different concentrations (½ x and 1 x of MIC) of CPV were used to determine the GIC. Both ½ x and 1 x of MIC concentrations caused significant growth inhibition for strains SH1000, COL, 13136 p−m+, Mu50, and N315. However, the VISA strain 13136 p−m+V20 exhibited reduced susceptibility to ½ x MIC of CPV (Fig 1).
Table 1.
Inhibitory effect of terpeneless cold pressed Valencia orange oil (CPV) and citronellal against S. aureus strains determined by a disk-diffusion assay
| S. aureus strain | Inhibition Zone (mm)a |
|
|---|---|---|
| CPV | Citronellal | |
| SH1000 | 31.50 ± 3.02 | 9.20 ± 0.84 |
| COL | 65.83 ± 3.76 | 19.83 ± 1.33 |
| 13136 p−m+ | 65.67 ± 4.59 | 18.83 ± 1.33 |
| 13136 p−m+V20 | 76.67 ± 4.08 | 11.00 ± 1.26 |
| N315 | 65.83 ± 3.76 | 11.17 ± 0.98 |
| Mu50 | 32.50 ± 2.74 | 8.33 ± 0.82 |
Inhibition zones are average values of three independent trials ± the standard deviation (SD, n=6) of the mean.
Figure 1.
Growth inhibitory effect of CPV on S. aureus strain SH1000 (a), COL (b), 13136 p−m+ (c), 13136 p−m+V20 (d), Mu50 (e), and N315 (f). ◇, control; △, 1x MIC; □, ½ x MIC.
Effect of CPV on the cell lysis related gene expression
S. aureus COL challenged with 0.1% CPV for 15 min showed upregulation of 431 genes and down regulation of 551 genes from a variety of functional categories (Supplementary Table S1 and S2). In the initial growth study, the CPV treated COL cells showed rapid lysis within 60 min of the treatment; also 24 fold induced expression of cwrA (SACOL2571) in the transcriptional profile supported the CPV induced cell wall damage. Therefore, we particularly focused on the altered expression pattern of the cell wall related genes to better understand the mechanism of the CPV action on S. aureus. In the transcriptional profiling analysis about 62 and 36cell envelope-related genes were under- and over-expressed, respectively. Some of the well recognized cell wall stress stimulon member genesinclude penicillin binding protein pbp1, pbp2(mecA), pbp3, and murein sacculus and peptidoglycan biosynthesis related murB, murC, muD, murE, murG, and autolysin related atl, lytM were downregulated (-3 to -2 fold). pbp4 and capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis related genes (cap) were upregulated in the cell envelope related category (Table 2).
Table 2.
Altered expression of genes associated with cell lysis in CPV treated S. aureus COL cells
| Locus ID | Genea | Gene/Protein Name | Sub-functional Category | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell envelope | ||||
| Downregulated Genes | ||||
| SACOL0938 | dltD | DltD protein | Biosynthesis and degradation of surface polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides | −10.41 |
| SACOL0054 | NA | Mur ligase family protein, authentic frameshift | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | −9.61 |
| SACOL0937 | dltC | D-alanyl carrier protein | Biosynthesis and degradation of surface polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides | −5.99 |
| SACOL0936 | dltB | DltB protein | −5.41 | |
| SACOL0247 | lrgA | holin-like protein LrgA | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | −4.64 |
| SACOL0052 | NA | glycosyl transferase, group 1 family protein | Biosynthesis and degradation of surface polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides | −4.19 |
| SACOL1195 | mraY | phospho-N-acetylmuramoyl-pentapeptide-transferase | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | −3.71 |
| SACOL0697 | tagX | teichoic acid biosynthesis protein X | −3.51 | |
| SACOL0801 | murB | UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvoylglucosamine reductase | −2.97 | |
| SACOL1023 | murE | UDP-N-acetylmuramoylalanyl-D-glutamate--2,6-diaminopimelate ligase | −2.89 | |
| SACOL1194 | pbp1 | penicillin-binding protein 1 | −2.5 | |
| SACOL1196 | murD | UDP-N-acetylmuramoylalanine--D-glutamate ligase | −2.45 | |
| SACOL2074 | NA | D-alanine--D-alanine ligase | −2.39 | |
| SACOL1687 | NA | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase, family 3 | Biosynthesis and degradation of surface polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides | −2.38 |
| SACOL0543 | glmU | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase | −2.21 | |
| SACOL2103 | NA | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase | −2.21 | |
| SACOL0033 | mecA | penicillin-binding protein 2 | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | −2.15 |
| SACOL1329 | femC | glutamine synthetase FemC | −2.15 | |
| SACOL0242 | NA | teichoic acid biosynthesis protein, putative | −2.12 | |
| SACOL1134 | kdtB | lipopolysaccharide core biosynthesis protein KdtB | Biosynthesis and degradation of surface polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides | −2.09 |
| SACOL1609 | pbp3 | penicillin-binding protein 3 | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | −2.01 |
| SACOL1453 | murG | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine--N-acetylmuramyl-(pentapeptide) pyrophosphoryl-undecaprenol N-acetylglucosamine transferase | −1.98 | |
| SACOL0263 | lytM | peptidoglycan hydrolase | −1.96 | |
| SACOL0695 | NA | tagG protein, teichoic acid ABC transporter protein, putative | −1.87 | |
| SACOL1066 | NA | fmt protein | −1.83 | |
| SACOL1062 | atl | bifunctional autolysin | Biosynthesis and degradation of surface polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides | −1.78 |
| SACOL1424 | NA | phosphate ABC transporter, phosphate-binding protein | Other | −1.74 |
| SACOL1790 | murC | UDP-N-acetylmuramate--alanine ligase | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | −1.58 |
| SACOL1951 | NA | Mur ligase family protein | −1.57 | |
| Upregulated Genes | ||||
| SACOL2571 | cwrA | conserved hypothetical protein | Conserved | 24.05 |
| SACOL1434 | NA | alanine racemase family protein | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | 21.26 |
| SACOL0147 | cap5L | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5L | Biosynthesis and degradation of surface polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides | 4.22 |
| SACOL0150 | cap5O | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5O | 4.02 | |
| SACOL0148 | cap5M | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis galactosyltransferase Cap5M | 3.98 | |
| SACOL0151 | cap5P | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase Cap5P | 3.61 | |
| SACOL0149 | cap5N | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5N | 3.55 | |
| SACOL1161 | murI | glutamate racemase | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | 3.11 |
| SACOL0146 | cap5K | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5K | Biosynthesis and degradation of surface polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides | 2.95 |
| SACOL0144 | cap5I | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5I | 2.83 | |
| SACOL0145 | cap5J | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5J | 2.79 | |
| SACOL0140 | cap5E | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5E | 2.67 | |
| SACOL0141 | cap5F | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5F | 2.17 | |
| SACOL2092 | murAA | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase 1 | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | 2.1 |
| SACOL0143 | cap5H | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5H | Biosynthesis and degradation of surface polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides | 2.04 |
| SACOL0699 | pbp4 | penicillin-binding protein 4 | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | 2.04 |
| SACOL0142 | cap5G | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase Cap5G | Biosynthesis and degradation of surface polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides | 1.99 |
| SACOL0136 | cap5A | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5A | 1.68 | |
| SACOL0137 | cap5B | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein Cap5B | 1.67 | |
| SACOL2116 | murAB | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase 2 | Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | 1.67 |
| Cellular processes | ||||
| Downregulated Genes | ||||
| SACOL0935 | dltA | D-alanine-activating enzyme/D-alanine-D-alanyl carrier protein ligase | Toxin production and resistance | −11.93 |
| SACOL2295 | NA | staphyloxanthin biosynthesis protein, putative | Pathogenesis | −8.55 |
| SACOL1535 | srrA | DNA-binding response regulator SrrA | −8 | |
| SACOL0244 | scdA | ScdA protein | Cell division | −6.24 |
| SACOL0270 | NA | staphyloxanthin biosynthesis protein, putative | Pathogenesis | −5.55 |
| SACOL0095 | spa | immunoglobulin G binding protein A precursor | −5.54 | |
| SACOL1437 | NA | cold shock protein, CSD family | Adaptations to atypical conditions | −4.87 |
| SACOL2126 | luxS | autoinducer-2 production protein LuxS | Other | −4.15 |
| SACOL0956 | kapB | kinase-associated protein B | Adaptations to atypical conditions | −3.8 |
| SACOL1193 | NA | cell division protein FtsL | Cell division | −3.6 |
| SACOL0608 | sdrC | sdrC protein | Cell adhesion | −3.53 |
| SACOL1328 | glnR | glutamine synthetase repressor | Toxin production and resistance | −3.35 |
| SACOL2291 | NA | staphyloxanthin biosynthesis protein | Pathogenesis | −3.33 |
| SACOL0552 | NA | general stress protein 13 | Adaptations to atypical conditions | −3.32 |
| SACOL1534 | srrB | sensor histidine kinase SrrB | Pathogenesis | −3.27 |
| SACOL0743 | bacA | bacitracin resistance protein | Toxin production and resistance | −3.23 |
| SACOL1396 | fmtC | fmtC protein | −3.18 | |
| SACOL2075 | ftsW | cell division protein, FtsW/RodA/SpoVE family | Cell division | −3.12 |
| SACOL1197 | divIB | cell division protein | −2.91 | |
| SACOL0766 | saeR | DNA-binding response regulator SaeR | Pathogenesis | −2.87 |
| SACOL1205 | NA | cell-division initiation protein, putative | Cell division | −2.86 |
| SACOL0452 | ahpC | alkyl hydroperoxide reductase, C subunit | Detoxification | −2.8 |
| SACOL1537 | scpB | segregation and condensation protein B | Cell division | −2.72 |
| SACOL1624 | era | GTP-binding protein Era | −2.46 | |
| SACOL1538 | scpA | segregation and condensation protein A | −2.31 | |
| SACOL1184 | NA | exfoliative toxin, putative | Toxin production and resistance | −2.14 |
| SACOL0746 | norR | transcriptional regulator, MarR family | −2.06 | |
| SACOL2731 | NA | cold shock protein, CSD family | Adaptations to atypical conditions | −2.06 |
| SACOL1383 | mscL | large conductance mechanosensitive channel protein | −1.96 | |
| SACOL2024 | agrD | accessory gene regulator protein D | Pathogenesis | −1.91 |
| SACOL0610 | sdrE | sdrE protein | Cell adhesion | −1.89 |
| SACOL1410 | femA | femA protein | Toxin production and resistance | −1.76 |
| SACOL0765 | saeS | sensor histidine kinase SaeS | Pathogenesis | −1.69 |
| SACOL0245 | lytS | sensor histidine kinase LytS | −1.66 | |
| SACOL1198 | ftsA | cell division protein FtsA | Cell division | −1.53 |
| Upregulated Genes | ||||
| SACOL1943 | vraS | sensor histidine kinase VraS | Toxin production and resistance | 5.22 |
| SACOL1450 | arlS | sensor histidine kinase ArlS | Pathogenesis | 4.74 |
| SACOL2353 | tcaR | transcriptional regulator TcaR | Toxin production and resistance | 4.18 |
| SACOL0672 | sarA | staphylococcal accessory regulator A | 4.11 | |
| SACOL2157 | NA | drug resistance transporter, EmrB/QacA subfamily | 3.75 | |
| SACOL1451 | arlR | DNA-binding response regulator ArlR | Pathogenesis | 3.61 |
| SACOL2289 | sarY | staphylococcal accessory regulator Y | Toxin production and resistance | 3.21 |
| SACOL2258 | sarV | staphylococcal accessory regulator V | 2.87 | |
| SACOL1942 | vraR | DNA-binding response regulator VraR | 2.61 | |
| SACOL1003 | NA | negative regulator of competence MecA, putative | DNA transformation | 2.01 |
| SACOL0608 | sdrC | sdrC protein | Cell adhesion | 1.82 |
| Protein fate | ||||
| Downregulated Genes | ||||
| SACOL1801 | NA | peptidase, M20/M25/M40 family | Degradation proteins, peptides, and glycopeptides | −3.45 |
| SACOL0806 | pepT | peptidase T | −2.89 | |
| SACOL2385 | NA | heat shock protein, Hsp20 family | Protein folding and stabilization | −2.77 |
| SACOL1946 | NA | methionine aminopeptidase, type I | Protein modification and repair | −2.62 |
| SACOL1777 | NA | serine protease HtrA, putative | Degradation proteins, peptides, and glycopeptides | −2.42 |
| SACOL0581 | secE | preprotein translocase, SecE subunit | Protein and peptide secretion and trafficking | −2.13 |
| SACOL1588 | NA | proline dipeptidase | Degradation proteins, peptides, and glycopeptides | −2.12 |
| SACOL2038 | NA | metalloendopeptidase, putative, glycoprotease family | −2.06 | |
| Upregulated Genes | ||||
| SACOL0979 | clpB | ATP-dependent Clp protease, ATP-binding subunit ClpB | Degradation proteins, peptides, and glycopeptides | 9.42 |
| SACOL1433 | NA | peptidase, M20/M25/M40 family | 8.7 | |
| SACOL2125 | NA | peptidase, M20/M25/M40 family | 7.13 | |
| SACOL0570 | clpC | ATP-dependent Clp protease, ATP-binding subunit ClpC, authentic frameshift | 5.92 | |
| SACOL1636 | dnaJ | dnaJ protein | Protein folding and stabilization | 4.94 |
| SACOL0833 | clpP | ATP-dependent Clp protease, proteolytic subunit ClpP | Degradation proteins, peptides, and glycopeptides | 3.72 |
| SACOL1638 | grpE | heat shock protein GrpE | Protein folding and stabilization | 3.5 |
| SACOL0968 | spsA | signal peptidase IA, inactive | Protein and peptide secretion and trafficking | 2.98 |
| SACOL1637 | dnaK | dnaK protein | Protein folding and stabilization | 2.67 |
| SACOL2438 | NA | endopeptidase, putative | Degradation proteins, peptides, and glycopeptides | 2.46 |
| SACOL1459 | NA | peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase, degenerate | Protein modification and repair | 2.38 |
| SACOL2016 | groEL | chaperonin, 60 kDa | Protein folding and stabilization | 2.36 |
| SACOL0556 | NA | chaperonin, 33 kDa | 2.17 | |
| SACOL0844 | secG | preprotein translocase, SecG subunit | Protein and peptide secretion and trafficking | 2.13 |
| SACOL0969 | spsB | signal peptidase IB | 2.02 | |
| SACOL2017 | groES | chaperonin, 10 kDa | Protein folding and stabilization | 1.81 |
NA – Gene symbol not available
Related to the cell envelope, classified under Cellular Processes, approximately 54 and 49 genes were down- and up-regulated, respectively. D-alanine-activating enzyme/D-alanine-D-alanyl carrier protein ligase encoding dltA, dltB, dltC, dltD, cell division related divIB, ftsA, ftsL, ftsW and, universal stress resistance family protein encoding SACOL1753, SACOL1759, SACOL0552, drug resistance transporter EmrB/QacA subfamily encoding SACOL2347 were downregulated (-11 to -2 fold). Two component response regulators encoding vraS, vraR, arlS, arlR and transcriptional regulator tcaR, staphylococcal accessory regulator sarA, sarV, sarY were upregulated between 2 to 5 fold (Table 2).
Another prominent category of genes altered by CPV treatment is the Protein Fate, set of genes which includes chaperones and proteases. Some of the genes encoding the chaperones and proteases are known as marker genes for cell wall stress condition. In this Protein Fate category 24 genes were downregulated and 26 genes were upregulated by CPV treatment. Most of the genes encoding for degradation of proteins, peptides, and glycopeptides were down regulated between -4 to -2 fold. However, CPV induced the expression of clpB and clpC (chaperone/protease), spsA and spsB (type 1 signal peptidases A and B), and SACOL2683 (putative methionine sulfoxide reductase). In addition, expression of genes encoding the major heat shock proteins GroEL, GroES, DnaK, DnaJ, GrpE had increased between 2 to 5 fold (Table 2).
In addition to cell wall related genes, a variety of genes involved in DNA metabolism that play a role in DNA replication, recombination, and repair were down- and up-regulated by CPV challenge (Supplementary Table S1 and S2). Some of the known DNA metabolism related genes affected by the CPV treatment encode DNA repair protein RecN, R subunit of type I restriction-modification enzyme, M subunit type I restriction-modification enzyme, DNA gyrase, single-stranded-DNA-specific exonuclease RecJ, ATP-dependent DNA helicase PcrA, DNA polymerase, and DNA ligase.
Electron microscopic analysis of CPV induced cell wall damage
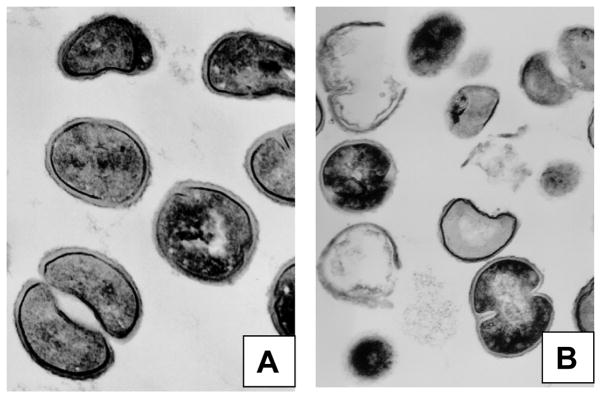
Actively growing COL cells exhibited an ultra structure typical of S. aureus, with septa that were normal in appearance and a trilaminar cell wall (Fig 2A), whereas, CPV (0.1%) treatment for 30 min led to extensive cell lysis in COL cells (Fig 2B). In addition to cell lysis, loss of cellular electron dense material, coagulation of cytoplasmic constituents, deformed septum and lack of a distinct midline were observed. As a consequence of profound structural alterations and breaks in the cell walls several ghosts of lysed cells appeared after the CPV treatment (Fig 2B). Electron microscopic observation of cell wall lysis in CPV treated cells substantiates the results of CPV induced altered expression of cell wall- and cell division-related genes in S. aureus.
Figure 2.
Electron micrograph of ½ x MIC of CPV treated S. aureus COL cells. A, control; B, cells after 30 min of CPV treatment. Magnification, × 30,000, 1 mm = 33.33 nm.
DISCUSSION
The infections caused by MRSA and VISA due to acquisition of resistance towards current antimicrobials pose a serious challenge for therapy (Payne 2008). In an effort to explore the potential use of orange EO against antibiotic resistant S. aureus, in this study inhibitory effects and mode of action of CPV against MRSA and VISA strains were studied. The inhibitory effect of CPV against each S. aureus strain varied in the disc diffusion screening assay. The VISA strain 13136 p−m+ V20 exhibited greater inhibition (76.67 ± 4.08 mm) than other MRSA strains. Similar to our results, inhibitory effects of various EOs against MRSA and other bacteria have previously been confirmed by disc diffusion and agar dilution methods (Prabuseenivasan et al. 2006, Chao et al. 2008, Fisher and Phillips 2006, Dorman and Deans 2000, Burt and Reinders 2003, Abulrob et al. 2004, Nostro et al. 2004, Busatta et al. 2008, Viuda-Martos et al. 2008, Goñi et al. 2009, Patharakorn et al. 2010).
In previous reports antimicrobial properties of EOs and their components have been reviewed extensively (Burt 2004). However, only a few studies have reported the mechanism of antibacterial action of EOs in great detail (Cox et al. 1998, Cox et al. 2000, Fisher and Phillips 2006). Therefore, based on the significant inhibitory effect we observed in our study, we selected CPV for the further experiments to study the mode of action on MRSA.
Numerous studies have investigated the changes in gene expression patterns in response to antibiotics at the sub-inhibitory concentration to obtain an in depth understanding of mode of action of antimicrobials (Wecke and Mascher 2011). Accordingly, in our study S. aureus genome microarrays were used to capture the genomic response of CPV treated S. aureus cells. Transcriptional profiling revealed alteration of gene expression in a variety of functional categories including amino acid biosynthesis, cell envelope, cellular processes, central intermediary metabolism, DNA metabolism, protein synthesis, and signal transduction. Specifically, the observation of 24 fold induced expression of cwrA (SACOL2571) (equivalent locus SA2343 in strain N315) along with rapid lysis of S. aureus cells during the CPV treatment supported the CPV induced cell wall damage in S. aureus. In previous research high level upregulation of cwrA has been reported in a variety of transcriptomic studies examining cell wall inhibition (McAleese et al. 2006, Sobral et al. 2007, Balibar et al. 2009) and recently, Balibar et al. showed that cwrA was robustly induced by cell wall-targeting antibiotics: vancomycin, oxacillin, penicillin G, phosphomycin, imipenem, hymeglusin and bacitracin, but not by antimicrobials with other mechanisms of action, including ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, chloramphenicol, triclosan, rifampicin, novobiocin and carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone (Balibar et al. 2010). Therefore, we focused on the cell wall related genes to elucidate the mechanisms of action of CPV. In support of our view in a similar study Cox et al. (2000) demonstrated that in Escherichia coli and S. aureus the antimicrobial activity of tea tree oil results from its ability to disrupt the permeability barrier of membrane structures. In a later study Carson et al. (2002) reported that the mechanism of action of tea tree oil on S. aureus is not specific on cytoplasmic membrane but due to induction of the release of membrane-bound cell wall autolytic enzymes and eventual cell lysis.
In earlier studies, based on the results of transcriptional profiling experiments after the exposure of S. aureus to cell wall-active agents a set of cell wall-associated genes were identified and assigned as a “cell wall stimulon”. These genes have been used as marker genes for cell wall related gene response (Kuroda et al. 2003, Utaida et al. 2003, Wilkinson et al. 2005, Gardete et al. 2006). In our study we observed the altered expression of several cell wall stimulon member genes in CPV treated S. aureus cells and those genes are discussed in the following sections.
The PBPs are membrane-associated proteins that catalyze the final step of murein biosynthesis of cell-wall peptidoglycan in S. aureus. PBP1 (pbp1) is essential and important for cell division (Pereira et al. 2007) and PBP2a, encoded by mecA, is responsible for methicillin resistance in S. aureus (Pinho and Errington 2005). It has been reported that inactivation of pbp3 caused a small but significant decrease in autolysis rates. Cells of abnormal size and shape and disoriented septa were reported when bacteria with inactivated pbp3 were grown in the presence of cell wall active antibiotic methicillin (Pinho et al. 2000). In our study downregulation of these PBPs encoding genes could very well be involved in the observed lysis of CPV treated S. aureus cells. Additionally, we believe that the observed upregulation of PBP4 encoding pbp4 and capsular polysaccharide related cap genes could be a protective response of S. aureus during the CPV induced cell wall damage. In support of our view it was recently demonstrated that PBP4 may play an important role in cell wall antibiotic resistance (Memmi et al. 2008, Navratna et al. 2010).
The S. aureus cell wall has been reported as a structure composed of highly cross-linked peptidoglycan, a complex structure composed of sugars and amino acids (murein), teichoicacids, and cell wall-associated proteins (Dmitriev et al. 2004). We observed the repression of these murein sacculus and peptidoglycan biosynthesis related murB, murC, muD, murE, murG, murAB genes upon the CPV treatment. Cell wall autolysis related atl and lytM genes were also downregulated by CPV treatment. Downregulation of atl and lytM has previously been reported in S. aureus exposed to cell wall-active agents and viewed as a response of the cell to preserve peptidoglycan when challenged with cell wall-active agents (Kuroda et al. 2003, Utaida et al. 2003, Wilkinson et al. 2005, Muthaiyan et al. 2008).
Along with cell envelope related group, genes belonging to S. aureus cellular processes were affected by CPV treatment. D-alanine-activating enzyme/D-alanine-D-alanyl carrier protein ligase encoding dltA, dltB, dltC, dltD were reportedly down regulated in CPV treated cells. dltABCD operon controls the alanylation of wall teichoicacids which are involved in the control of autolysin activity in S. aureus. Previous research by Peschel et al. (1999; 2000) demonstrated that mutation in dlt genes lead to failure of alanylation in the teichoic acids and consequently S. aureus cells become sensitive to human defensin HNP1–3, animal-derived protegrins, tachyplesins, and magainin II, and to the bacteria-derived peptides gallidermin and nisin, and cell wall antibiotics. Thus, the repression of dlt genes by the CPV could be viewed as one of the reasons for the rapid lysis of CPV treated cells.
Genes involved in cell division and stress resistance were also downregulated in the CPV treated cells. In previous transcriptional profiling studies cell division proteins encoding genes were shown to be induced by cell wall antibiotics but downregulated by membrane active compounds (Muthaiyan et al. 2008). Downregulation of these genes in response to CPV treatment indicates that CPV potentially acts on both cell walls as well as membranes of the S. aureus cells.
In S. aureus vraSR is a two-component system that positively regulates a number of genes involved in cell wall synthesis and arlSR is an another two-component system involved in several cell wall activities including rate of autolysis as well as the attachment to a polymer (Fournier and Hooper 2000, Kuroda et al. 2003). Induction two component of these response regulators along with arlSR associated accessory regulators sarA, sarV, sarY in response to CPV treatment could be contemplated as a S. aureus protective response to the cell wall damage caused by the down regulation of cell wall synthesis associated genes.
Some of the known cell wall stress stimulon genes encoding the chaperones and proteases were affected during exposure to CPV. Electron microscopic analysis of CPV treated cells revealed that CPV acted on S. aureus cell walls and caused profound cell wall damage and cell lysis. Treatment of S. aureus cells with cell wall-active agents is considered to result in the accumulation of misfolded and damaged proteins (Utaida et al. 2003, Wilkinson et al. 2005, Muthaiyan et al. 2008). Presumably in an attempt to counter the CPV mediated peptidoglycan biosynthesis inhibition and subsequent cell lysis S. aureus increased the chaperones to restore the lysed proteins. Therefore, we speculate that the genes associated with degradation of proteins and peptides clpB and clpC (chaperone/protease), spsA and spsB (type 1 signal peptidases A and B), and SACOL2683 (putative methionine sulfoxide reductase) and genes encoding the major heat shock proteins GroEL, GroES, DnaK, DnaJ, GrpE were induced in CPV treated cells.
In addition to cell wall related genes, DNA-replication, -recombination, and -repair related genes were also apparently down- and up-regulated in CPV treated cells. In previous studies some of these genes have been identified as members of the cell wall stress stimulon. In S. aureus altered expression of genes involved in DNA metabolism has been recognized as a characteristic mode of cell-wall active agent’s action and reported as a part of SOS response (Maiques et al. 2006). Also, in E. coli it has been reported that transcription of genes encoding DNA polymerase and DNA repair, is induced during the inhibition of cell wall synthesis caused by β-lactam antibiotics (Perez-Capilla et al. 2005). Interestingly, in our study approximately 31 genes related to DNA replication and repair were repressed and 20 genes were upregulated upon CPV treatment. Therefore, we speculate that along with cell wall damage CPV may possibly repress the S. aureus SOS system that normally used by the bacterial cells to survive during the adverse condition.
The electron microscopic observation of cell morphology of CPV treated cells confirmed the transcriptional response of CPV treated S. aureus cells exhibiting down regulation of cell envelope related genes and corroborated the cell wall active and lytic effect of CPV on S. aureus. Electron micrographs illustrated the cell wall and membrane damage and loss of cytoplasmic materials and several cell-wall ghosts that accompanied in CPV treatment of S. aureus cells. Similar cytoplasmic losses have also been reported in tea tree oil treated S. aureus cells (Carson et al. 2002). Apparently the down regulation of the autolysis related gene observed in the transcriptional profiling may serve as a protective response of cells from the CPV mediated cell wall lysis observed in the electron microscope.
Results of this in vitro study indicate that CPV effectively inhibits the S. aureus by affecting the cell wall. While the MRSA is becoming a significant public health problem, the findings of the present study are promising and reveal the potential of CPV as an alternative natural therapeutic antimicrobial agent against MRSA. However, prior to the use of CPV for MRSA decolonization issues of safety and toxicity will need to be addressed.
Supplementary Material
Table S1. S. aureus COL genes upregulated in response to CPV treatment
Table S2. S. aureus COL genes downregulated in response to CPV treatment
Acknowledgments
The Staphylococcus aureus microarrays were obtained through NIAID’s Pathogen Functional Genomics Resource Center, managed and funded by Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, NIAID, NIH, DHHS and operated by The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR). B.J.W. was supported by National Institute of Health (BJW NIH 1R15AI084006).
References
- Abulrob A, Suller MTE, Gumbleton M, Simons C, Russell AD. Identification and biological evaluation of grapefruit oil components as potential novel efflux pump modulators in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacterial strains. Phytochemistry. 2004;65:3021–3027. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.08.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balibar CJ, Shen X, McGuire D, Yu D, McKenney D, Tao J. cwrA, a gene that specifically responds to cell wall damage in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology. 2010;156:1372–1383. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.036129-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balibar CJ, Shen X, Tao J. The mevalonate pathway of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 2009;191:851–861. doi: 10.1128/JB.01357-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady A, Loughlin R, Gilpin D, Kearney P, Tunney M. In vitro activity of tea-tree oil against clinical skin isolates of meticillin-resistant and -sensitive Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci growing planktonically and as biofilms. J Med Microbiol. 2006;55:1375–1380. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46558-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown DF, Reynolds PE. Intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett. 1980;122:275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt SA, Reinders RD. Antibacterial activity of selected plant essential oils against Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2003;36:162–167. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-765x.2003.01285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt S. Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods: a review. Inter J Food Microbiol. 2004;94:223–253. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.03.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busatta C, Vidal RS, Popiolski AS, Mossi AJ, Dariva C, Rodrigues MRA, Corazza FC, Corazza ML, Vladimir Oliveira J, Cansian RL. Application of Origanum majorana L. essential oil as an antimicrobial agent in sausage. Food Microbiol. 2008;25:207–211. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2007.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caelli M, Porteous J, Carson CF, Heller R, Riley TV. Tea tree oil as an alternative topical decolonization agent for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Hosp Infect. 2000;46:236–237. doi: 10.1053/jhin.2000.0830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson CF, Mee BJ, Riley TV. Mechanism of action of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil on Staphylococcus aureus determined by time-kill, lysis, leakage, and salt tolerance assays and electron microscopy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:1914–1920. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.6.1914-1920.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao S, Young G, Oberg C, Nakaoka K. Inhibition of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) by essential oils. Flavour Fragrance J. 2008;23:444–449. [Google Scholar]
- Cox S, Gustafson J, Mann C, Markham J, Liew Y, Hartland R, Bell H, Warmington J, Wyllie S. Tea tree oil causes K+ leakage and inhibits respiration in Escherichia coli. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1998;26:355–358. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-765x.1998.00348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox S, Mann C, Markham J, Bell H, Gustafson J, Warmington J, Wyllie S. The mode of antimicrobial action of the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree oil) J Appl Microbiol. 2000;88:170–175. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.00943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo FR, Otto M, Kreiswirth BN, Chambers HF. Community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 2010;375:1557–1568. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61999-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitriev BA, Toukach FV, Holst O, Rietschel ET, Ehlers S. Tertiary structure of Staphylococcus aureus cell wall murein. J Bacteriol. 2004;186:7141–7148. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.21.7141-7148.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran AL, Morden WE, Dunn K, Edwards-Jones V. Vapour-phase activities of essential oils against antibiotic sensitive and resistant bacteria including MRSA. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2009;48:387–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2009.02552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman HJD, Deans SG. Antimicrobial agents from plants: antibacterial activity of plant volatile oils. J Appl Microbiol. 2000;88:308–316. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.00969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryden MS, Dailly S, Crouch M. A randomized, controlled trial of tea tree topical preparations versus a standard topical regimen for the clearance of MRSA colonization. J Hosp Infect. 2004;56:283–286. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2004.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar R, Domrachev M, Lash AE. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucl Acids Res. 2002;30:207–210. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards-Jones V, Buck R, Shawcross SG, Dawson MM, Dunn K. The effect of essential oils on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using a dressing model. Burns. 2004;30:772–777. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2004.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsom GKF, Hide D. Susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to tea tree oil and mupirocin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1999;43:427–428. doi: 10.1093/jac/43.3.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher K, Phillips CA. The effect of lemon, orange and bergamot essential oils and their components on the survival of Campylobacter jejuni, Escherichia coli O157, Listeria monocytogenes, Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in food systems. J Appl Microbiol. 2006;101:1232–1240. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier B, Hooper DC. An new two-component regulatory system involved in adhesion, autolysis, and extracellular proteolytic activity of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 2000;182:3955–3964. doi: 10.1128/jb.182.14.3955-3964.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardete S, Wu SW, Gill S, Tomasz A. Role of VraSR in antibiotic resistance and antibiotic-induced stress response in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:3424–3434. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00356-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goñi P, López P, Sánchez C, Gómez-Lus R, Becerril R, Nerín C. Antimicrobial activity in the vapour phase of a combination of cinnamon and clove essential oils. Food Chem. 2009;116:982–989. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson J, Liew Y, Chew S, Markham J, Bell H, Wyllie S, Warmington J. Effects of tea tree oil on Escherichia coli. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1998;26:194–198. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-765x.1998.00317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer KA, Carson CF, Riley TV. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils and other plant extracts. J Appl Microbiol. 1999;86:985–990. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer KA, Carson CF, Riley TV, Nielsen JB. A review of the toxicity of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006;44:616–625. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2005.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh MJ, Aish JL, White IJ, Shaw L, Lithgow JK, Foster SJ. sigmaB modulates virulence determinant expression and stress resistance: characterization of a functional rsbU strain derived from Staphylococcus aureus 8325-4. J Bacteriol. 2002;184:5457–67. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.19.5457-5467.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy AD, Otto M, Braughton KR, Whitney AR, Chen L, Mathema B, Mediavilla JR, Byrne KA, Parkins LD, Tenover FC, Kreiswirth BN, Musser JM, DeLeo FR. Epidemic community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Recent clonal expansion and diversification. Proc Natn Acad Sci. 2008;105:1327–1332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710217105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda M, Ohta T, Uchiyama I, Baba T, Yuzawa H, Kobayashi I, Cui L, Oguchi A, Aoki K, Nagai Y. Whole genome sequencing of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 2001;357:1225–1240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(00)04403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda M, Kuroda H, Oshima T, Takeuchi F, Mori H, Hiramatsu K. Two-component system VraSR positively modulates the regulation of cell-wall biosynthesis pathway in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol. 2003;49:807–821. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiques E, Ubeda C, Campoy S, Salvador N, Lasa I, Novick RP, Barbe J, Penades JR. {beta}-Lactam antibiotics induce the SOS response and horizontal transfer of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:2726–2729. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.7.2726-2729.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J, Chan CH, King A, Williams L, French GL. Time-kill studies of tea tree oils on clinical isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000;45:639–643. doi: 10.1093/jac/45.5.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAleese F, Wu SW, Sieradzki K, Dunman P, Murphy E, Projan S, Tomasz A. Overexpression of genes of the cell wall stimulon in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus exhibiting vancomycin-intermediate-S. aureus -type resistance to vancomycin. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:1120–1133. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.3.1120-1133.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McChesney JD, Venkataraman SK, Henri JT. Plant natural products: Back to the future or into extinction? Phytochemistry. 2007;68:2015–2022. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.04.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Memmi G, Filipe SR, Pinho MG, Fu Z, Cheung A. Staphylococcus aureus PBP4 is essential for {beta}-lactam resistance in community-acquired methicillin-resistant strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:3955–3966. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00049-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthaiyan A, Silverman JA, Jayaswal RK, Wilkinson BJ. Transcriptional profiling reveals that daptomycin induces the Staphylococcus aureus cell wall stress stimulon and genes responsive to membrane depolarization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:980–990. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01121-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nannapaneni R, Chalova VI, Crandall PG, Ricke SC, Johnson MG, O’Bryan CA. Campylobacter and Arcobacter species sensitivity to commercial orange oil fractions. Int J Food Microbiol. 2009;129:43–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nannapaneni R, Muthaiyan A, Crandall PG, Johnson MG, O’Bryan CA, Chalova VI, Callaway TR, Carroll JA, Arthington JD, Nisbet DJ. Antimicrobial activity of commercial citrus-based natural extracts against Escherichia coli O157: H7 isolates and mutant strains. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2008;5:695–699. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2008.0124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navratna V, Nadig S, Sood V, Prasad K, Arakere G, Gopal B. Molecular basis for the role of Staphylococcus aureus penicillin binding protein 4 in antimicrobial resistance. J Bacteriol. 2010;192:134–144. doi: 10.1128/JB.00822-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nostro A, Blanco AR, Cannatelli MA, Enea V, Flamini G, Morelli I, Sudano Roccaro A, Alonzo V. Susceptibility of methicillin-resistant staphylococci to oregano essential oil, carvacrol and thymol. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004;230:191–195. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00890-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Bryan CA, Crandall PG, Chalova VI, Ricke SC. Orange essential oils antimicrobial activities against Salmonella spp. J Food Sci. 2008;73:M264–M267. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patharakorn T, Arpornsuwan T, Wetprasit N, Promboon A, Ratanapo S. Antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of the leaf essential oil of Morus rotunbiloba Koidz. J Med Plant Res. 2010;4:837–843. [Google Scholar]
- Payne DJ. Desperately seeking new antibiotics. Science. 2008;321:1644–1645. doi: 10.1126/science.1164586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira SFF, Henriques AO, Pinho MG, de Lencastre H, Tomasz A. Role of PBP1 in Cell Division of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:3525–3531. doi: 10.1128/JB.00044-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Capilla T, Baquero M, Gomez-Gomez J, Ionel A, Martin S, Blazquez J. SOS-independent induction of dinB transcription by {beta}-lactam-mediated inhibition of cell wall synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 2005;187:1515–1518. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.4.1515-1518.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschel A, Otto M, Jack RW, Kalbacher H, Jung G, Götz F. Inactivation of the dlt operon in Staphylococcus aureus confers sensitivity to defensins, protegrins, and other antimicrobial peptides. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:8405–8410. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.13.8405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschel A, Vuong C, Otto M, Gotz F. The D-alanine residues of Staphylococcus aureus teichoic acids alter the susceptibility to vancomycin and the activity of autolytic enzymes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44:2845–2847. doi: 10.1128/aac.44.10.2845-2847.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeltz RF, Singh VK, Schmidt JL, Batten MA, Baranyk CS, Nadakavukaren MJ, Jayaswal RK, Wilkinson BJ. Characterization of passage-selected vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains of diverse parental backgrounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44:294–303. doi: 10.1128/aac.44.2.294-303.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinho MG, de Lencastre H, Tomasz A. Cloning, characterization, and inactivation of the gene pbpC, encoding penicillin-binding protein 3 of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 2000;182:1074–1079. doi: 10.1128/jb.182.4.1074-1079.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinho MG, Errington J. Recruitment of penicillin-binding protein PBP2 to the division site of Staphylococcus aureus is dependent on its transpeptidation substrates. Mol Microbiol. 2005;55:799–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirri G, Giuliani A, Nicoletto SF, Pizzuto L, Rinaldi AC. Lipopeptides as anti-infectives: a practical perspective. Centr Eur J Biol. 2009;4:258–273. [Google Scholar]
- Prabuseenivasan S, Jayakumar M, Ignacimuthu S. In vitro antibacterial activity of some plant essential oils. BMC Complem Alt Med. 2006;6:39. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-6-39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath LD, Wallace SJ, Byers K, Toftegaard I. Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to penicillins and cephalosporins: reversal of intrinsic resistance with some chelating agents. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;236:435–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeed AI, Sharov V, White J, Li J, Liang W, Bhagabati N, Braisted J, Klapa M, Currier T, Thiagarajan M, Sturn A, Snuffin M, Rezantsev A, Popov D, Ryltsov A, Kostukovich E, Borisovsky I, Liu Z, Vinsavich A, Trush V, Quackenbush J. TM4: a free, open-source system for microarray data management and analysis. BioTechniques. 2003;34:374–378. doi: 10.2144/03342mt01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saleem M, Nazir M, Ali MS, Hussain H, Lee YS, Riaz N, Jabbar A. Antimicrobial natural products: an update on future antibiotic drug candidates. Nat Prod Rep. 2010;27:238–254. doi: 10.1039/b916096e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saravolatz LD, Markowitz N, Arking L, Pohlod D, Fisher E. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982;96:11–16. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena S, Kumar D. Tailoring biodiversity for the development of new therapeutics. Nat Prod Rad. 2002;1:18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon EM, Milillo SR, Johnson MG, Ricke SC. Efficacy of cold-pressed terpeneless Valencia oil and its primary components on inhibition of Listeria species by direct contact and exposure to vapors. J Food Sci. 2011;76:M500–M503. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry E, Warnke PH. Successful use of an inhalational phytochemical to treat pulmonary tuberculosis: A case report. Phytomedicine. 2004;11:95–97. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry E, Boeck H, Warnke P. Percutaneous treatment of chronic MRSA osteomyelitis with a novel plant-derived antiseptic. BMC Surgery. 2001;1:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2482-1-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobral RG, Jones AE, Des Etages SG, Dougherty TJ, Peitzsch RM, Gaasterland T, Ludovice AM, de Lencastre H, Tomasz A. Extensive and genome-wide changes in the transcription profile of Staphylococcus aureus induced by modulating the transcription of the cell wall synthesis gene murF. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:2376–2391. doi: 10.1128/JB.01439-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takarada K, Kimizuka R, Takahashi N, Honma K, Okuda K, Kato T. A comparison of the antibacterial efficacies of essential oils against oral pathogens. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2002;19:61–4. doi: 10.1046/j.0902-0055.2003.00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohidpour A, Sattari M, Omidbaigi R, Yadegar A, Nazemi J. Antibacterial effect of essential oils from two medicinal plants against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Phytomedicine. 2010;17:142–145. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2009.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Nation Acad Sci. 2001;98:5116–5121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091062498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utaida S, Dunman PM, Macapagal D, Murphy E, Projan SJ, Singh VK, Jayaswal RK, Wilkinson BJ. Genome-wide transcriptional profiling of the response of Staphylococcus aureus to cell-wall-active antibiotics reveals a cell-wall-stress stimulon. Microbiology. 2003;149:2719–2732. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26426-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viuda-Martos M, Ruiz-Navajas Y, Fernandez-Lopez J, Perez-Álvarez J. Antibacterial activity of lemon (Citrus lemon L.), mandarin (Citrus reticulata L.), grapefruit (Citrus paradisi L.) and orange (Citrus sinensis L.) essential oils. J Food Saf. 2008;28:567–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wecke T, Mascher T. Antibiotic research in the age of omics: from expression profiles to interspecies communication. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:2689–2704. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson BJ, Muthaiyan A, Jayaswal RK. The cell wall stress stimulon of Staphylococcus aureus and other gram-positive bacteria. Curr Med Chem Anti-Infect Agents. 2005;4:259–276. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. S. aureus COL genes upregulated in response to CPV treatment
Table S2. S. aureus COL genes downregulated in response to CPV treatment