Abstract
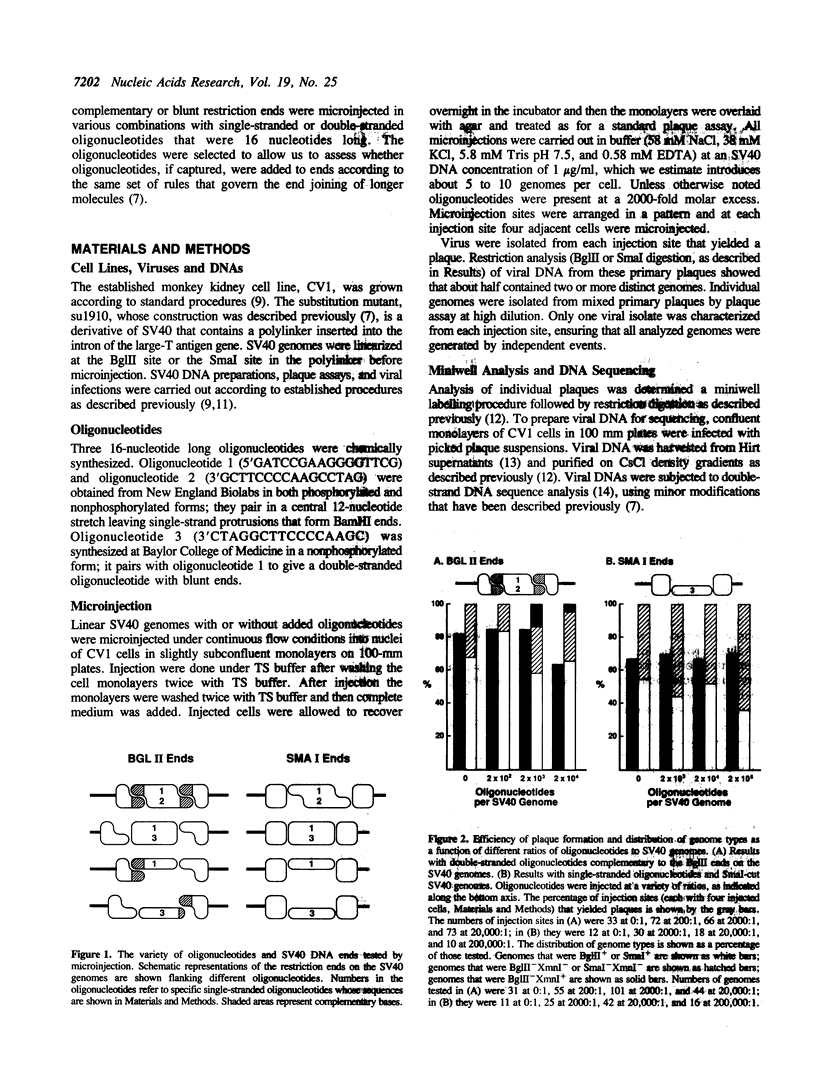
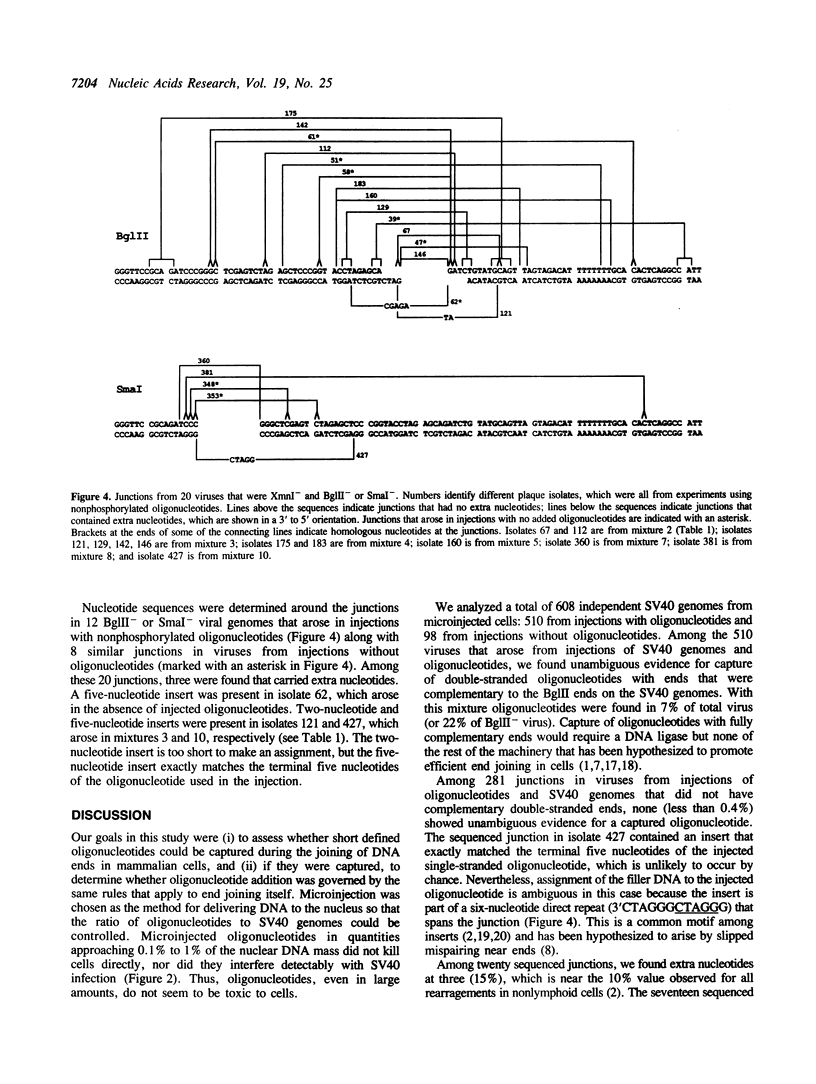
Extra nucleotides (termed filler DNA) are found at about 10% of the junctions of the genetic rearrangements that arise by illegitimate recombination in mammalian cells. Such filler DNAs could arise by the joining of oligonucleotide fragments to broken ends prior to end joining. We tested this possibility by microinjecting mixtures of defined oligonucleotides with SV40 genomes that were linearized in the intron for T antigen, a site where incorporation of extra nucleotides does not impair viability. Using an injection ratio of 1000 oligonucleotides per DNA end, we screened viable genomes for incorporation of single-stranded and double-stranded oligonucleotides with varying degrees of complementarity to the ends of the linear SV40 molecules. Genomes from 510 independent plaques were screened by restriction digestion to identify those that had picked up a restriction site unique to the injected oligonucleotides. Double-stranded oligonucleotides that were fully complementary to the SV40 ends were readily incorporated, but uptake of the other oligonucleotides was not detected by restriction analysis. Nucleotide sequences of junctions from 12 genomes derived from co-injection of noncomplementary oligonucleotides revealed two with filler DNA, but neither could be assigned unambiguously to the injected oligonucleotides.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Baltimore D. Joining of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene segments: implications from a chromosome with evidence of three D-JH fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4118–4122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang X. B., Wilson J. H. Modification of DNA ends can decrease end joining relative to homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4959–4963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen G., Villarroel R., Van Montagu M. Illegitimate recombination in plants: a model for T-DNA integration. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):287–297. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafaille J. J., DeCloux A., Bonneville M., Takagaki Y., Tonegawa S. Junctional sequences of T cell receptor gamma delta genes: implications for gamma delta T cell lineages and for a novel intermediate of V-(D)-J joining. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):859–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90609-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau N. R., Schatz D. G., Rosa M., Baltimore D. Increased frequency of N-region insertion in a murine pre-B-cell line infected with a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase retroviral expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3237–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. Joining of nonhomologous DNA double strand breaks in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):907–924. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter T., Pennington S. L., Adair G. M., Nairn R. S., Wilson J. H. A novel selection system for recombinational and mutational events within an intron of a eucaryotic gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5173–5180. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Chang X. B., Wilson J. H. Comparison of filler DNA at immune, nonimmune, and oncogenic rearrangements suggests multiple mechanisms of formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3049–3057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Porter T. N., Wilson J. H. Mechanisms of nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells: role for short sequence homologies in the joining reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4295–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Relative rates of homologous and nonhomologous recombination in transfected DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3355–3359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Baltimore D. The V(D)J recombination activating gene, RAG-1. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90760-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thode S., Schäfer A., Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. A novel pathway of DNA end-to-end joining. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90340-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Gudewicz T., Porter T., White A., Wilson J. H. How damaged is the biologically active subpopulation of transfected DNA? Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):387–398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S., Tarpley A., Purugganan M., Spell M., Okagaki R. Filler DNA is associated with spontaneous deletions in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8731–8735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Berget P. B., Pipas J. M. Somatic cells efficiently join unrelated DNA segments end-to-end. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1258–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., DePamphilis M., Berg P. Simian virus 40-permissive cell interactions: selection and characterization of spontaneously arising monkey cells that are resistant to simian virus 40 infection. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):391–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.391-399.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


