Abstract
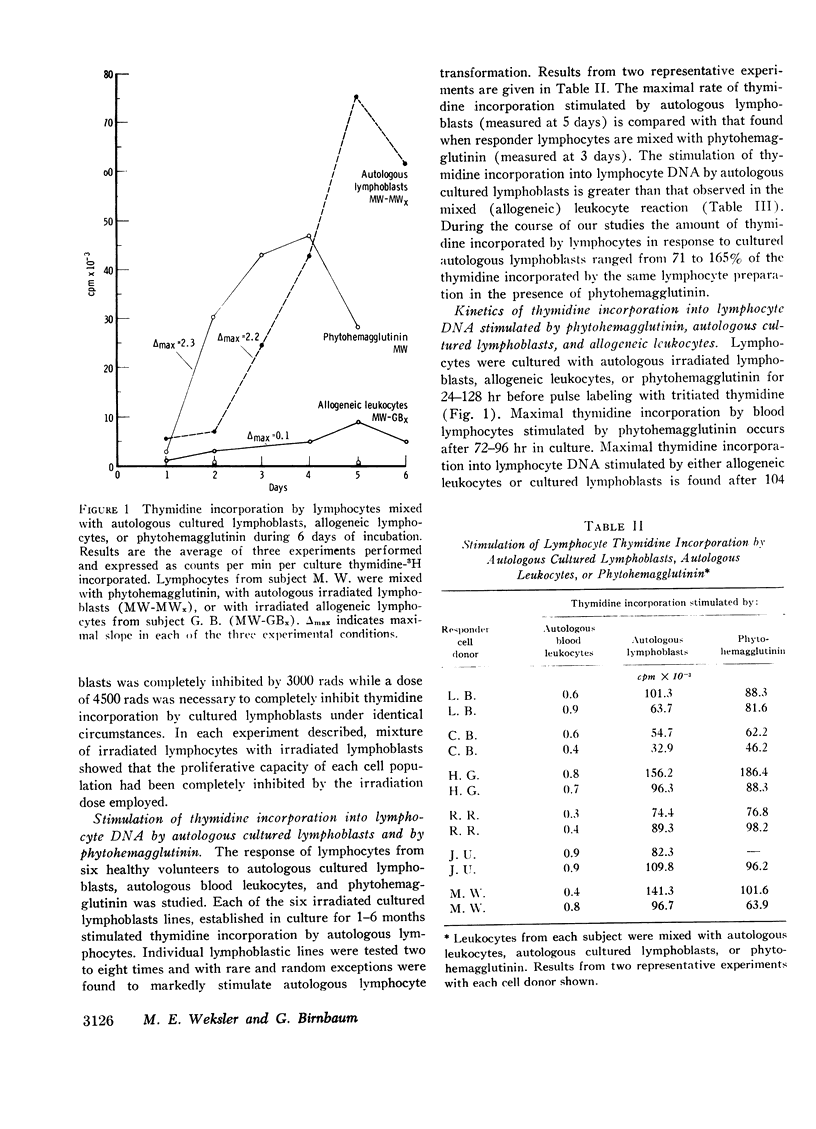
The ability of cultured lymphoblasts to stimulate autologous lymphocyte transformation in “one-way” mixed leukocyte culture has been studied. Intact, cultured lymphoblasts required physical contact with responding lymphocytes to induce transformation. In quantitative terms, lymphocytes incorporate as much thymidine when mixed with irradiated cultured lymphoblasts as they do in response to phytohemagglutinin. The stimulation of lymphocyte transformation by allogeneic cultured lymphoblasts did not parallel the stimulation of lymphocyte transformation by leukocytes from the donor of the lymphoblast culture. The stimulatory determinants on the cultured lymphoblast are unaffected by neuraminidase but destroyed by trypsin. The trypsin-treated cultured lymphoblasts regain their capacity to stimulate autologous lymphocyte transformation within 48 hr in culture. Cultured lymphoblasts possess concanavalin A binding sites. Concanavalin A inhibits the capacity of cultured lymphoblasts to stimulate autologous lymphocyte transformation. The relevance of these findings to EB virus infection of cultured lymphoblasts and to immune surveillance is discussed.
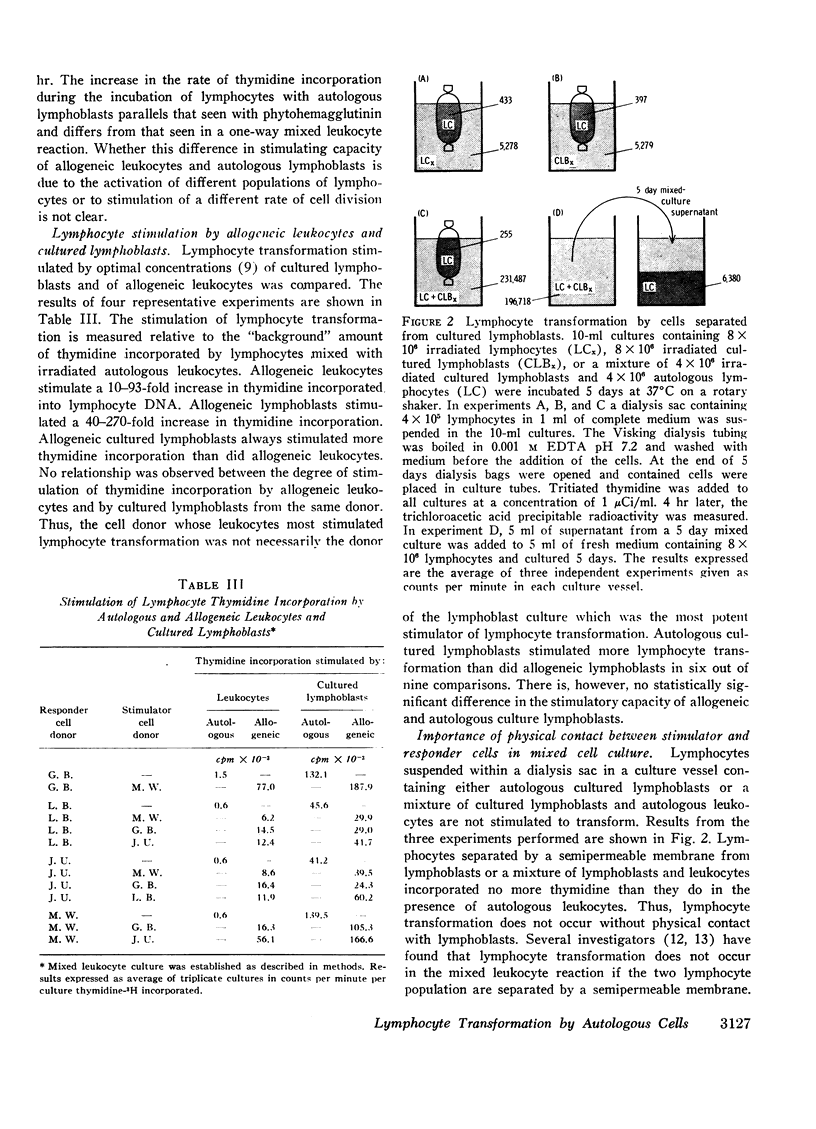
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos D. B., Bach F. H. Phenotypic expressions of the major histocompatibility locus in man (HL-A): leukocyte antigens and mixed leukocyte culture reactivity. J Exp Med. 1968 Oct 1;128(4):623–637. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.4.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYSE E. A., OLD L. J., CHOUROULINKOV I. CYTOTOXIC TEST FOR DEMONSTRATION OF MOUSE ANTIBODY. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. L., Bach F. H., Joo P. Leukemia-associated antigens in the mixed leukocyte culture test. Science. 1969 Dec 19;166(3912):1520–1522. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3912.1520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum G., Siskind G. W., Weksler M. E. Autologous and allogeneic stimulation of peripheral human leukocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jan;3(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90224-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S. W., Glade P. R., Hirschhorn K. Establishment of long-term lines from small aliquots of normal lymphocytes. Blood. 1970 Apr;35(4):539–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M. A difference in the architecture of the surface membrane of normal and virally transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):994–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M., Noonan K. D. Restoration of normal growth by covering of agglutinin sites on tumour cell surface. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):512–515. doi: 10.1038/228512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN N. D., DUTTON R. W. THE STIMULATION OF DNA SYNTHESIS IN CULTURES OF RABBIT LYMPH NODE AND SPLEEN CELL SUSPENSIONS BY HOMOLOGOUS CELLS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:85–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Glade P. R., Broder S. W., Hirschhorn K. Lymphocyte stimulation by allogeneic and autochthonous cultured lymphoid cells. Cell Immunol. 1970 Dec;1(6):596–602. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman W. H., Kourilsky F. M. Stimulation of lymphocytes by autologous leukaemic cells in acute leukaemia. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):277–279. doi: 10.1038/224277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLD P., FREEDMAN S. O. DEMONSTRATION OF TUMOR-SPECIFIC ANTIGENS IN HUMAN COLONIC CARCINOMATA BY IMMUNOLOGICAL TOLERANCE AND ABSORPTION TECHNIQUES. J Exp Med. 1965 Mar 1;121:439–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P. Activation of Epstein-Barr virus by 5-bromodeoxyuridine in "virus-free" human cells (complement-fixing antigen-immunofluorescence-leukocytes). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):83–85. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerper P., Whang-Peng J., Monroe J. H. Transformation and chromosome changes induced by Epstein-Barr virus in normal human leukocyte cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):740–747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold P. Antigenic reversion in human cancer. Annu Rev Med. 1971;22:85–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.22.020171.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. S., Sell K. W. Mixed leukocyte stimulation of normal peripheral leukocytes by autologous lymphoblastoid cells. Science. 1970 Nov 27;170(3961):989–990. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3961.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampar B., Derge J. G., Martos L. M., Walker J. L. Synthesis of Epstein-Barr virus after activation of the viral genome in a "virus-negative" human lymphoblastoid cell (Raji) made resistant to 5-bromodeoxyuridine (thymidine kinase-virus antigen-immunofluorescence-herpesvirus fingerprints). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):78–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han T., Moore G. E., Sokal J. E. In vitro lymphocyte response to autologous cultured lymphoid cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Mar;136(3):976–979. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy D. A., Knight S., Ling N. R. The interaction of normal lymphocytes and cells from lymphoid cell lines. I. The nature of the activation process. Immunology. 1970 Aug;19(2):329–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B. Serological analysis of cell surface antigens of tumors induced by murine leukemia virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Jan;48(1):265–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Sachs L. Interaction of the carbohydrate-binding protein concanavalin A with normal and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1418–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. C., Moore G. E., Clarkson B. D. Stimulation of autochthonous lymphocytes by cells from normal and leukaemic lines. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 10;229(6):185–187. doi: 10.1038/newbio229185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kourilsky F. M., Silvestre D., Levy J. P., Dausset J., Nicolai M. G., Senik A. Immunoferritin study of the distribution of HL-A antigens on human blood cells. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):454–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Rogentine G. N., Halterman R., Leventhal B. Detection of an antigen associated with acute leukemia. Science. 1971 Dec 10;174(4014):1136–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4014.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn J., Skinner A., Kornfeld S. The rapid induction by phytohemagglutinin of increased alpha-aminoisobutyric acid uptake by lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):818–826. doi: 10.1172/JCI106553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Gerner R. E., Franklin H. A. Culture of normal human leukocytes. JAMA. 1967 Feb 20;199(8):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Grace J. T., Jr, Citron P., Gerner R., Burns A. Leukocyte cultures of patients with leukemia and lymphomas. N Y State J Med. 1966 Nov 1;66(21):2757–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Woods L. Isoantigens of cultured human lymphoid cells. Transplantation. 1972 Feb;13(2):155–159. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197202000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead J. F., Connolly J. J., McFarland W. Factors affecting the reactivity of human lymphocytes in vitro. I. Cell number, duration of culture and surface area. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):413–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A. Embryonic and neoplastic cell surfaces: availability of receptors for concanavalin A and wheat germ agglutinin. Science. 1971 Mar 5;171(3974):905–907. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3974.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G. The establishment of lymphoblastoid lines from adult and fetal human lymphoid tissue and its dependence on EBV. Int J Cancer. 1971 Nov 15;8(3):443–450. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Pagano J. S. Detection of Epstein-Barr viral genome in nonproductive cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 22;233(38):103–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio233103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perper R. J., Yu T. Z., Kooistra J. B. The in vitro specificity of antilymphocyte sera produced by either cultured or noncultured lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;37(4):418–431. doi: 10.1159/000230804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. H. Establishment of cell lines from peripheral leucocytes in infectious mononucleosis. Nature. 1967 Nov 25;216(5117):810–811. doi: 10.1038/216810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens P. T., Eijsvoogel V. P. Lymphocyte transformation in vitro. 3. Mechanism of stimulation in the mixed lymphocyte culture. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):229–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


