Abstract
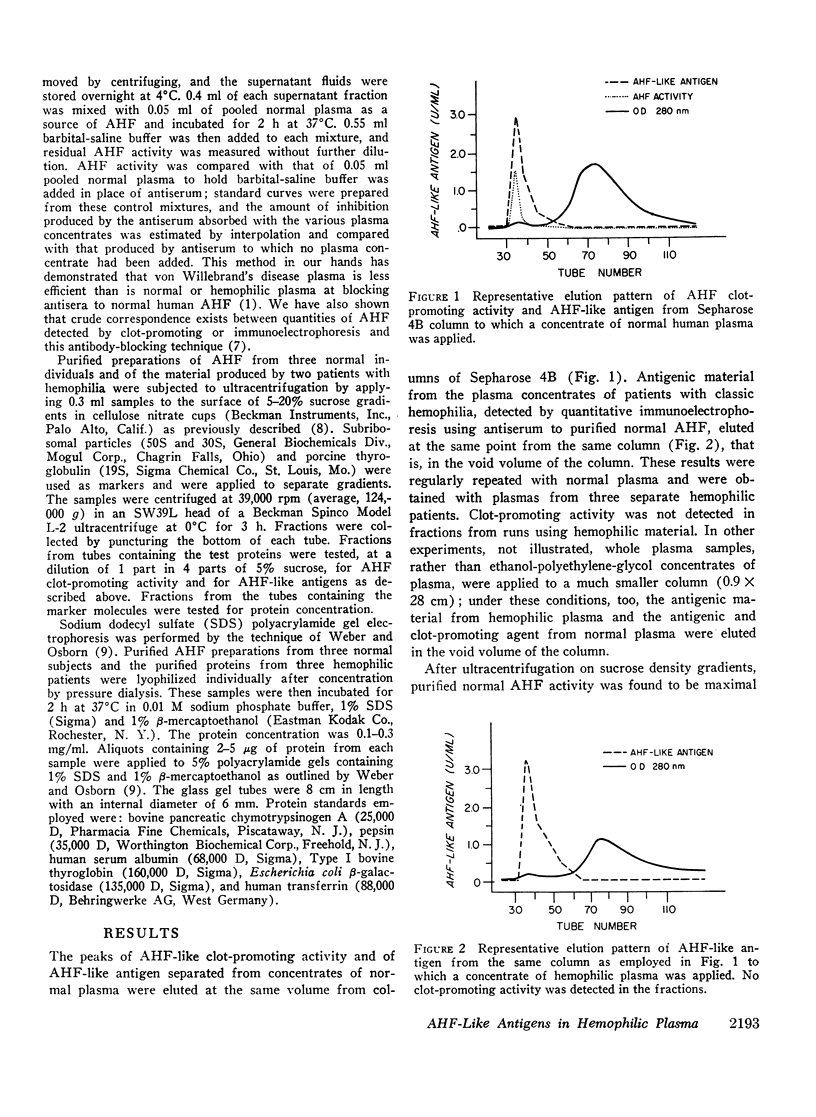
Normal human antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII) and the protein antigenically related to it in hemophilic plasma both appeared in the void volume of columns of agarose (Sepharose 4B) during purification of these agents. On ultracentrifugation upon sucrose gradients, both agents had sedimentation characteristics similar to those of an S30 marker. After reduction, the polypeptide chains of purified normal AHF and of the nonfunctional agent from hemophilic patients had an apparent molecular weight of 200,000 as determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. These observations suggest that AHF, purified as described, exists as a large molecule with subunits of molecular weight of approximately 200,000.
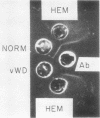
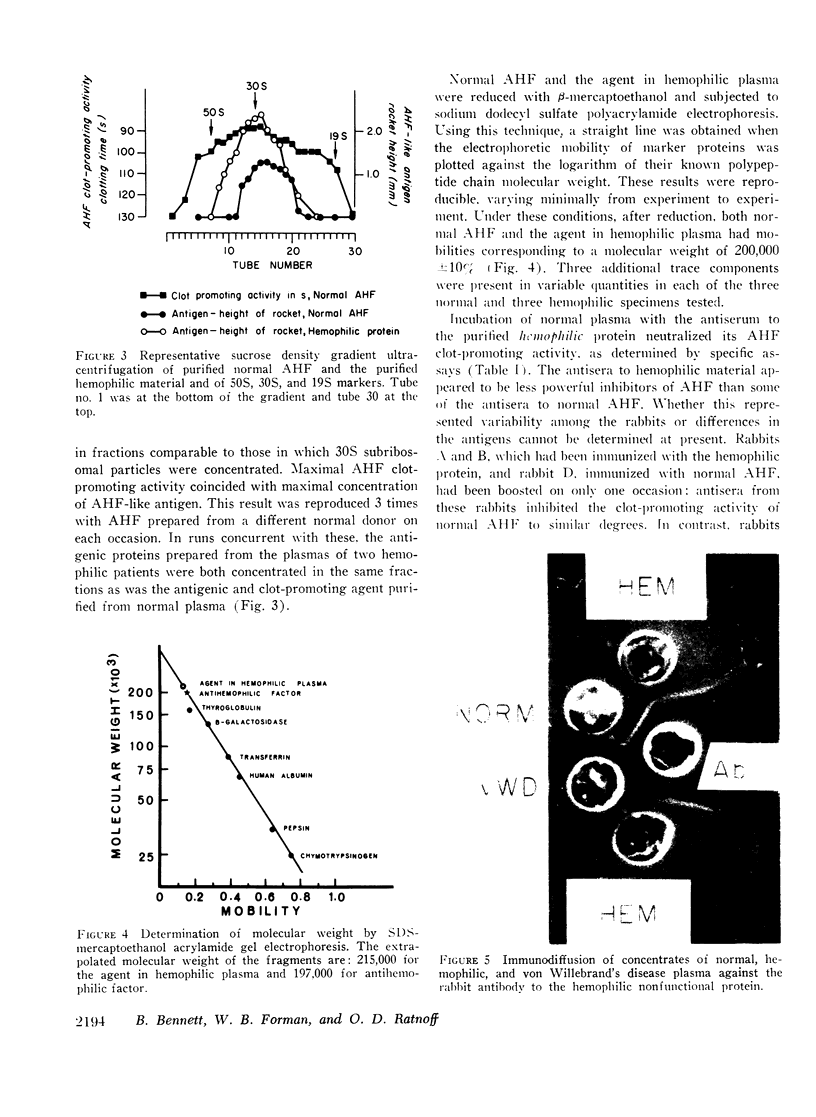
Antisera to normal AHF and the nonfunctional agent from hemophilic plasma appeared to be directed against antigens of similar electrophoretic mobility and precipitating characteristics, present in normal and hemophilic plasma but deficient in severe von Willebrand's disease plasma. Both antisera neutralized the AHF clot-promoting activity present in normal plasma, and this property was removed by absorption of the antisera with concentrates of normal or hemophilic plasma but to a greatly reduced extent by concentrates of von Willebrand's disease plasma. These findings suggest that the antigen detected in normal plasma by the antisera appears on a molecule participating in the AHF clot-promoting reaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett B., Ratnoff O. D. Changes in antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor 8) procoagulant activity and AHF-like antigen in normal pregnancy, and following exercise and pneumoencephalography. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Aug;80(2):256–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma B. N., Wiegerinck Y., Sixma J. J., Van Mourik J. A., Mochtar I. A. Immunological characterization of purified anti-haemophilic factor A (factor VIII) which corrects abnormal platelet retention in Von Willebrand's disease. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 29;236(65):104–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio236104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). 3. Comparative binding properties of human and rabbit anti-AHF. Blood. 1972 Apr;39(4):481–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass L., Ratnoff O. D., Leon M. A. Studies on the purification of antihemophilic factor (factor 8. I. Precipitation of antihemophilic factor by concanavalin A. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):351–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI105991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi S. L., Shulman N. R., Gralnick H. R. Studies on the purification and characterization of human factor 8. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2151–2161. doi: 10.1172/JCI107022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stites D. P., Hershgold E. J., Perlman J. D., Fudenberg H. H. Factor 8 detection by hemagglutination inhibition: hemophilia A and von Willebrand's disease. Science. 1971 Jan 15;171(3967):196–197. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3967.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ratnoff O. D., Powell A. E. Immunologic differentiation of classic hemophilia (factor 8 deficiency) and von Willebrand's dissase, with observations on combined deficiencies of antihemophilic factor and proaccelerin (factor V) and on an acquired circulating anticoagulant against antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI106480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]