Abstract
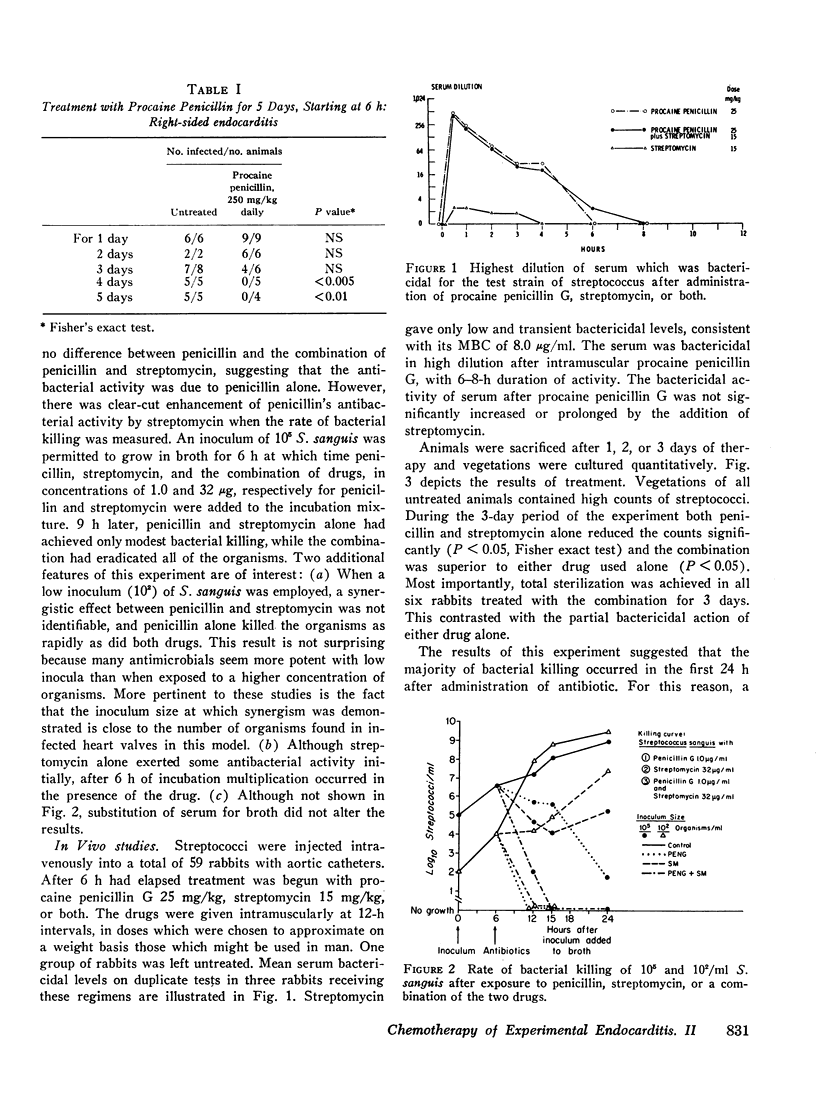
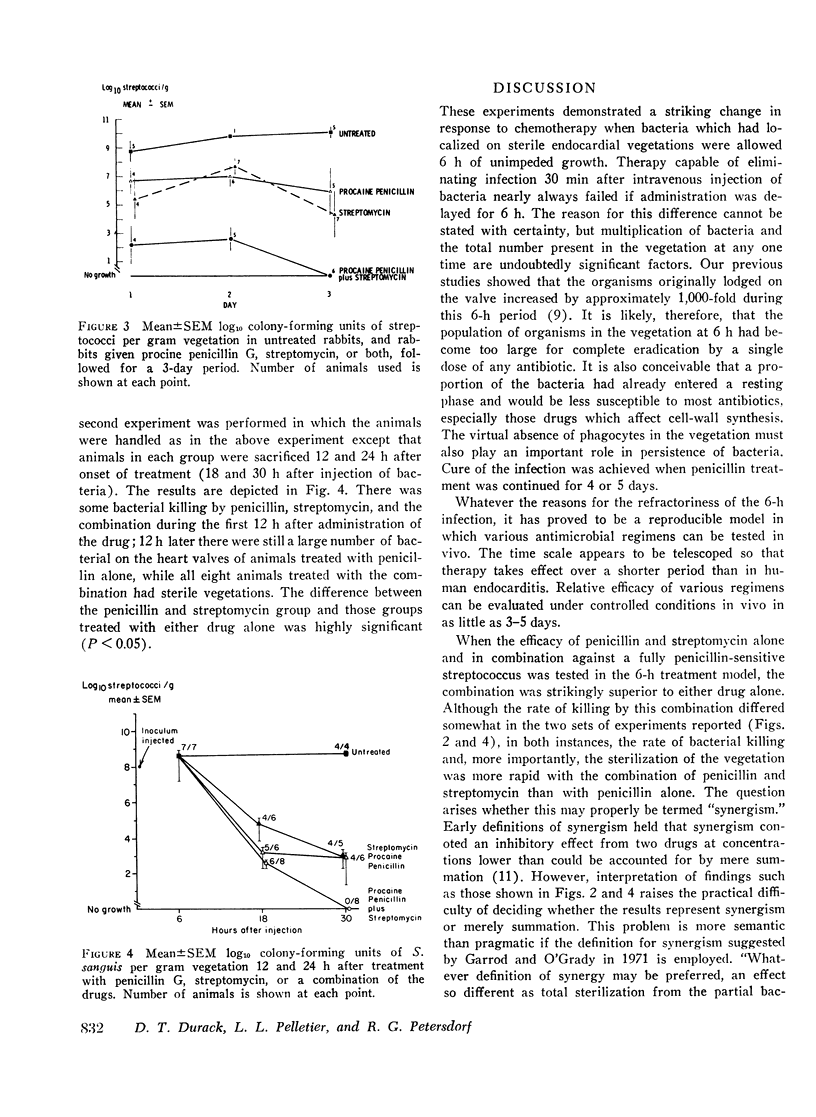
Bacterial endocarditis was produced by intravenous injection of Streptococcus viridans into rabbits with preexisting sterile endocardial vegetations. After 6 h had elapsed, bacteria in the vegetations could not be eradicated by brief treatment with antimicrobials to which the streptococci were sensitive. However, when treatment with penicillin was continued for 4 days, the animals were cured. The 6-h infection therefore offered a model in which treatments could be conveniently compared over a short period. Synergism was demonstrated between penicillin and streptomycin in endocarditis due to a fully penicillin-sensitive streptococcus, a point which had not been previously proved in vivo. The clinical implications are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Durack D. T., Beeson P. B. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. I. Colonization of a sterile vegetation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Feb;53(1):44–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Beeson P. B., Petersdorf R. G. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. 3. Production and progress of the disease in rabbits. Br J Exp Pathol. 1973 Apr;54(2):142–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Petersdorf R. G. Chemotherapy of experimental streptococcal endocarditis. I. Comparison of commonly recommended prophylactic regimens. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):592–598. doi: 10.1172/JCI107220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD L. P. The bactericidal action of streptomycin. Br Med J. 1948 Feb 28;1(4547):382–386. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4547.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERACI J. E. The antibiotic therapy of bacterial endocarditis: therapeutic data on 172 patients seen from 1951 through 1957: additional observations on short-term therapy (two weeks) for penicillin-sensitivie streptococcal endocarditis. Med Clin North Am. 1958 Jul;42(4):1101–1140. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)34262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison P. K., Freedman L. R. Experimental endocarditis I. Staphylococcal endocarditis in rabbits resulting from placement of a polyethylene catheter in the right side of the heart. Yale J Biol Med. 1970 Jun;42(6):394–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL B., DOWLING H. F., KELLOW W. Successful short-term therapy of streptococcal endocarditis with penicillin and streptomycin. Am J Med Sci. 1955 Jul;230(1):73–81. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195507000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER T. H. The treatment of some bacterial infections of the heart and pericardium. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1952 Apr;28(4):213–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. S., Kaplan S., Terhune C. A., Jr, Hamburger M. Successful two-week treatment schedule for penicillin-susceptible streptococcus viridans endocarditis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 18;2(7738):1340–1343. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92360-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


