Abstract
It is well established that in normal man the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is responsive to changes in volume. The present study was performed to determine whether sodium has an action apart from volume in the regulation of the secretion of renin and aldosterone. Acute volume expansion was induced either by saline, dextran, or glucose infusion in supine, normal subjects in balance on a 10 meq sodium/100 meq potassium diet. Plasma renin activity (PRA), angiotensin II (A II), aldosterone (PA), cortisol, serum sodium, and potassium were measured every 10 min for the first 30 min and then at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h.
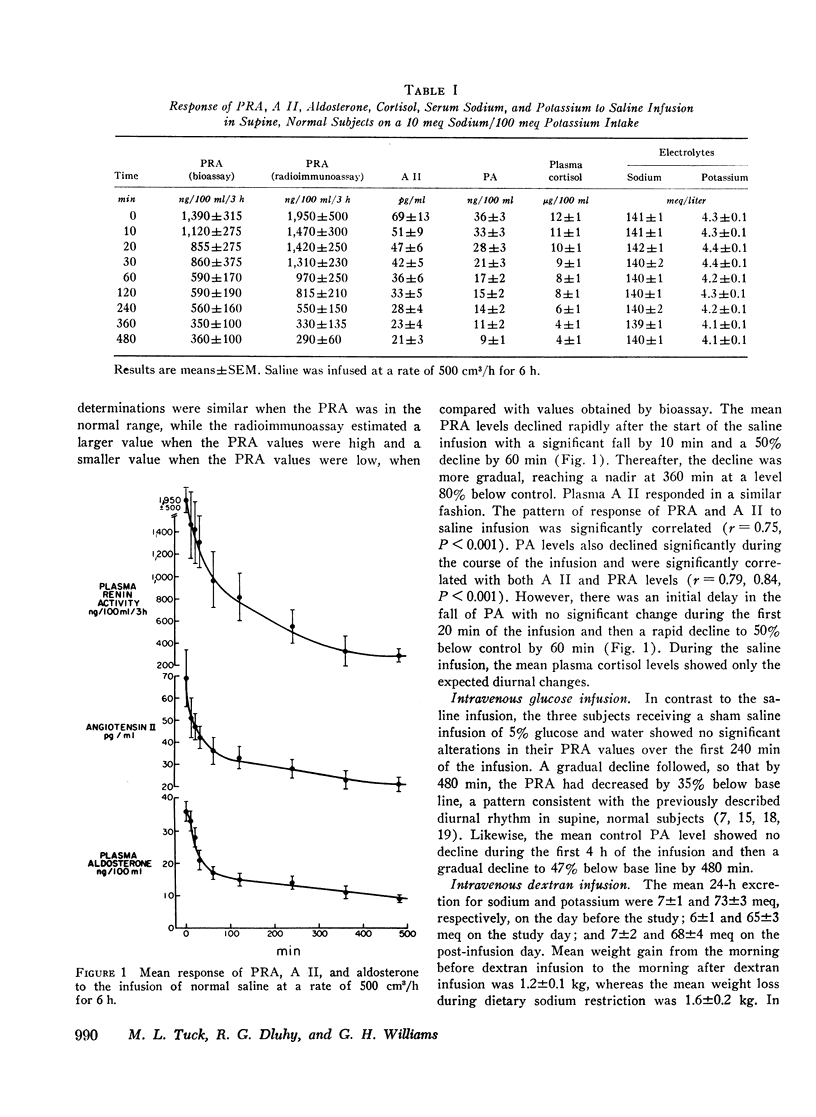
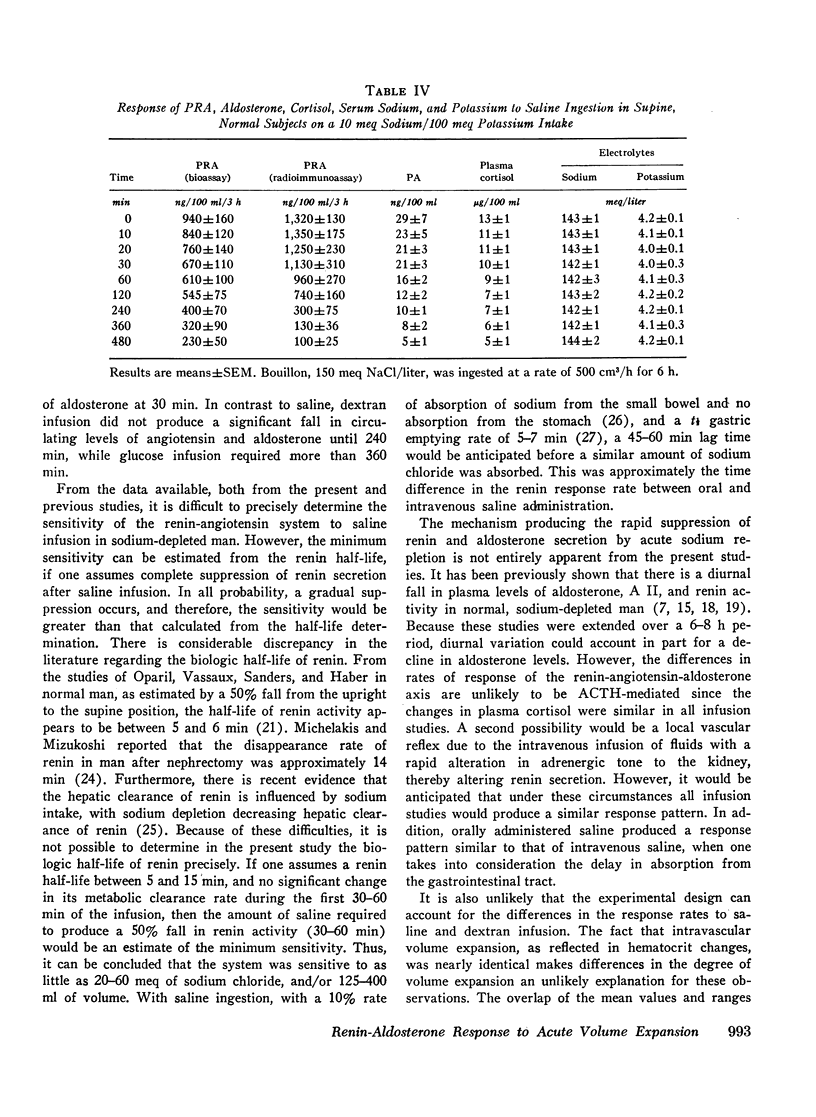
During saline infusion (500 cm3/h for 6 h) mean PRA and A II levels declined very rapidly, falling significantly below control at 10 min (P < 0.01) and by 50% at 60 min. Thereafter, the rate of fall was more gradual, reaching a nadir at 360 min (70-80% below control). PA declined in a parallel pattern except that a significant fall did not occur until 30 min.
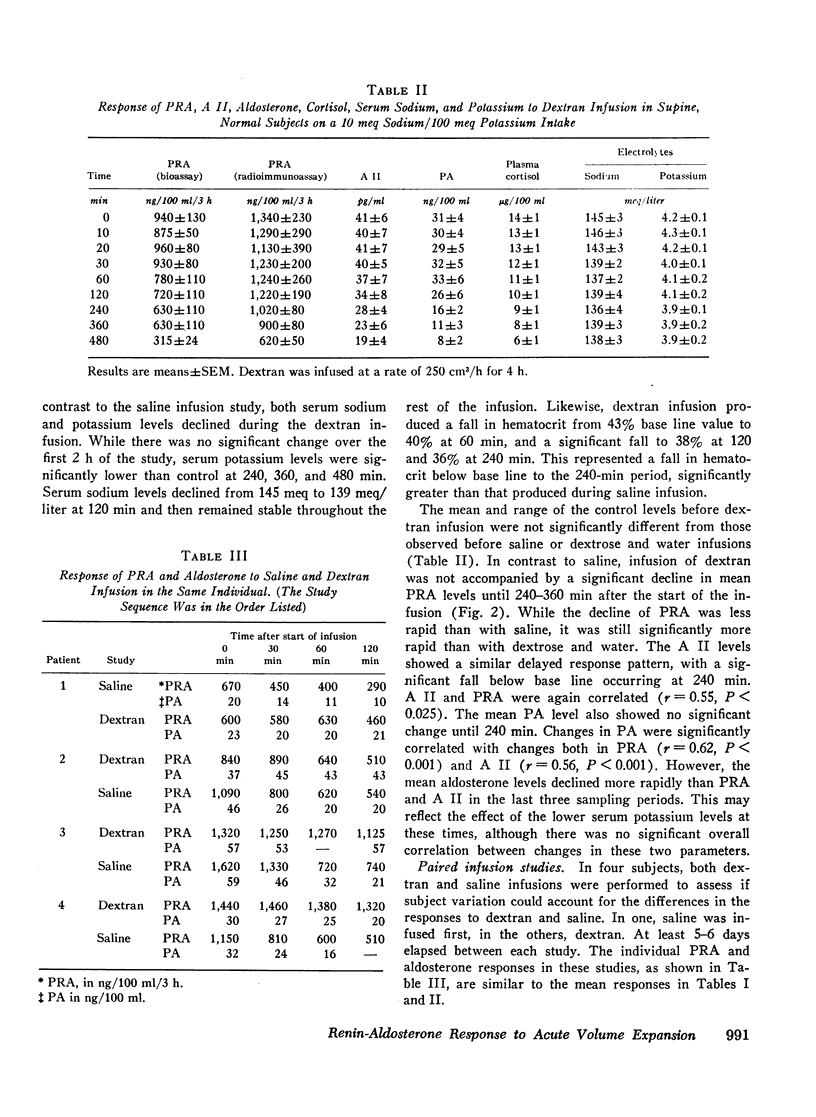
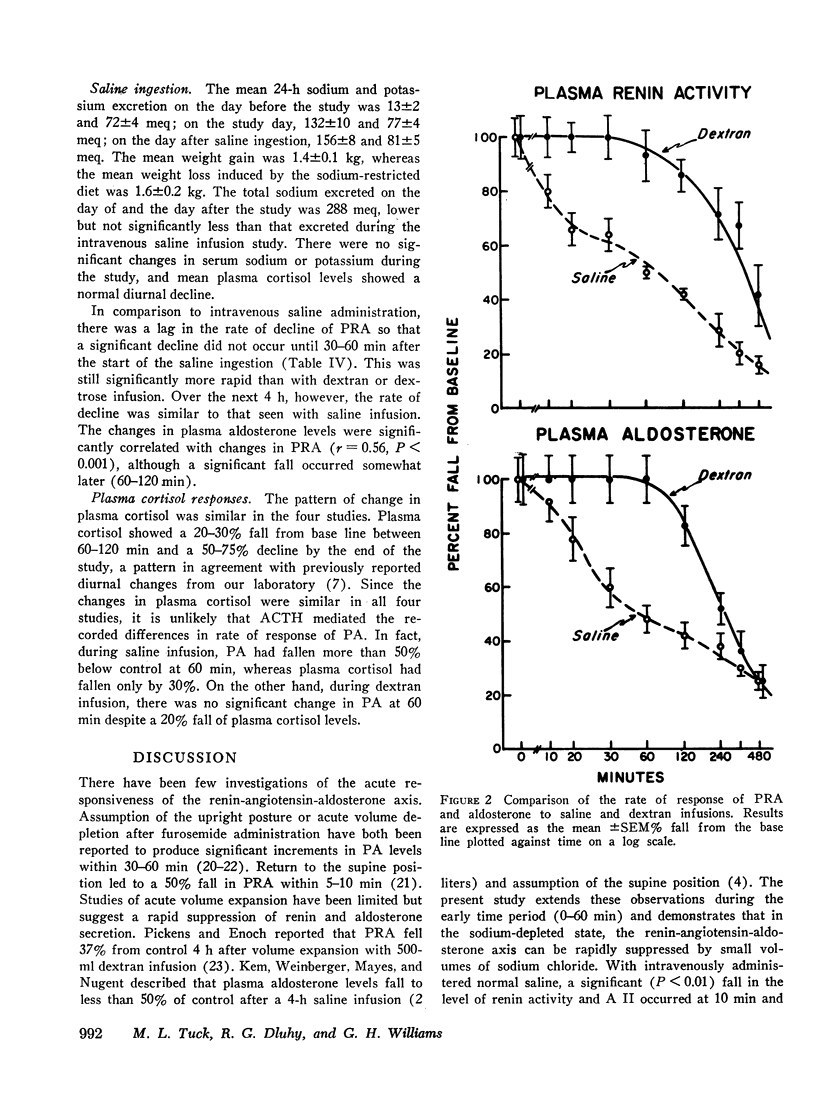
In contrast to saline, dextran infusion (250 cm3/h for 4 h) did not produce a significant fall in PRA, A II, or PA until 4 h after the start of the infusion despite equivalent volume expansion. On the other hand, the infusion of 5% glucose and water (500 cm3/h for 6 h) did not produce a significant decline in PRA, A II, or PA over the first 6 h of the study. Although the response rate of PRA, A II, and PA was different in each of the three infusion studies, these parameters were significantly correlated within each study. Serum sodium and potassium levels did not change during any study except dextran infusion, where a significant fall in both occurred at 120 min. In all the infusion studies, plasma cortisol levels gradually declined during the 8-h study period consistent with its expected rhythm of diurnal secretion.
These results demonstrate that rate of response of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system to acute volume expansion with saline differed from that with dextran and glucose infusion in sodium-depleted man. The data support a specific role for volume expansion with saline or the sodium ion per se in the regulation of renin and aldosterone.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTTER F. C., DUNCAN L. E., Jr, LIDDLE G. W. The effect of changes in body sodium on extracellular fluid volume and aldosterone and sodium excretion by normal and edematous men. J Clin Invest. 1956 Nov;35(11):1299–1305. doi: 10.1172/JCI103385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balikian H. M., Brodie A. H., Dale S. L., Melby J. C., Tait J. F. Effect of posture on the metabolic clearance rate, plasma concentration and blood production rate of aldosterone in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Nov;28(11):1630–1640. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-11-1630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayard F., Alicandri C. L., Beitins I. Z., Lubash G. D., Kowarski A., Migeon C. J. A dynamic study of plasma renin activity and aldosterone concentration in normal and hypertensive subjects. Metabolism. 1971 May;20(5):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best J. B., Coghlan J. P., Bett J. H., Cran E. J., Scoggins B. A. Circulating angiotensin-II and aldosterone levels during dietary sodium restriction. Lancet. 1971 Dec 18;2(7738):1353–1354. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dluhy R. G., Axelrod L., Underwood R. H., Williams G. H. Studies of the control of plasma aldosterone concentration in normal man. II. Effect of dietary potassium and acute potassium infusion. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1950–1957. doi: 10.1172/JCI107001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel R. L., Cain J. P., Williams G. H. Double antibody radioimmunoassay of renin activity and angiotensin II in human peripheral plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Apr;81(4):632–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge R. L., Lowe R. D., Vane J. R. Increased angiotensin formation in response to carotid occlusion in the dog. Nature. 1966 Jul 30;211(5048):491–493. doi: 10.1038/211491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Davis J. O., Baumber J. S., Schneider E. G. Effects of hemorrhage and chronic sodium depletion on hepatic clearance of renin. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jun;220(6):1677–1682. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.6.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. H., Romfh P., Smith J. A. Episodic secretion of aldosterone in supine man; relationship to cortisol. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jul;35(1):178–181. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-1-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kem D. C., Weinberger M. H., Mayes D. M., Nugent C. A. Saline suppression of plasma aldosterone in hypertension. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Sep;128(3):380–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakoff L. R., Goodwin F. J., Baer L., Torres M., Laragh J. H. The role of renin in the exaggerated natriuresis of hypertension. Circulation. 1970 Aug;42(2):335–346. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.42.2.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Horton R. The relationship between plasma renin and aldosterone in normal man. Circ Res. 1970 Jul;27(1 Suppl 1):185–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Mizukoshi H. Distribution and disappearance rate of renin in man and dog. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Jul;33(1):27–34. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr P. A., Monson D. O., Owczarski C., Shoemaker W. C. Sequential cardiorespiratory events during and after dextran-40 infusion in normal and shock patients. Circulation. 1969 Mar;39(3):379–393. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.39.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash F. D., Rostorfer H. H., Bailie M. D., Wathen R. L., Schneider E. G. Renin release: relation to renal sodium load and dissociation from hemodynamic changes. Circ Res. 1968 Apr;22(4):473–487. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.4.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oparil S., Vassaux C., Sanders C. A., Haber E. Role of renin in acute postural homeostasis. Circulation. 1970 Jan;41(1):89–95. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.41.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickens P. T., Enoch B. A. Changes in plasma renin activity produced by infusions of dextran and dextrose. Cardiovasc Res. 1968 Apr;2(2):157–160. doi: 10.1093/cvr/2.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J., Boucher R., Nowaczynski W., Genest J. Acute changes in plasma volume, renin activity, and free aldosterone levels in healthy subjects following Fursemide administration. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1968 Jan;46(1):85–91. doi: 10.1139/y68-015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood R. H., Williams G. H. The simultaneous measurement of aldosterone, cortisol, and corticosterone in human peripheral plasma by displacement analysis. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 May;79(5):848–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. H., Cain J. P., Dluhy R. G., Underwood R. H. Studies of the control of plasma aldosterone concentration in normal man. I. Response to posture, acute and chronic volume depletion, and sodium loading. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1731–1742. doi: 10.1172/JCI106974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. H., Rose L. I., Dluhy R. G., McCaughn D., Jagger P. I., Hickler R. B., Lauler D. P. Abnormal responsiveness of the renin aldosterone system to acute stimulation in patients with essential hypertension. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Mar;72(3):317–326. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-72-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. H., Tuck M. L., Rose L. I., Dluhy R. G., Underwood R. H. Studies of the control of plasma aldosterone concentration in normal man. 3. Response to sodium chloride infusion. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2645–2652. doi: 10.1172/JCI107082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe L. K., Gordon R. D., Island D. P., Liddle G. W. An analysis of factors determining the circadian pattern of aldosterone excretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Nov;26(11):1261–1266. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-11-1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


