Abstract
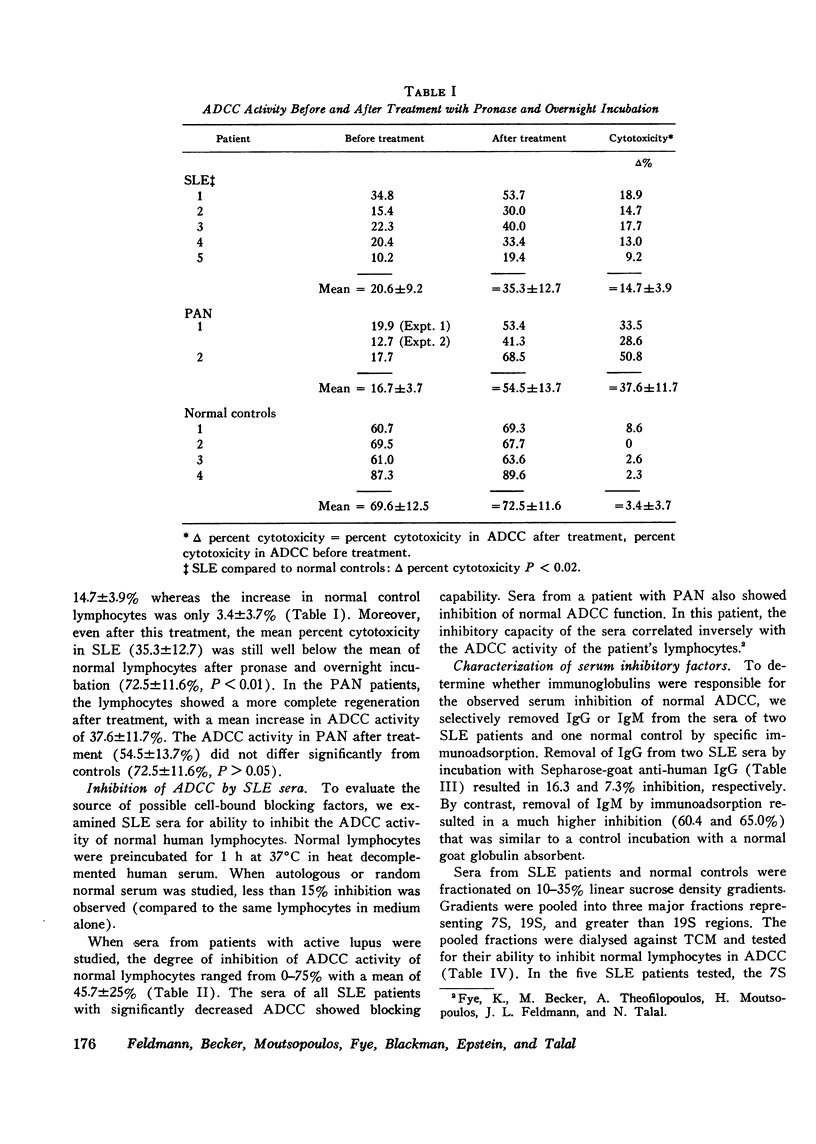
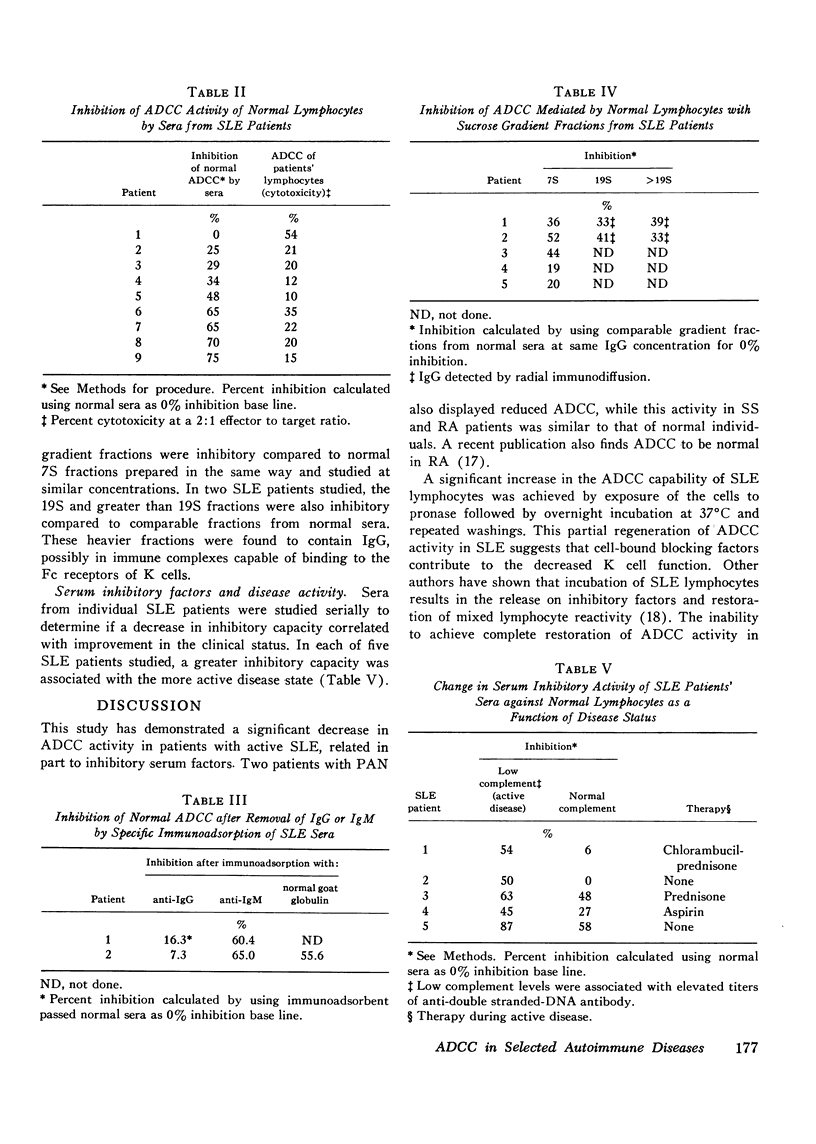
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity mediated by peripheral blood lymphocytes was studied in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, polyarteritis nodosa. Sjogren's syndrome, and rheumatoid arthritis. The target cells were chicken erythrocytes coated with rabbit anti-chicken erythrocyte antibody. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity was normal in Sjogren's syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis but significantly decreased (P is less than 0.001) in active systemic lupus erythematosus and in two patients with polyarteritis nodosa. A partial regeneration of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity was obtained by treatment with pronase and DNase followed by overnight incubation. Sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus inhibited antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity of normal lymphocytes. The inhibitory activity was studied by specific immunoadsorption and sucrose density geadient ultracentrifugation. Removal of IgG but not IgM greatly reduced inhibition. Inhibitory factors were present in 7S and heavier fractions containing IgG. Five systemic lupus erythematosus patients were studied serially to determine if improvement in clinical status could be correlated with a decrease in serum inhibitory factors as studied by inhibition of normal antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Indeed, a greater serum inhibitory capacity was found in each patient during periods of greater disease activity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashman R. F. Enzymatic modification of lymphocyte receptors for antigen III. loss of antigen-responsiveness with recovery after adoptive transfer. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(4):337–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., Penhale W. J., McLeman D., Barnes E. W., Irvine W. J. Lymphocyte-dependent antibody-mediated cytotoxicity in Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jun;14(2):153–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale R. P., Zighelboim J. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1047–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocke D. J., Hsu K., Morgan C., Bombardieri S., Lockshin M., Christian C. L. Association between polyarteritis and Australia antigen. Lancet. 1970 Dec 5;2(7684):1149–1153. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halloran P., Schirrmacher V., Festenstein H. A new sensitive assay for antibody against cell surface antigens based on inhibition of cell-dependent antibody-mediated cytotoxicity. I. Specificity and sensitivity. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1348–1363. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersey P., Cullen P., MacLennan I. C. Lymphocyte-dependent cytotoxic antibody activity against human transplantation antigens. Transplantation. 1973 Jul;16(1):9–16. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197307000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedar E., Otiz de Landazuri M., Fahey J. L. Enzymatic enhancement of cell-mediated cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):26–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler H., Kaplan D. R., Strayer D. S. Clonal depletion in neonatal tolerance. Science. 1974 Nov 15;186(4164):643–644. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4164.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson A., Perlmann P., Natvig J. B. Cytotoxicity of human lymphocytes induced by rabbit antibodies to chicken erythrocytes. Inhibition by normal IgG and by human myeloma proteins of different IgG subclasses. Immunology. 1973 Oct;25(4):675–686. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C. Antibody in the induction and inhibition of lymphocyte cytotoxicity. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:67–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C. Competition for receptors for immunoglobulin on cytotoxic lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Feb;10(2):275–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Lindström F. D., Williams R. C., Jr Peripheral blood lymphocyte cell surface markers during the course of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3046–3056. doi: 10.1172/JCI107503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole C., Stejskal V., Perlmann P., Karlsson M. Lymphoid cells mediating tumor-specific cytotoxicity to carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Separation of the effector population using a surface marker. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):457–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Induction and inhibition by humoral antibody and nature of effector cells. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:91–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Chin W., Friou G. J., Cooper S. M., Harding B., Hill R. L., Quismorio F. P. Reduced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):187–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Pillarisetty R. IgM and IgG antibodies to DNA, RNA, and DNA:RNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):24–31. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman J., von Stedingk L. V., Perlmann P., Jonsson J. Antibody-induced in vitro lymphocyte cytotoxicity in Hashimoto thyroiditis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;47(4):473–482. doi: 10.1159/000231241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, Emmons J. D., Yunis E. J. Studies of human sera with cytotoxic activity. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1514–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI106637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Winfield J. B., Siegal F., Wernet P., Bentwich Z., Kunkel H. G. Analyses of lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Occurrence of interfering cold-reactive antilymphocyte antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1082–1092. doi: 10.1172/JCI107852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisløff F., Frøland S. S., Natvig J. B. Deficient lymphoid cell-mediated, PHA-induced cytotoxicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(3):303–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


