Abstract
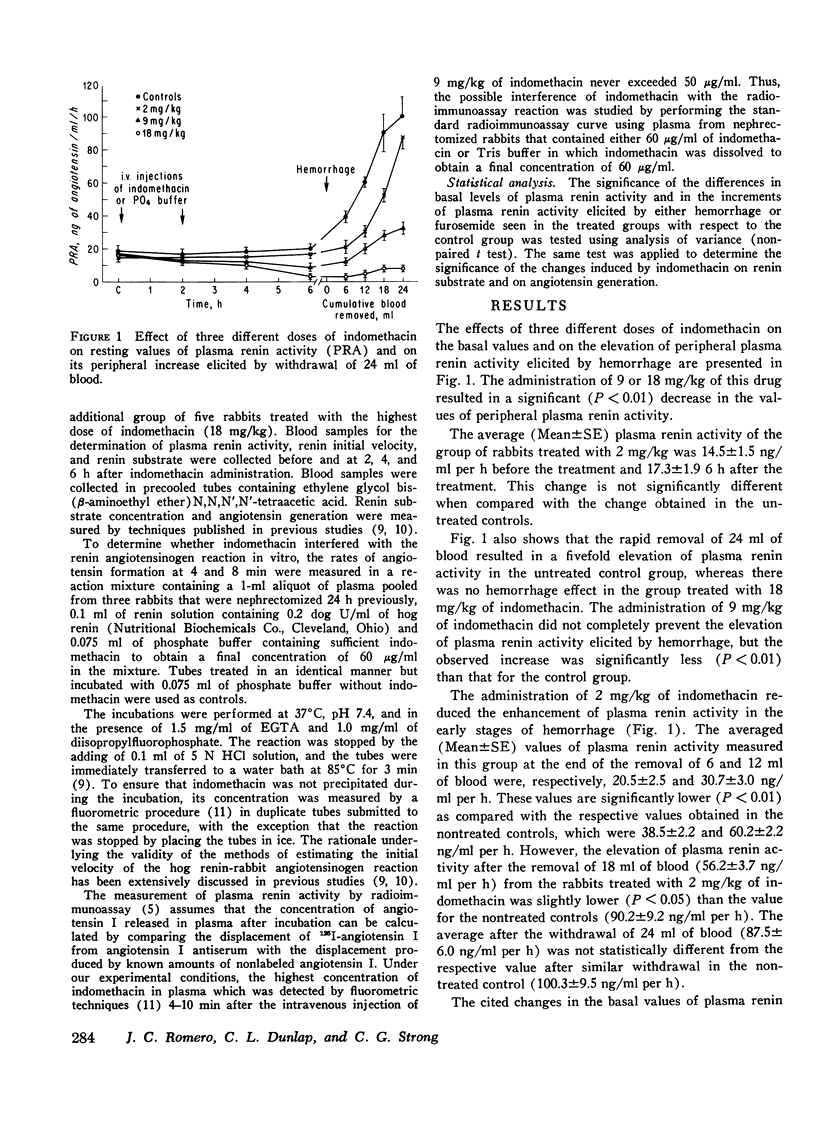
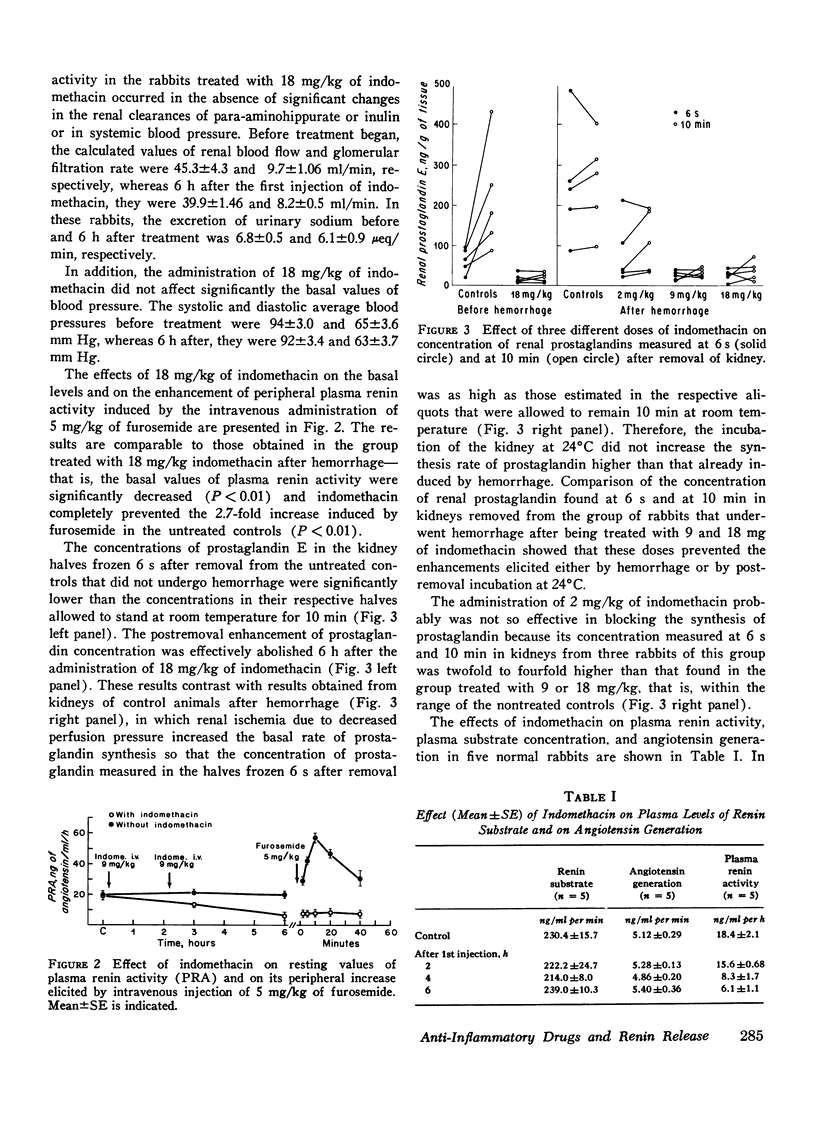
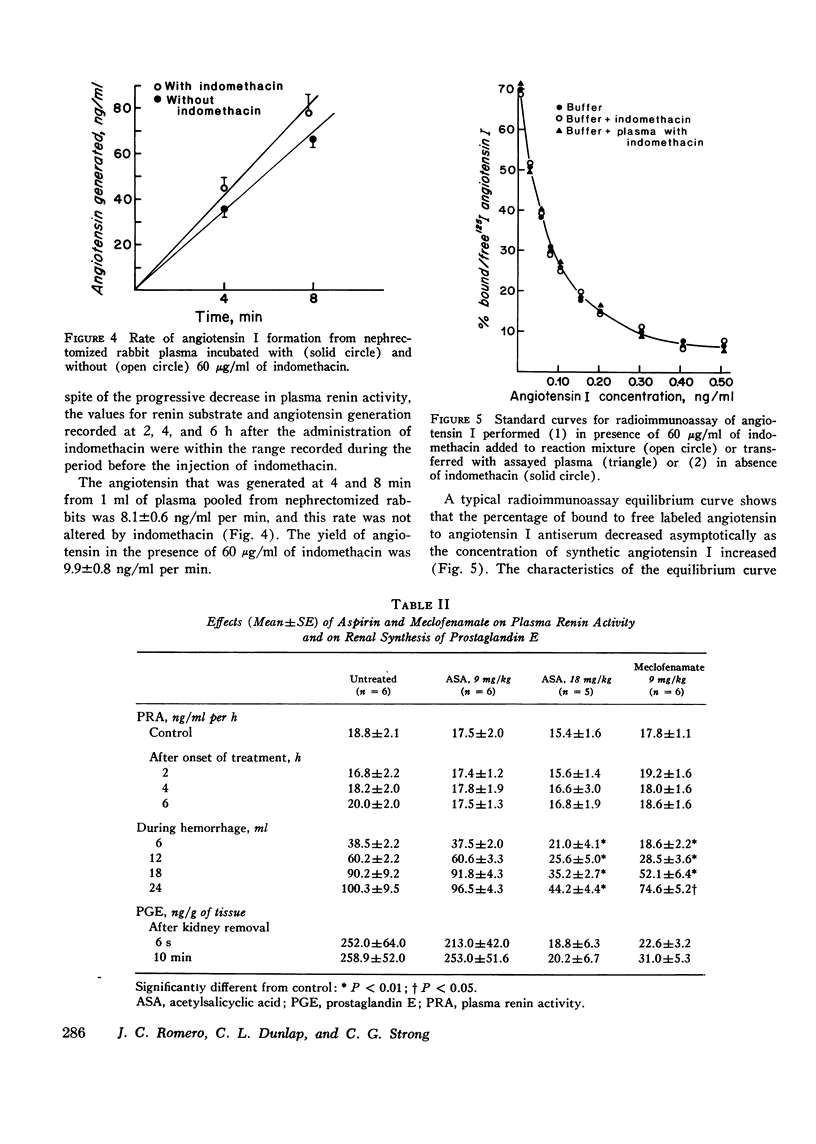
The administration of two different doses of indomethacin, 9 and 18 mg/kg, to two different groups of rabbits was followed 6 h later by a significant decrease in plasma renin activity, and these levels were not increased by hemorrhage. The administration of 2 mg/kg of indomethacin did not alter the basal levels of plasma renin activity, but it was effective in diminishing the peripheral increase of renin produced by hemorrhage. Similar effects were obtained in other groups of rabbits treated with 9 mg/kg of meclofenamate or 18 mg or aspirin. The lowering effect of indomethacin on plasma renin activity is not specifically related to hemorrhage because it also prevented the increase in plasma renin activity elicited by 5 mg/kg of furosemide. Further studies showed that indomethacin did not exert any significant effect in vivo on the plasma level of renin substrate or on the generation of angiotensin from normal plasma by exogenous renin. And indomethacin did not interfere with the binding capacity of anti-angiotensin I for angiotensin I in the radioimmunoassay reaction or with the in vitro formation of angiotensin from hog renin-nephrectomized rabbit plasma reaction. The results thus indicate that the lowering effect of indomethacin on plasma renin activity is due to the interference with renal renin release. That this effect may be related to the blockade of prostaglandin synthesis is suggested by the similar effect exhibited by other blockers of prostaglandin synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anggård E., Bohman S. O., Griffin J. E., 3rd, Larsson C., Maunsbach A. B. Subcellular localization of the prostaglandin system in the rabbit renal papilla. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Feb;84(2):231–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar J., Romero J. C., Hoobler S. W. Renin kinetics in experimental renal hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jan;220(1):191–195. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.1.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. K., Lee M. R., Cook W. F. Effect of hemorrhage on arterial plasma renin activity in the rabbit. Circ Res. 1966 Aug;19(2):269–273. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer P., Menard J., Papanicolaou N., Alexandre J. M., Devaux C., Milliez P. Mechanism of renin release following furosemide diuresis in rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1968 Oct;215(4):908–915. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.4.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero J. C., Hoobler S. W. Changes in renin kinetics induced by nephrectomy. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1076–1080. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero J. C., Hoobler S. W., Kozak T. J., Warzynski R. J. Effect of antirenin on blood pressure of rabbits with experimental renal hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1973 Oct;225(4):810–817. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.4.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres V. E., Romero J. C., Strong C. G., Wilson D. M., Walker V. R. Renal prostaglandin E during acute renal failure. Prostaglandins. 1974 Nov 25;8(4):353–360. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres V. E., Strong C. G., Romero J. C., Wilson D. M. Indomethacin enhancement of glycerol-induced acute renal failure in rabbits. Kidney Int. 1975 Mar;7(3):170–178. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J., Carlson J. Mechanism of the effects of furosemide on renin secretion in anesthetized dogs. Circ Res. 1969 Aug;25(2):145–152. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.2.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman R. M., Spector D., Caldwell B. V., Speroff L., Schneider G., Mulbow P. J. The effect of chronic sodium loading and sodium restriction on plasma prostaglandin A, E, and F concentrations in normal humans. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1093–1098. doi: 10.1172/JCI107274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


